1. About
About SecHub
SecHub stands for "Security Hub" and serves as an unified API to scan for various security issues. With SecHub, users don’t need to worry about the specific scanning product used on the server side; they simply configure their desired security goals.
|
The SecHub server alone does NOT provide a security infrastructure but orchestrates different security products/tools. Please check our ready to use security open source tools: PDS solutions for integration with SecHub server. |
It was designed to be very easy to integrate into existing build / contionus integration (CI) pipelines and helps to provide SecDevOps.
|
You can get more documentation from the SecHub web page . The project is hosted at https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub |
About documentation
This documentation is part of SecHub.
| Key | Value | Information |
|---|---|---|
LICENSE |
MIT License |
Please look at https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub/blob/master/LICENSE |
Documentation version: Server 2.14.0 - Build date: 2025-09-01 14:49 (UTCZ)
Target audience for this document are SecHub Developers only!
2. Development Setup
2.1. Preparation
2.1.1. Tool installation
You need
-
JAVA 17 JDK
-
Go Lang (min. 1.24.4)
-
GIT
| A Go installation is only necessary for client development. All tools must be accessible from PATH variable. |
2.1.2. GIT setup
2.1.2.1. Clone
git clone https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub.git
2.1.2.2. GIT Configuration
After Git clone is done, please go into the repository’s root folder and define
2.1.2.2.1. User name and email
Only necessary when not like your global configuration:
git config user.email $yourEmailAddress git config user.name "$firstName $lastName"
2.1.2.2.2. SecHub wanted setup
git config branch.autosetuprebase always
git config branch.master.rebase true
git config push.default current
git config core.autocrlf input
git config color.ui auto
git config --add remote.origin.fetch +refs/tags/*:refs/tags/*2.1.3. IDE setup
2.1.3.1. Eclipse
2.1.3.1.1. Import projects
Open a console in SecHub’s repository root folder and type:
./gradlew cleanEclipse eclipse assemble
This will setup all your eclipse settings and you are able to import the now existing projects into a workspace of your choice.
2.1.3.1.2. Create localhost server certificate
This is automatically done by former gradle call, so not necessary here.
2.1.3.1.3. Add Sechub Java Code Formatter
-
Download the formatter xml file here and unzip it.
-
Open Java Formatter page in preferences (Window→Preferences). Then press the import button and select the former unpacked xml file.
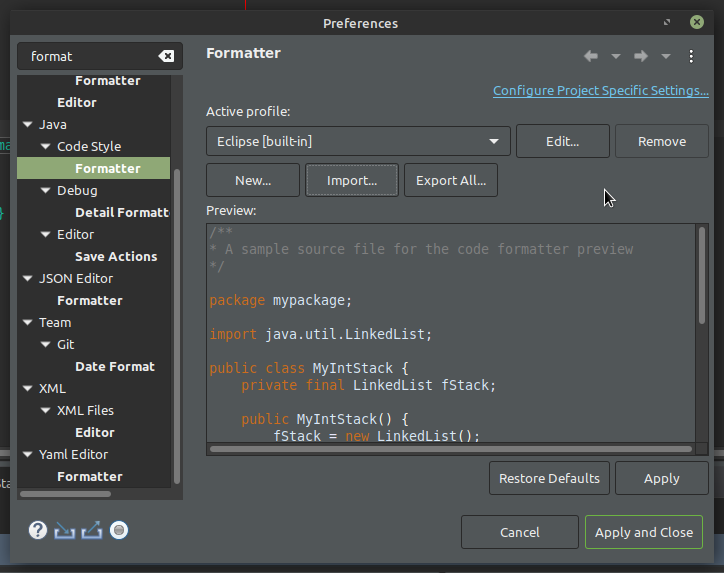
-
Ensure SecHub is your active profile. Select
SecHubas active profile, then press apply and close.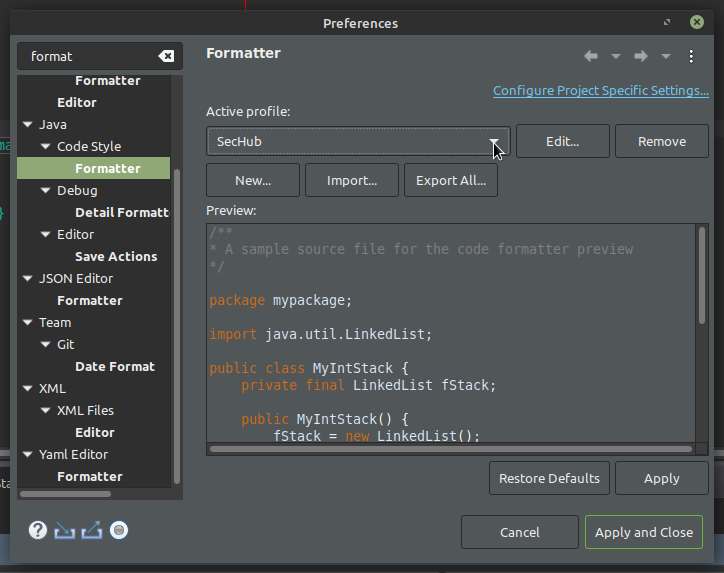
-
Before pushing your code please check your java format by executing spotless check.
./gradlew clean spotlessCheck
2.1.3.2. Others
2.1.3.2.1. Import projects
Import as you would normally do in your IDE.
2.1.3.2.2. Create localhost server certificate
To get the localhost server certificate created, open a console
just call ./gradlew ensureLocalhostCertificate
This will generate a self signed server certificate for localhost.
2.1.3.2.3. Add Sechub Java Code Formatter (IntelliJ)
-
Download the formatter xml file here and unzip it.
-
Open Java Formatter page in preferences (File→Settings). Then press the import button and select the former unpacked xml file.
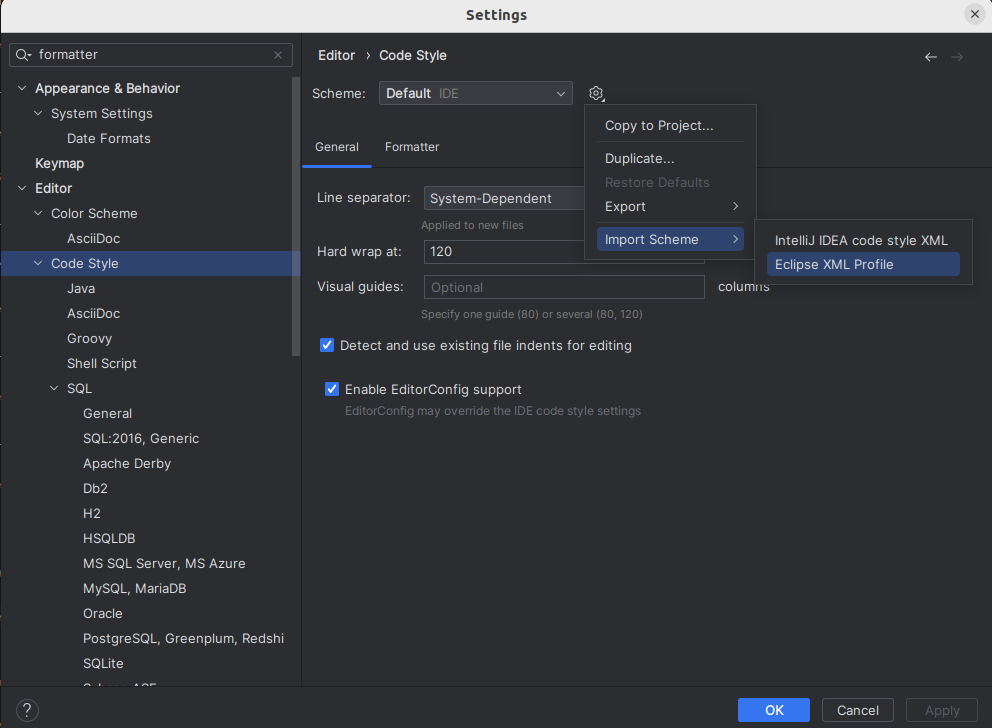
-
Ensure SecHub is your active profile. Select
SecHubas active profile, then press apply and close.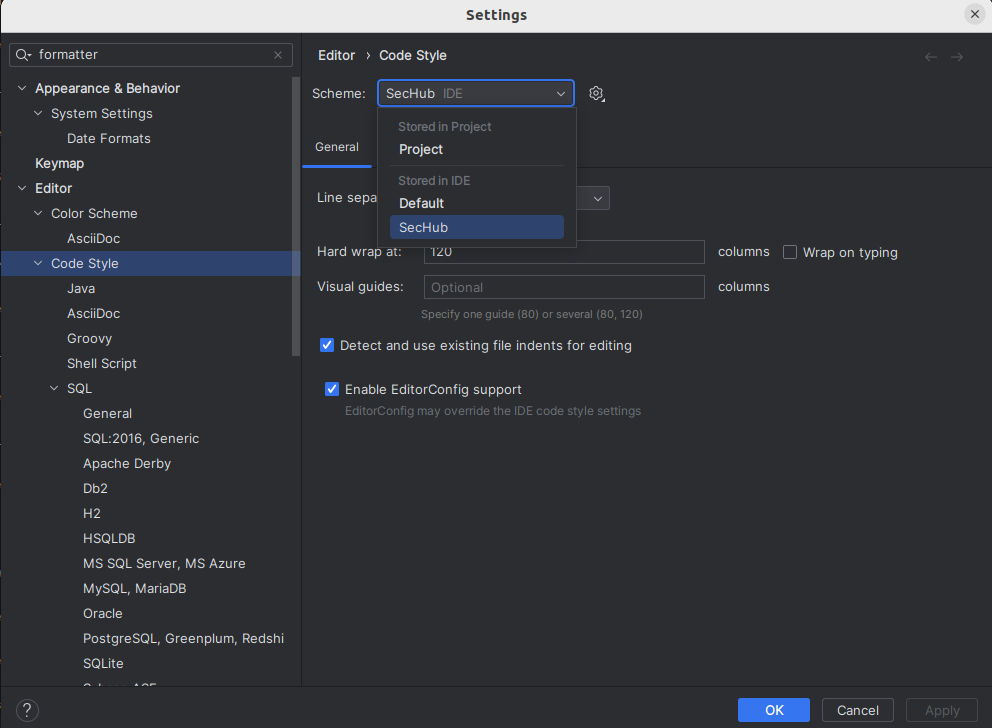
-
Before pushing your code please check your java format by executing spotless check.
./gradlew clean spotlessCheck
2.1.4. Special developer files
2.1.4.1. Developer property file
Inside ~/.sechub/sechub-developer.properties you can define some special default behaviours
| Key | Possible values/types | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.integrationtest.running |
boolean |
When |
See LocalDeveloperFileSetupSupport.java for details.
2.2. First steps
Here are some first steps to get SecHub running and being able to start developing.
2.2.1. Integration test scenario
With this setup we will start a SecHub server instance ready for executing integration tests. It does use only security product mocks, so we got no long running sessions. We need no running security suite… but of course we have no real products and can not make real scans.
2.2.1.1. Start integration test servers
2.2.1.1.1. IDE
To start Spring Boot application SecHubServerApplication create a new launch configuration with
following arguments:
class: com.mercedesbenz.sechub.SecHubServerApplication
-Dspring.profiles.active=integrationtest,mocked_products,h2 (1)
-Dsechub.server.debug=true (2)
-Dsechub.storage.sharedvolume.upload.dir=temp (3)| 1 | Starts server with
|
| 2 | When debug flag is set, rest call response error messages do also contains stacktraces. |
| 3 | We use temp which is a marker to create a temp folder for shared volume
(necessary for source upload) |
2.2.1.1.2. Console
./gradlew startIntegrationTestInstances
2.2.1.2. Start integration tests
Integration tests do completely execute commands like done on real system - except there is no real communication with security products but only with mocked variants.
| Integration tests do need always a running integration test server instance. |
2.2.1.2.1. IDE
When you have running integration test server instance, just execute JUnit at complete project sechub-integrationtest
with
-Dsechub.integrationtest.running=true
|
To make things easier there is the possibility to define system properties also
inside file:
This file is used inside integration tests automatically.
If you add a line with |
To execute the integration tests, you can use the following command:
./gradlew integrationtest
|
The gradle task But be aware: If you have executed a |
2.2.1.3. Stop integration test server
To stop your running server run:
2.2.1.3.1. Console
./gradlew stopIntegrationTestInstances
2.3. Developer Tools
The developer tools are a set of tools that help you to develop and test SecHub.
2.3.1. Shell scripts
The scripts are located in the sechub-developertools/scripts module.
They are used to start and stop the SecHub server, run integration tests, and perform other tasks related to development (sdc.sh).
The api scripts can communicate with the SecHub API (sechub-api.sh) or with a PDS API (pds-api.sh).
Execute the scripts with -h to get a list of available commands and options.
2.3.2. Test containers: PostgreSQL and OAuth2 server (Keycloak)
The test containers are used to run a PostgreSQL database and an OAuth2 server in a docker container for testing purposes. Both container can be started and stopped with gradle tasks, with bash scripts or as Java applications.
Please see to the README of the sechub-developertools module for more information about the test containers.
2.3.3. Developer administration UI
There exists a very simple user interface for developers to test out the behaviour of the SecHub server. There will be all functions of server available, but in a very reduced way.
|
The developer administration UI is only a tool for developers and should be handled with care. It’s an extreme simple client for administrative parts. For real administration a frontend for admins will be developed in future! It’s not purposed to be in a deployment, but only for development. |
2.3.3.1. General launch setup
To start simple swing application DeveloperAdministrationUI create a new launch configuration with
following arguments:
class: com.mercedesbenz.sechub.developertools.admin.ui.DeveloperAdministrationUI
-Dsechub.developertools.admin.server=${yourServerAddress}Environment entries:
SECHUB_ADMIN_USERID=${yourAdminAccount}
SECHUB_ADMIN_APITOKEN=${yourAdminAPIToken}
SECHUB_ADMIN_ENVIRONMENT=PROD|INT|Specific[TEST](1)
| 1 | Optional: Your environment. This will be shown inside Application as Title.
Also the variable content will provide some color effects: PROD will have red, INT yellow and
any content having TEST (case insensitive) inside will have cyan credential page inside.
When not set UNKNOWN will be used in title and no special color is used for credential panel. |
2.3.3.2. Integration test variant
To start simple swing application DeveloperAdministrationUI create a new launch configuration with
following arguments:
class: com.mercedesbenz.sechub.developertools.admin.ui.DeveloperAdministrationUI
-Dsechub.developertools.admin.server=localhost (1) -Dsechub.developertools.admin.serverport=8443(2) -Dsechub.developertools.admin.integrationtestserver=true (3) -Dsechub.developertools.admin.serverprotocol=https(4)
Environment entries:
SECHUB_ADMIN_USERID=int-test_superadmin(5) SECHUB_ADMIN_APITOKEN=int-test_superadmin-pwd(5)
| We use environment variables for credentials because otherwise everybody able to list running processes can see the user id and API token… |
| 1 | Please replace this with your server location. For development localhost |
| 2 | Optional: This is the server port - default
is 443. For development servers at your local machine
you should normally set to 8443. |
| 3 | Optional: Enable special integration test actions - e.g. create test data, start jobs etc. |
| 4 | Optional: Per default https will be used. If you have started (not recommended) SecHub
with SSL disabled and spring security disabled |
| 5 | These are the credentials used for administrative access. For integration tests we got fix credentials - so never use in production! |
Please see to the README of the sechub-developertools module for more information about the DAUI.
2.4. Branching model
Overview of branch types:
| Name-Pattern | Parent branch | Details |
|---|---|---|
|
none |
This is the leading branch. Versions, Tags etc. are done here! Direct commits to master have to be avoided. Version build is done here. |
|
master |
Hotfix branch. This is the branch we use for hot fixes.
So we ensure changes from After a hotfix has been merged to master the changes must be applied
to |
|
master |
Development branch. This branch will be part of the next release. Do not commit into this branch. Instead create a dedicated feature-branch. |
|
develop |
For each feature we create a |
3. SecHub infrastructure setup
3.1. Spring boot
3.1.1. SecHub Spring Profiles
SecHub provides multiple Spring profiles
3.1.1.1. Server
3.1.1.1.1. Overview
3.1.1.1.2. PROD
As name offers, this profile is designed for production.
|
For production the profile |
3.1.1.1.3. DEV
For development this profile must be combinated with others to get server starting - but its extreme flexible and has only a dependency to localserver
3.1.1.1.4. Integration-Test
SecHub itself
We use integrationtest profile for server integration tests. You must add some
additional profiles. We use h2 and mocked_products for unit testing
of sechub server itself.
The profile local_keycloak can be used to connect to a local keycloak server.
Default server can be started with ./gradlew runLocalTestKeycloakStarter command which will also generated a ready-to-use property file.
Test your security tool suite installation
You can use this profile also for testing your security product suite in combination with sechub server - e.g. when you have done an update at your product suite and you are not sure if its compatible or the products have bugs.
But (at least currently) you have to write your own tests then. Following could be done:
-
Write some simple bash scripts which are using SecHub client
-
Use
sechub-integrationtestproject as dependency and write some junit tests using TestAPI.
if you want to test your installed environment is working you can also use
real_products.
|
We got dedicated profile constants. For adapters the constants can be found at |
3.1.2. Database configuration
3.1.2.1. PostgreSQL
First of all, install a PostgreSQL database.
Then define following environment entries before you start the server with active postgres profile:
-
POSTGRES_DB_URL
-
POSTGRES_DB_USERNAME
-
POSTGRES_DB_PASSWORD
Examples:
POSTGRES_DB_URL=jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:49152/sechub POSTGRES_DB_USERNAME=sechub-pg-admin POSTGRES_DB_PASSWORD=a-very-strong-password...
3.1.3. General configuration
SecHub can be configured by keys on server startup.
Using the spring @Value annotation we are able to
use these keys as Java system properties but also as environment entries.
E.g. a key like sechub.server.baseurl can be set with
java ... -Dsechub.server.baseurl=https://sechub.example.org
or with an environment entry SECHUB_SERVER_BASEURL which
is e.g. more suitable for a kubernetes cluster deployment.
The next text blocks describe the keys available on SecHub:
The system properties described here are automatically
generated into this document by build server when
developers are using spring annotation @Value in conjunction with the
SecHub annotation @MustBeDocumented annotation inside code!
|
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.user.onetimetoken.outdated.millis |
86400000 |
One time token time when outdating |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.feature.showProductResultLink |
false |
Administrators can turn on this mode to allow product links in json and HTML output |
sechub.initialadmin.apitoken |
An apitoken for initial admin, will only be used in DEV and INTEGRATIONTEST profiles and is optional! |
|
sechub.initialadmin.email |
Mail of initial administrator |
|
sechub.initialadmin.userid |
Userid of initial administrator |
|
sechub.server.baseurl |
Base url of SecHub server - e.g. https://sechub.example.org |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.notification.email.mock.cache.enabled |
false |
When email mock shall cache the mails this must be configured to true, per default disabled! |
sechub.server.debug |
false |
When debug flag is set, rest call reponse error messages do also contain stacktraces. |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.email.rule.allowed-domains |
The allowed domains for email addresses of SecHub users. A comma separated list of strings like: 'example.com,company.org'. If nothing is specified all domains are allowed. |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.schedule.encryption.refresh.accept-outdated.milliseconds |
1800000 |
The maximum amount of milliseconds an outdated encryption pool is still accepted in refresh phase |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.config.trigger.healthcheck.enabled |
true |
When enabled each trigger will do an health check by monitoring service. If system has too much CPU load or uses too much memory, the trigger will not execute until memory and CPU load is at normal level! |
sechub.config.trigger.nextjob.delay |
10000 |
Define delay for next job execution trigger after last executed. |
sechub.config.trigger.nextjob.initialdelay |
5000 |
Define initial delay for next job execution trigger. Interesting inside a cluster - just define this value different inside your instances (e.g. random value). This avoids write operations at same time. |
sechub.config.trigger.nextjob.maxwaitretry |
300 |
When retry mechanism is enabled by |
sechub.config.trigger.nextjob.retries |
5 |
Inside a cluster the next job fetching can lead to concurrent access. When this happens a retry can be done for the 'looser'. This value defines the amount of *tries*If you do not want any retries set the value to a value lower than 2. 2 Means after one execution failed there is one retry. Values lower than 2 will lead to one try of execution only. |
sechub.project.joblist.page.max |
100 |
|
sechub.project.joblist.size.max |
100 |
Maximum limit for job information list entries per page |
sechub.schedule.nextjob.suspend.miniumum-duration.milliseconds |
60000 |
The scheduler automatically restarts the next suspended jobs, regardless of the defined schedule strategy. This is done to get suspended jobs of another shut down instance back up and running as quickly as possible. To avoid suspended jobs being restarted too quickly, you can use this value to set the minimum time that must pass before the next suspended job can be restarted. The value is defined in milliseconds. The (previous) end date of the suspended job is used. For example, this value is important for K8s redeployment, because the servers that have not yet been updated should not immediately continue with the suspended jobs - they will also be shut down soon and would suspend the restarted jobs again… |
sechub.scheduler.strategy.id |
Define the scheduler strategy by given identifier. This strategy determines the next job which shall be executed by job scheduler. Possible values are:first-come-first-serve,only-one-scan-per-project-at-a-time and only-one-scan-per-project-and-module-group |
|
sechub.server.upload.validate.checksum |
true |
With |
sechub.server.upload.validate.zip |
true |
With |
sechub.upload.binaries.maximum.bytes |
52428800 |
Define the maximum amount of bytes accepted for uploading |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.security.encryption |
||
sechub.security.encryption.secret-key |
The secret key for encryption (used for cookies etc.). Must be an exactly 256 bit long string |
|
sechub.security.login |
||
sechub.security.login.classic-auth |
Configuration for classic mode, only relevant when login modes contain 'classic' |
|
sechub.security.login.classic-auth.cookie-age-seconds |
Cookie age in seconds. |
|
sechub.security.login.enabled |
Defines if login enabled or not |
|
sechub.security.login.login-page |
The login page which can be used by external client (like WebUI) |
|
sechub.security.login.modes |
The login modes to use as a comma separated list. Possible values are 'oauth2' and 'classic' |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2 |
Configuration for oauth2, only relevant when login modes contain 'oauth2' |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2.authorization-uri |
URI that identifies the Authorization Server. For example: https://idp.example.org/oauth2/v2/auth |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2.client-id |
The client id used for oauth2 login handling |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2.client-secret |
The client secret used for oauth2 login handling |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2.issuer-uri |
URI that identifies the issuer. For example: https://idp.example.org |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2.jwk-set-uri |
URI for jwk. For example: https://idp.example.org/oauth2/v3/certs |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2.provider |
Name of the oauth2 provider. For example 'keycloak' |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2.redirect-uri |
This is the callback URI where the IDP will redirect the user after successful login; 'https://<sechub-server-host>/login/oauth2/code/<provider>'. For most IDPs this URI has to be configured inside the IDP client |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2.token-uri |
Represents the URI for the token endpoint. For example: https://idp.example.org/oauth2/v4/token |
|
sechub.security.login.oauth2.user-info-uri |
URI for user information. For example: https://idp.example.org/oauth2/v3/userinfo |
|
sechub.security.login.redirect-uri |
The redirect URI after a succesful login is done |
|
sechub.security.minimum-token-validity |
The minimum token expiration time, used as a minimum for cookie ages and token validity. If set higher than the default values it will always overwrite the default values. Uses standard java duration syntax. For example '60m' means sixty minutes, '1d' means one day. |
|
sechub.security.server |
||
sechub.security.server.modes |
The server modes to use as a comma separated list. Possible values are 'oauth2' and 'classic' |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2 |
||
sechub.security.server.oauth2.jwt |
||
sechub.security.server.oauth2.jwt.jwk-set-uri |
URI for jwk. For example: https://idp.example.com/oauth2/v3/certs |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2.mode |
The oauth2 mode to use. Can be either 'jwt' or 'opaque-token' |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token |
||
sechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.client-id |
Client id for oauth2 client being used for opaque token handling |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.client-secret |
The secret for the oauth2 client being used for opaque token handling |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.cluster-cache-clear-period |
The period until the in cluster cache will trigger a cleanup which removes expired values. Uses standard java duration syntax. For example '10s' means 10 seconds, '1m' means one minute. |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.default-token-expires-in |
The default token expiration time. Is used as fallback when IDP does not provide an expiration time. Uses standard java duration syntax. For example '60m' means sixty minutes, '1d' means one day. |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.inmemory-cache-clear-period |
The period until the in memory cache will trigger a cleanup which removes expired values. Uses standard java duration syntax. For example '10s' means 10 seconds, '1m' means one minute. |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.introspection-uri |
Introspection URI of the identify provider, will be used to check if the given opaque token from login is valid. |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.max-cache-duration |
The maximum cache duration. To avoid that the IDP is always asked again about the validity of an opaquetoken, the acceptance is cached. When this time exceeds,the introspection will be done and cached again. Uses standard java duration syntax. For example '60m' means sixty minutes, '1d' means one day. |
|
sechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.pre-cache-duration |
The pre cache duration: If a cluster wide cache is provided by the application, the in memory cache is acting as a precache to avoid too many cluster checks. In this case the in memory cache will not use the IDP expiration as cache timeout, but this one. If a value is no longer found in the short cache it will be retrieved by cluster cache. Uses standard java duration syntax. For example '10s' means 10 seconds, '1m' means one minute. |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.migration.flyway.autorepair |
true |
When enabled, flyway migration problems will be automatically repaired |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.monitoring.accepted.cpu.average.max |
2.0 |
Maximum CPU load average accepted by sechub system. Value is calculated by measured system load average divided by available processors. A value above 1.0 usually means that a processor is very heavily loaded. |
sechub.monitoring.accepted.memory.usage.max |
90.0 |
Maximum memory usage percentage accepted by sechub system. Can be a value from 50 up to 100 for 100% |
sechub.monitoring.cache.time.millis |
2000 |
Time in milliseconds monitoring fetch results are cached before fetching again |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.adapter.nessus.defaultpolicyid |
deprecated |
Default policy ID for nessus scans |
sechub.adapter.nessus.internet.baseurl |
deprecated |
Base url of nessus used for internet scans |
sechub.adapter.nessus.internet.password |
deprecated |
Password for nessus instance used for internet scans |
sechub.adapter.nessus.internet.userid |
deprecated |
User id of nessus user (internet) |
sechub.adapter.nessus.intranet.baseurl |
deprecated |
Base url of nessus used for intranet scans |
sechub.adapter.nessus.intranet.password |
deprecated |
Password for nessus instance used for intranet scans |
sechub.adapter.nessus.intranet.userid |
deprecated |
User id of nessus user (intranet) |
sechub.adapter.nessus.proxy.hostname |
Proxy hostname for nessus server connection, when empty no proxy is used. When not empty proxy port must be set too! |
|
sechub.adapter.nessus.proxy.port |
0 |
Proxy port for nessus server connection, default is 0. If you are setting a proxy hostname you have to configure this value correctly |
sechub.adapter.nessus.scanresultcheck.period.minutes |
-1 |
Time in minutes when adapter result check will automatically time out and adapter stops execution automatically. When -1 timeout is 7200 minutes |
sechub.adapter.nessus.scanresultcheck.timeout.minutes |
-1 |
Time in minutes when adapter result check will automatically time out and adapter stops execution automatically. When -1 timeout is 7200 minutes |
sechub.adapter.nessus.trustall |
true |
Turns off certification checks for this product only. Should only be used in test or development environments! |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.adapter.netsparker.agentname |
deprecated |
The name of the agent to be used by netsparker. If a agent group name is already defined the group will be superiour. If no group set and no agent name netsparker will use a agent but seems to be unpredictable which agent will be used. |
sechub.adapter.netsparker.apitoken |
deprecated |
API token for netsparker user |
sechub.adapter.netsparker.baseurl |
deprecated |
Base url for netsparker installation |
sechub.adapter.netsparker.defaultpolicyid |
deprecated |
Default policy ID for netsparker scans |
sechub.adapter.netsparker.internet.agentgroupname |
deprecated |
The name of the agent group to be used by netsparker for intranet scans. If not set no agent group will be used. |
sechub.adapter.netsparker.intranet.agentgroupname |
deprecated |
The name of the agent group to be used by netsparker for intranet scans. If not set no agent group will be used. |
sechub.adapter.netsparker.licenseid |
deprecated |
|
sechub.adapter.netsparker.scanresultcheck.period.minutes |
-1 |
Time in minutes when adapter result check will automatically time out and adapter stops execution automatically. When -1 timeout is 7200 minutes |
sechub.adapter.netsparker.scanresultcheck.timeout.minutes |
-1 |
Time in minutes when adapter check operation is called next. When -1 value is 1 minutes |
sechub.adapter.netsparker.trustall |
true |
Turns off certification checks for this product only. Should only be used in test or development environments! |
sechub.adapter.netsparker.userid |
deprecated |
user id of netsparker user |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.notification.email.administrators |
Single email address used for emails to administrators. This should be a NPM (non personalized mailbox) |
|
sechub.notification.email.from |
Address used for emails sent by sechub system |
|
sechub.notification.email.replyto |
Address used for reply when email was sent by sechub system |
|
sechub.notification.scheduler.startup.enabled |
true |
When enabled, administrators will be informed by notification when new scheduler instances are started. Those notifications will also contain information about potential zombie jobs. When disabled, incoming events will be ignored and no notification sent. |
sechub.notification.smtp.config |
mail.smtp.auth=false,mail.transport.protocol=smtp |
SMTP configuration map. You can setup all java mail smtp settings here in comma separate form with key=value. For Example: |
sechub.notification.smtp.credential.password |
Password on SMPTP server, empty value means no password |
|
sechub.notification.smtp.credential.username |
Username on SMPTP server, empty value means no username |
|
sechub.notification.smtp.hostname |
Hostname of SMPTP server |
|
sechub.notification.smtp.port |
25 |
Port of SMPTP server, per default:25 |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.assistant.ai.openai.api-token |
API token |
|
sechub.assistant.ai.openai.completions-uri |
Completions URI for open AI. Examples: https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions or https://your-apigateway.example.com/connect/opeanai/chat-gpt40o/chat/completions?version=2024-02-01 |
|
sechub.assistant.ai.openai.model |
Model to use |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.badrequest.retry.max |
3 |
Amount of retries done when a 400 bad request happened on Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.badrequest.retry.wait |
2000 |
Time to wait until retry is done when a 400 bad request happened on Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.servererror.retry.max |
1 |
Amount of retries done when a 500 server internal error happened on Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.servererror.retry.wait |
5000 |
Time to wait until retry is done when a 500 server internal error happened on Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.pds.default.check.timetowait.milliseconds |
30000 |
Time in milliseconds when adapter check operation is called next. When -1 value is 60000 minutes |
sechub.adapter.pds.default.timeout.minutes |
240 |
Time in minutes when adapter result check will automatically time out and adapter stops execution automatically. When -1 timeout is 7200 minutes |
sechub.adapter.pds.resilience.encryption-out-of-sync.retry.max |
3 |
Amount of retries done when a PDS encryption out of sync problem happens |
sechub.adapter.pds.resilience.encryption-out-of-sync.retry.wait |
2000 |
Time to wait until retry is done when a PDS encryption out of sync problem happens |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.badrequest.retry.max |
3 |
Maximum amount of possible retries for situations when a 400 bad request happened on Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.badrequest.retry.wait |
2000 |
Time to wait until retry is done when a 400 bad request happened on Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.networkerror.retry.max |
100 |
Maximum amount of possible retries for situations when a network error happened on communication to Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.networkerror.retry.wait |
5000 |
Time to wait until retry is done when a network server happened on communication to Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.servererror.retry.max |
1 |
Maximum amount of possible retries for situations when a 500 server internal error happened on Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.resilience.servererror.retry.wait |
5000 |
Time to wait until retry is done when a 500 server internal error happened on Checkmarx server |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.scanresultcheck.period.minutes |
-1 |
Time in minutes when adapter check operation is called next. When -1 value is 1 minutes |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.scanresultcheck.timeout.minutes |
-1 |
Time in minutes when adapter result check will automatically time out and adapter stops execution automatically. When -1 timeout is 7200 minutes |
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.trustall |
false |
Turns off certification checks for this product only. Should only be used in test or development environments! |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.config.check.canceljob.delay |
60000 |
Define delay in milliseconds, for before next job cancellation check will be executed. |
sechub.config.scan.scanconfig.refresh.delay |
5000 |
Define delay (in milliseconds) for next job execution trigger after last executed. |
sechub.config.scan.scanconfig.refresh.initialdelay |
0 |
Define initial delay (in milliseconds) for scan config refresh check operation. |
sechub.report.sensitivedata.max.nonobfuscated.characters |
0 |
Define the amount of visible characters which are NOT obfuscated. |
sechub.target.resolve.strategy.ip |
Strategy to decide target types by given IP. |
|
sechub.target.resolve.strategy.uri |
One ore more strategies to decide target types by given URI. |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.security.diffiehellman.length |
Define diffie hellman key length, see https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub/issues/689 for details |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.storage.s3.accesskey |
undefined |
Defines the access key for used S3 bucket |
sechub.storage.s3.bucketname |
undefined |
Defines the S3 bucket name |
sechub.storage.s3.connection.idle.max.milliseconds |
60000 |
S3 client maximum idle time (in milliseconds) for a connection in the connection pool. |
sechub.storage.s3.connection.idle.validate.milliseconds |
5000 |
S3 client time (in milliseconds) a connection can be idle in the connection pool before it must be validated that it’s still open. |
sechub.storage.s3.connection.max.poolsize |
50 |
S3 client max connection pool size. |
sechub.storage.s3.connection.ttl.milliseconds |
-1 |
S3 client expiration time (in milliseconds) for a connection in the connection pool. -1 means deactivated |
sechub.storage.s3.endpoint |
undefined |
Defines the S3 endpoint - e.g. https://play.min.io |
sechub.storage.s3.region |
undefined |
S3 client region. Supported are offical AWS region names and additionally: |
sechub.storage.s3.secretkey |
undefined |
Defines the secret key for used S3 bucket |
sechub.storage.s3.signer.override |
AWSS3V4SignerType |
Can be used to override the default name of the signature algorithm used to sign requests. |
sechub.storage.s3.timeout.connection.milliseconds |
10000 |
S3 client timeout (in milliseconds) for creating new connections. |
sechub.storage.s3.timeout.execution.milliseconds |
0 |
S3 client timeout (in milliseconds) for execution. 0 means it is disabled. |
sechub.storage.s3.timeout.request.milliseconds |
0 |
S3 client timeout (in milliseconds) for a request. 0 means it is disabled. |
sechub.storage.s3.timeout.socket.milliseconds |
50000 |
S3 client timeout (in milliseconds) for reading from a connected socket. |
sechub.storage.sharedvolume.upload.dir |
undefined |
Defines the root path for shared volume uploads - e.g. for sourcecode.zip etc. When using keyword temp as path, this will create a temporary directory (for testing). |
3.1.4. Scheduling definitions
The schedule setup described here is generated into this document
by build server when developers are using spring annotation @Scheduled in conjunction with the
sechub annotation @MustBeDocumented annotation inside code!
|
| Type | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
Fixed |
initial delay:${sechub.config.trigger.autoclean.initialdelay:5000} fixed delay:${sechub.config.trigger.autoclean.delay:86400000} |
Auto cleanup is triggered by a cron job operation - default is one day to delay after last execution. As initial delay 5000 milliseconds are defined. It can be configured differently. This is useful when you need to startup a cluster. Simply change the initial delay values in to allow the cluster to startup. |
| Type | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
Fixed |
initial delay:${sechub.schedule.encryption.refresh.initialdelay:5000} fixed delay:${sechub.schedule.encryption.refresh.delay:300000} |
Defines the initial and also the fixed delay for the refresh interval. These values are also used for calculation of remaining run time of outdated encrytion pools (when refresh fails) |
| Type | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
Fixed |
initial delay:${sechub.config.trigger.nextjob.initialdelay:5000} fixed delay:${sechub.config.trigger.nextjob.delay:10000} |
Job scheduling is triggered by a cron job operation - default is 10 seconds to delay after last execution. For initial delay 5000 milliseconds are defined. It can be configured differently. This is useful when you need to startup a cluster. Simply change the initial delay values in to allow the cluster to startup. |
3.1.5. Configuration properties for mocked adapters
The system properties described here are automatically
generated into this document by build server when
developers are using spring annotation @Value inside instances implementing MockedAdapter.
If you want details about the mock behavior you have to read the comments inside the java
class being named in description column.
|
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.adapter.mock.sanitycheck.enabled |
false |
See AbstractMockedAdapter.java |
| Key or variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.adapter.checkmarx.clientsecret |
014DF517-39D1-4453-B7B3-9930C563627C |
See MockedCheckmarxAdapter.java |
sechub.adapter.mock.setup.filepath |
./../sechub-other/mockdata/mockdata_setup.json |
See MockedAdapterSetupService.java |
3.2. Spring Boot Security
SecHub uses Spring Boot Security to secure the application. Spring Security can be split into two modes:
-
Resource Server -
Login
3.2.1. Resource Server
In Resource Server mode you tell Spring to authenticate incoming requests using existing credentials and tokens. SecHub
allows for Basic Authentication or OAuth2.
In SecHub we call anything that has to do with basic authentication the Classic mode. The classic mode is the default
authentication mode for SecHub. In classic mode the server validates the credentials itself using the database.
SecHub requires you to activate at least Classic mode or OAuth2. If you don’t have any requirements for OAuth2
you can simply use the classic mode.
|
OAuth2 can be split further into two modes: JWT and Opaque Token.
With JWT mode enabled the server checks the token itself using signature validation.
Below is an example configuration with Classic mode and OAuth2 in JWT mode:
sechub:
security:
server:
modes: oauth2,classic (1)
oauth2:
mode: jwt
jwt:
jwk-set-uri: <jwk-set-uri-of-your-idp>| 1 | A list of comma separated resource server modes. Supported values are: oauth2 and classic.
At least one mode must be defined. |
In Opaque Token mode the server forwards the token to an introspection endpoint for every request.
Opaque Token mode increases the load on the IDP server hence caching is very important. Adjust the caching settings to your
IDPs needs. If you don’t have high security requirements you can simply use JWT mode.
|
Below is an example configuration with Classic mode and OAuth2 in Opaque Token mode:
sechub:
security:
server:
modes: oauth2
oauth2:
mode: opaque-token
opaque-token:
introspection-uri: <introspection-uri-of-your-idp>
client-id: <client-id>
client-secret: <client-secret>
default-token-expires-in: 60m # default is '1d' if this property is not set
max-cache-duration: 1d-
default-token-expires-in: The default expiration time for tokens. This is used when the IDP does not provide an expiration time. -
max-cache-duration: The maximum time a token is cached on SecHub side. After this time, the token is introspected again.
3.2.2. Login
SecHub can also be configured to act as a login provider. With login enabled SecHub will serve a login mask under the
configured path. After successful authentication the user will be redirected to the configured redirect uri. The redirect
will also include the authentication details in the Cookies. With this any browser based client will be automatically
authenticated in subsequent requests unless the cookies are cleared or the authentication expires.
Like with the Resource Server mode you can choose between Classic and OAuth2.
The authentication credentials are securely encrypted in the cookies. For that AES 256 Encryption is used. You
have to configure a secret key for the encryption.
|
While the cookie age is defined by the IDP in OAuth2 mode, in Classic mode you can configure the cookie age
yourself. The default is 24 hours.
|
Below is a full configuration example with Login enabled in Classic and OAuth2 mode:
sechub:
security:
server:
modes: oauth2,classic (1)
oauth2:
mode: jwt
jwt:
jwk-set-uri: <jwk-set-uri-of-your-idp>
login:
enabled: true
# This is the path where the login mask will be served on the SecHub server
# You can choose any other path as long as it does not conflict with existing paths
login-page: /login
# Here you can configure the target application where the user will be redirected after successful login
redirect-uri: <your-target-application>
modes: oauth2,classic
oauth2:
client-id: <client-id>
client-secret: <client-secret>
provider: <provider> # e.g. keycloak
# This is the callback uri where the IDP will redirect the user after successful login
# For most IDPs this URI has to be configured inside the IDP client
redirect-uri: https://<sechub-server-host>/login/oauth2/code/<provider>
issuer-uri: <issuer-uri>
authorization-uri: <authorization-uri>
token-uri: <token-uri>
user-info-uri: <user-info-uri>
jwk-set-uri: <jwk-set-uri>
classic-auth:
cookie-age-seconds: 86400 # This is the default
encryption:
secret-key: <aes-256-compatible-secret-key> (3)| 1 | Provided server resource mode. In this case classic and oauth2 are enabled and
resource server provides both modes. |
| 2 | Provided login modes. In this case classic and oauth2 are enabled and user will
have both login possibilities. |
| 3 | SecHub uses AES encryption to provide temporary but still sensitive information in a secure way.
This is the secret key for the encryption. The key can be anything, but must
have exactly a length of 32 bytes. For example: example-key-32-byte-long-1234567. |
3.2.2.1. Customizing the Login Mask
The static content of the login mask can be customized by providing a custom background image, custom logo and custom colors. This can be done by using the following property:
spring:
web:
resources:
static-locations: file:/custom/static, classpath:/staticThe files in your custom static location will be served before the default static files are served,
as long as they follow the same structure as the default files.
See the 'sechub-commons-security-spring' module for more information about the static file structure.
Example:
/custom/static/login/css/main.css will be served before /static/login/css/main.css which allows you to override the default colors.
3.3. Local development
This section describes the start on local machine (development/presentation).
Only SecHub itself is described. The products must be either running and well
configured, or profile mocked_products must be active.
See product infrastructure sections for details.
3.3.1. Java launch configuration setup
Because it takes too much time - even when security products are configured with
test profiles (for testing persistence, transaction rollback etc.) a
mocked_products profile was introduced which can be used.
See Spring Profiles.
It does use normal product executors but injects mocked adapters
(e.g. MockedNessusAdapter, MockedNetsparkerAdapter, ..)
which do not really communicate with the real security products but return
instead preconfigured values (which where recorded from real communications).
Startup is done by using active spring profile mocked_products.
Some mocks have special options to change their behaviour at runtime.
Please refer to Mock options for details.
3.3.1.1. Launch configuration for development
3.3.1.1.1. Custom configuration files
If you want to have your own custom configuration do following steps:
-
Create a file
sechub-server/src/main/resources/application-local.${user}.yml.${user}is the value of your system user name (e.g.application-local.johndoe.yml) -
Use the spring profile
localinside your launch configuration (it delegates to the file)
All application-local.${user}.yml files are ignored by git. So developers don’t have to
be aware about committing accidently changes.
|
3.3.1.1.2. DEV profile
With activated DEV spring profile it is possible to define an api-token programmatically
and it will not be generated by SecHub server on startup.
It also enables debug logging and includes the localserver profile which
automatically uses the generated local server certificates.
3.3.1.1.3. Example for DEV profile combined with custom configuration file
To start Spring Boot application SecHubServerApplication create a new launch configuration with
following arguments:
class: com.mercedesbenz.sechub.SecHubServerApplication
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev,h2,mocked_products,local (1)| 1 | Enables debug logging, localserver certificates, uses mocked products,
starts server with h2 database and uses custom configurations.
|
Create custom configuration file (assumed the the user has id: johndoe):
sechub:
server:
debug: true #To have REST call reponse error messages do also contains stacktraces.
# Storage - just juse local file system and generated temp folder
storage:
sharedvolume:
upload:
dir: temp (1)
# Only in DEV profile available: we can set the initial admin with wanted api token
initialadmin:
userid: sechub-developer
email: sechub-developer@example.org
apitoken: pseudo-token-development-only
# Web UI parts:
# Provide here only the classic resource server + login mask (no oAuth2 here)
security:
server:
modes: classic
login:
enabled: true
login-page: /login # For ui development login will be at https://localhost:8443/login
redirect-uri: http://localhost:3000 #redirect to web ui (2)
modes: classic
encryption:
secret-key: example-key-32-byte-long-1234567| 1 | We use temp which is a marker to create a temporary folder for shared volume.
This is also a marker that the storage is a NFS/local folder and SecHub will not insist
an a S3 storage setup.Remark: It is also possible to define here an explicit path! |
| 2 | For development with VITE, no TLS (https) is used. For development with VITE this is okay, but NEVER for production! |
|
Details about the user initialization process by using different profiles can be found at |
|
The If you want to test the SecHub server login page mechanism in combination with a
sechub-web-ui in development mode, you can use former sechub-web-ui/.env
If |
3.3.1.2. Launch configuration for integration tests
To start Spring Boot application SecHubServerApplication create a new launch configuration with
following arguments:
class: com.mercedesbenz.sechub.SecHubServerApplication
-Dspring.profiles.active=integrationtest,mocked_products,h2 (1)
-Dsechub.server.debug=true (2)
-Dsechub.storage.sharedvolume.upload.dir=temp (3)| 1 | Starts server with
|
| 2 | When debug flag is set, rest call response error messages do also contains stacktraces. |
| 3 | We use temp which is a marker to create a temp folder for shared volume
(necessary for source upload) |
3.3.1.3. Launch configurationfor production
| To run a local server like in production please refer How to start localserver like in production |
To start Spring Boot application SecHubServerApplication create a new launch configuration with
following arguments:
class: com.mercedesbenz.sechub.SecHubServerApplication
-Dspring.profiles.active=prod (1)
...
-Dsechub.adapter.name.something.specific=${necessaryData} (2)
...
-Dsechub.storage.sharedvolume.upload.dir=/srv/storage/persistent-volume1 (3)
-Dsechub.initialadmin.userid=real-superadmin(4)
-Dsechub.initialadmin.email=real-superadmin@example.org(4)
-Dserver.ssl.key-store=path/to/keystore.p12 (5)
-Dserver.ssl.key-store-type=PKCS12 (5)
-Dserver.ssl.key-alias=yourKeyAlias (5)
-Dserver.ssl.key-store-password=yourKeyStorePassword (5)
-Dsechub.notification.smtp.hostname=intranet.example.org (6)
-Dsechub.notification.smtp.port=50(6)
-Dsechub.notification.smtp.config=mail.smtp.auth=false(6)| 1 | Starts server with
|
| 2 | This is just an example for a adapter specific setting. Please look into system property definitions and look for adapter parts. |
| 3 | Define here the absolute path used for shared volume storage (necessary for source upload) |
| 4 | When there is no existing admin inside SecHub database on startup,
the given user credentials will be automatically created. Look at the log output to get the initial, generated API token for admin. Be aware that you must regenerate a new api token for this user, or delete the initial admin account after creating another admin, because credentials are inside logs… |
| 5 | This is PROD environment SSL configuration. The example shows setup for p12 certificate storage - see spring boot documentation for exact syntax. |
| 6 | Setup for smtp server for mail sending. Port and config are optional. See system property definitions for details. |
|
Your server will not start if you forget an adapter key ! (this will change in future when SecHub becomes more modular) |
|
Please don’t forget to have at least one server running with active profile Servers without having this profile activated, will provide only standard API access. Reason for this behavior: Administrators can reduce access to administrative API by IP and port firewall settings. This is only necessary for production! Development and Integrationtest profiles do automatically include
the An example for production: |
3.4. Security product integrations
3.4.1. PDS solutions
SecHub provides multiple security products via the PDS (product delegation server) containerized and also K8s ready (helm charts). These solutions are always cluster ready and work "out of the box".
Please visit https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub/tree/develop/sechub-pds-solutions for details and a complete list of supported products.
3.4.2. Sereco
Sereco is not a product to buy but a own developed sechub report collector.
Why an own report collector? We formerly did try to use an commercial tool, but we were stuck with many problems, e.g.
-
crucial problems with installation
-
no clustering
-
missing REST API for imports
-
not supporting some product results
-
… more…
3.4.2.1. Install
The software comes currently up with SecHub server installation. So nothing more is to do.
Scaling etc. is done with SecHub scaling.
3.4.2.1.1. Future
Currently Sereco is an embedded component of SecHub. Maybe there comes a time where Sereco will become a seperate server component which will be deployed standalone.
If so there are some changes to do (e.g. creating a rest API) etc. But as long as there is no need for a separate installation
it makes no sense to change this.
3.4.3. Prepare (Remote Data Preparation)
Prepare is not a scan product, but a developed wrapper application to prepare remote sources for scans.
It is used to download remote sources and upload them to the shared storage make them available to the scan products.
This allows the user to scan remote data without having to store it locally on a computer and upload it with the client.
The remote section can be defined in the sechub configuration instead of the filesystem.
Please note the PDS prepare can only be executed with a shared storage setup. These limitations are due to the fact, that the sechub server can not download sources from a PDS and copy them to another.
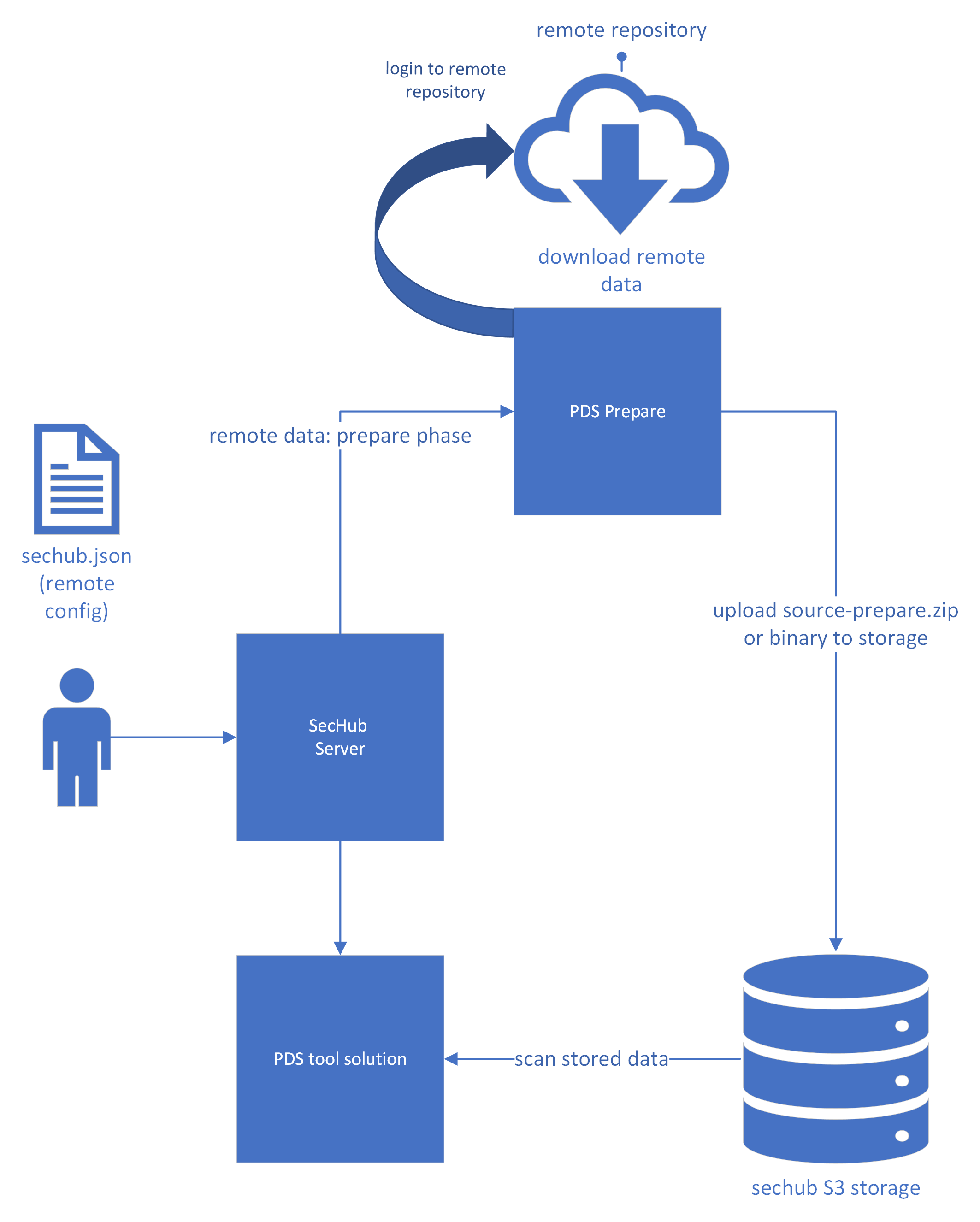
3.4.4. Checkmarx
|
Currently we provide Checkmarx as direct product inside SecHub and also as a PDS solution. The aim is to provide Checkmarx only as pds} solution in future. So the direct product integration will vanish. |
Static code analyzer see http://www.checkmarx.com/
3.4.5. Netsparker
|
Netsparker support inside SecHub is deprecated and will vanish. As a replacement we have: https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub/tree/develop/sechub-pds-solutions/owaspzap |
Netsparker is a web scanner.
3.4.6. Nessus
|
Nessus support inside SecHub is deprecated and will vanish when there is another infrastructure scan product integration available as an replacement. |
3.5. Docker-Compose
Change into the product’s folder and issue:
docker-compose up
| Please also see the README file in the respective folder. |
3.6. Kubernetes
We provide container images and Helm charts: https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub/packages
4. Test / Use real products
4.1. Mandatory configuration
| Next lines will show java launcher properties which MUST be set because there are no defaults defined. You have to define those values when not starting in mock mode! The example her is generated and will always show the current necessary parts. |
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev,postgres,real_products -Dsechub.initialadmin.email=value -Dsechub.initialadmin.userid=value -Dsechub.server.baseurl=value -Dsechub.email.rule.allowed-domains=value -Dsechub.security.encryption=value -Dsechub.security.encryption.secret-key=value -Dsechub.security.login=value -Dsechub.security.login.classic-auth=value -Dsechub.security.login.classic-auth.cookie-age-seconds=value -Dsechub.security.login.enabled=value -Dsechub.security.login.login-page=value -Dsechub.security.login.modes=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2.authorization-uri=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2.client-id=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2.client-secret=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2.issuer-uri=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2.jwk-set-uri=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2.provider=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2.redirect-uri=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2.token-uri=value -Dsechub.security.login.oauth2.user-info-uri=value -Dsechub.security.login.redirect-uri=value -Dsechub.security.minimum-token-validity=value -Dsechub.security.server=value -Dsechub.security.server.modes=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.jwt=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.jwt.jwk-set-uri=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.mode=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.client-id=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.client-secret=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.cluster-cache-clear-period=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.default-token-expires-in=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.inmemory-cache-clear-period=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.introspection-uri=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.max-cache-duration=value -Dsechub.security.server.oauth2.opaque-token.pre-cache-duration=value -Dsechub.notification.email.administrators=value -Dsechub.notification.email.from=value -Dsechub.notification.smtp.hostname=value -Dsechub.assistant.ai.openai.api-token=value -Dsechub.assistant.ai.openai.completions-uri=value -Dsechub.assistant.ai.openai.model=value -Dsechub.security.diffiehellman.length=value
| Instead of java system properties you can also define environment entries at your launch configuration or your shell and reduce parameter hell: |
export SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=dev,postgres,real_products export SECHUB_INITIALADMIN_EMAIL=value export SECHUB_INITIALADMIN_USERID=value export SECHUB_SERVER_BASEURL=value export SECHUB_EMAIL_RULE_ALLOWEDDOMAINS=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_ENCRYPTION=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_ENCRYPTION_SECRETKEY=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_CLASSICAUTH=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_CLASSICAUTH_COOKIEAGESECONDS=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_ENABLED=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_LOGINPAGE=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_MODES=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2_AUTHORIZATIONURI=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2_CLIENTID=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2_CLIENTSECRET=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2_ISSUERURI=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2_JWKSETURI=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2_PROVIDER=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2_REDIRECTURI=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2_TOKENURI=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_OAUTH2_USERINFOURI=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_LOGIN_REDIRECTURI=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_MINIMUMTOKENVALIDITY=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_MODES=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_JWT=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_JWT_JWKSETURI=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_MODE=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_OPAQUETOKEN=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_OPAQUETOKEN_CLIENTID=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_OPAQUETOKEN_CLIENTSECRET=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_OPAQUETOKEN_CLUSTERCACHECLEARPERIOD=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_OPAQUETOKEN_DEFAULTTOKENEXPIRESIN=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_OPAQUETOKEN_INMEMORYCACHECLEARPERIOD=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_OPAQUETOKEN_INTROSPECTIONURI=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_OPAQUETOKEN_MAXCACHEDURATION=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_SERVER_OAUTH2_OPAQUETOKEN_PRECACHEDURATION=value export SECHUB_NOTIFICATION_EMAIL_ADMINISTRATORS=value export SECHUB_NOTIFICATION_EMAIL_FROM=value export SECHUB_NOTIFICATION_SMTP_HOSTNAME=value export SECHUB_ASSISTANT_AI_OPENAI_APITOKEN=value export SECHUB_ASSISTANT_AI_OPENAI_COMPLETIONSURI=value export SECHUB_ASSISTANT_AI_OPENAI_MODEL=value export SECHUB_SECURITY_DIFFIEHELLMAN_LENGTH=value
|
Please don’t forget to have at least one server running with active profile Servers without having this profile activated, will provide only standard API access. Reason for this behavior: Administrators can reduce access to administrative API by IP and port firewall settings. This is only necessary for production! Development and Integrationtest profiles do automatically include
the An example for production: |
4.1.1. Storage configuration
In SecHub we need to store job data (e.g. zipped source code).
At least one storage setup must be defined- otherwise SecHub server will not start! You can either define a shared volume (normally a NFS) or a S3 storage.
Look at Storage configuration for configuration details.
4.2. Start server in DEV mode
To start Spring Boot application SecHubServerApplication create a new launch configuration with
following arguments:
class: com.mercedesbenz.sechub.SecHubServerApplication
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev,h2,mocked_products,local (1)| 1 | Enables debug logging, localserver certificates, uses mocked products,
starts server with h2 database and uses custom configurations.
|
Create custom configuration file (assumed the the user has id: johndoe):
sechub:
server:
debug: true #To have REST call reponse error messages do also contains stacktraces.
# Storage - just juse local file system and generated temp folder
storage:
sharedvolume:
upload:
dir: temp (1)
# Only in DEV profile available: we can set the initial admin with wanted api token
initialadmin:
userid: sechub-developer
email: sechub-developer@example.org
apitoken: pseudo-token-development-only
# Web UI parts:
# Provide here only the classic resource server + login mask (no oAuth2 here)
security:
server:
modes: classic
login:
enabled: true
login-page: /login # For ui development login will be at https://localhost:8443/login
redirect-uri: http://localhost:3000 #redirect to web ui (2)
modes: classic
encryption:
secret-key: example-key-32-byte-long-1234567| 1 | We use temp which is a marker to create a temporary folder for shared volume.
This is also a marker that the storage is a NFS/local folder and SecHub will not insist
an a S3 storage setup.Remark: It is also possible to define here an explicit path! |
| 2 | For development with VITE, no TLS (https) is used. For development with VITE this is okay, but NEVER for production! |
|
Details about the user initialization process by using different profiles can be found at |
|
The If you want to test the SecHub server login page mechanism in combination with a
sechub-web-ui in development mode, you can use former sechub-web-ui/.env
If |
| Please refer also Howto integrate new products |
4.3. Start server in PROD mode
To start Spring Boot application SecHubServerApplication create a new launch configuration with
following arguments:
class: com.mercedesbenz.sechub.SecHubServerApplication
-Dspring.profiles.active=prod (1)
...
-Dsechub.adapter.name.something.specific=${necessaryData} (2)
...
-Dsechub.storage.sharedvolume.upload.dir=/srv/storage/persistent-volume1 (3)
-Dsechub.initialadmin.userid=real-superadmin(4)
-Dsechub.initialadmin.email=real-superadmin@example.org(4)
-Dserver.ssl.key-store=path/to/keystore.p12 (5)
-Dserver.ssl.key-store-type=PKCS12 (5)
-Dserver.ssl.key-alias=yourKeyAlias (5)
-Dserver.ssl.key-store-password=yourKeyStorePassword (5)
-Dsechub.notification.smtp.hostname=intranet.example.org (6)
-Dsechub.notification.smtp.port=50(6)
-Dsechub.notification.smtp.config=mail.smtp.auth=false(6)| 1 | Starts server with
|
| 2 | This is just an example for a adapter specific setting. Please look into system property definitions and look for adapter parts. |
| 3 | Define here the absolute path used for shared volume storage (necessary for source upload) |
| 4 | When there is no existing admin inside SecHub database on startup,
the given user credentials will be automatically created. Look at the log output to get the initial, generated API token for admin. Be aware that you must regenerate a new api token for this user, or delete the initial admin account after creating another admin, because credentials are inside logs… |
| 5 | This is PROD environment SSL configuration. The example shows setup for p12 certificate storage - see spring boot documentation for exact syntax. |
| 6 | Setup for smtp server for mail sending. Port and config are optional. See system property definitions for details. |
|
Your server will not start if you forget an adapter key ! (this will change in future when SecHub becomes more modular) |
|
Please don’t forget to have at least one server running with active profile Servers without having this profile activated, will provide only standard API access. Reason for this behavior: Administrators can reduce access to administrative API by IP and port firewall settings. This is only necessary for production! Development and Integrationtest profiles do automatically include
the An example for production: |
5. Special setup
5.1. Terminate SSL and use HTTP only
Per default SecHub will always use HTTPS for communication.
Its not recommended, but if somebody wants to use SecHub with HTTP only
(e.g. when running behind a SSL proxy) this can be done in this way:
Start your server as described before but add following additional system properties:
-Dserver.ssl.enabled=false -Dsecurity.require-ssl=false
| This will disable ssl encryption and also Spring security which requires ssl. |
If you want to administrate this by developer admin ui, you should also switch to the HTTP protocol as described in section developer admin UI setup
6. Security in development
We enable security even in early stage of development! There is no test, no integration test or anything else which would use http only!
|
6.1. CLI client
There are some options for CLI client which were not supposed to be used in production. So instead of exposing such options by help we use those by explicit ENV entries
| ENV-NAME | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
SECHUB_DEBUG |
"true" |
Activates debug logging |
SECHUB_DEBUG_HTTP |
"true" |
Shows HTTP request+response contents including headers |
SECHUB_TRUSTALL |
"true" |
Trust all certificates (only for development). The SecHub client shows a warning when |
6.2. Server
6.2.1. Spring Boot Security
Spring boot security is always turned on, no matter if development or in production.
6.2.2. Security Configuration
SecHub Server supports two different modes when it comes to security.
-
1) Classic Mode: This is the standard SecHub authentication mode. In this mode
Basic Authis available for authentication. Whenever we speak ofBasic Auth, we refer to this mode.
It is the default, but if you want to define it explicit you can use:
sechub:
security:
server:
modes: classic-
2) OAuth2 Mode: Like the name suggests, this mode enables
OAuth2for authentication.
Both modes can be enabled at the same time, but at least one of them must be enabled.
When running SecHub Server, Classic Mode is enabled. This means that you can use Basic Auth to authenticate yourself
against the API. Your credentials are provided when starting up the server. You don’t have to configure anything else
when running this mode only.
If you want to test OAuth2 integration with IDPs (Identity Providers) like Keycloak, you can do so like this:
sechub:
security:
server:
modes: oauth2
oauth2:
mode: jwt
jwt:
jwk-set-uri: <jwk-set-uri-of-your-idp>Note that above configuration assumes that your IDP is configured to work with JWT tokens. This is the standard use case
for most applications, but SecHub also supports a different type of token, namely Opaque Tokens. If you want to use Opaque
Tokens, you have to configure the mode to opaque-token instead of jwt:
sechub:
security:
server:
modes: oauth2
oauth2:
mode: opaque-token
opaque-token:
introspection-uri: <introspection-uri-of-your-idp>
client-id: <client-id>
client-secret: <client-secret>
default-token-expires-in: 60m
max-cache-duration: 1dWe recommend Keycloak as an IDP for testing purposes. It is easy to set up and provides a lot of features for free.
But you are free to use any other IDP you like.
-
3) OAuth2 + Classic Mode
It is possible to use both modes at same time - for example:
sechub:
security:
server:
modes: oauth2,classic
oauth2:
mode: jwt
jwt:
jwk-set-uri: <jwk-set-uri-of-your-idp>6.2.3. Certificates
For development gradle task ensureLocalhostCertificate in sechub-server will automatically generate a
localhost server certificate. For details look into task and called bash script.
7. Coding conventions
7.1. Commit messages
We always commit with an issue id inside the headline message means e.g. on command line:
commit -m "Some short summary #${issueNr}"When having details we always add an empty new line after summary and list details, maybe using "-" at
the beginning to have a pretty output in GitHub
7.2. Database
|
Currently, we use H2 and PostgreSQL in parallel (dev/testing + production). |
7.2.1. Naming in DB
-
We are using PostgreSQL which does automatically use lower_case names
-
Numbering starts at
01; maximum is99 -
Naming scheme for constraints:
c<number>_<table name>_<constraint title>
Example:c01_adm_user_emailaddress -
Naming scheme for indices:
i<number>_<table name>_<index title>
Example:i01_statistic_job_run_data_filter
7.2.2. Naming in JPA
We are using upper cased names
7.3. YAML
|
Currently we still have a lot of unconventional YAML files. But there is a GitHub issue to adopt them. If you are writing new YAML files or adding new content to existing files, please follow always the instructions below. |
7.3.1. General
-
YAML files have the file ending
.yamlor.yml
(but.yamlshould be preferred when possible) -
Define SPDX header with MIT license as first line comment
-
Use always same indention inside a YAML document
(2 spaces should be preferred) -
Define strings with single apostrophes or double apostrophes
(to make it clear that the value is a string) -
If possible, define integers, long numbers etc. as numbers
-
Prefer hierarchical key structure to long key variants
-
Use comments to explain details (when really necessary)
-
Use one space between key and value definitions (e.g.
key-alias: 'tomcat')
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
# This configuration setup is only for local development and needs
# a generated certificate which is never shared. Because of this
# it is valid to define the credentials inside this file.
server:
ssl:
keyStoreType: 'PKCS12'
# we use a keystore location which is never tracked by git.
# see dev-create_localhost_certificate.sh and dev-ensure_localhost_certificate.sh
key-store: 'classpath:certificates-untracked/generated-dev-localhost-keystore.p12'
key-store-password: '123456'
key-alias: 'tomcat'
port: 8444
pds:
server:
baseurl: "https://localhost:${server.port}"
config:
trigger:
nextjob:
initialdelay: 100
delay: 5007.3.2. Templates
When defining YAML templates - e.g. for HELM charts
-
a template statement (e.g.
- ifor- end) shall start at the first column without indention -
nested template statements shall be indented (see example below)
-
place inserted values indented like normal YAML. (Use
| trimif appropriate)
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
{{- if .Values.networkPolicy.enabled }}
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: {{ .Chart.Name }}-policy
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
name: {{ .Chart.Name }}
{{- if .Values.networkPolicy.ingress }}
ingress:
{{ .Values.networkPolicy.ingress | toYaml | indent 4 | trim }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}7.4. Java
7.4.1. Classes
Defined class names
-
Rest controllerwill be called${name}RestController.java -
A
serviceis something that will be called by controllers and will be named${name}Service.java -
A factory creating a
targetwill be called${target}Factory.java -
Something implementing an interface will be called
${nameWithAtLeastInterfacePartAtEnd}Impl.java
7.4.1.1. Subclassing/ Inheritance
Normally sub classes shall add their custom part in front of the name as a prefix:
E.g. Interface JobRepository extends Repository
7.4.1.2. Adding additional parts without inheritance
An exception are Custom parts
E.g. Interface JobRepositoryCustom is a special addon to JobRepository without inheritance
7.5. Logging
7.5.1. General
We try to avoid massive logging but we want to log relevant parts!
7.5.2. Audit Logging
We use a service from shared kernel: AuditLogService
7.5.3. Security Logging
We use a service from shared kernel: SecurityLogService
7.5.4. Functional Logging
We use a dedicated static log field for functional logging.
Normal logging contains INFO level. Problems which are just annoying will come up to WARN level.
Bigger problems are logged in level ERROR.
Technology used is slf4j. We always use logging with parameters - to avoid log injections (should be handled
by logging framework automatically) and also to speed up.
For example:
LOG.info("This is user:{} which is from department:{}",userId,department);
7.5.5. Debug Logging
As described in functional logging, but with log level DEBUG.
7.6. Services
We try to create small spring services, in most cases a
service with annotation @Service should have only one public method
So pretty simple and easy to maintain.
The name should provide information what the service does and has to
end with Service.
Some examples:
-
MailService -
CreateUserService -
InformAdminsThatSchedulerJobProcessingHasBeenDisabledService
7.6.1. Special service variants
7.6.1.1. Transaction services
Sometimes it is necessary to divide transactions. E.g. When a service triggers a message into event bus and we need to ensure that data is stored in transaction before the message has been sent.
In this case we insist service ends with TransactionService.
For an example look into ProjectTransactionService.
|
Only add the special transactional parts to the "transactional" service and put all other parts inside "normal" services! |
7.7. RestController
Rest controller should not do any business logic by themselves, but delegate only to a dedicated service which contains the logic and does the execution.
7.8. Code2Doc
7.8.1. Spring values
All spring @Value annotations which are necessary for documentation (except adapters. They have
no access to SecHub internal parts and are pretty dumb) have to be tagged
with @MustBeDocumented annotation. See documentation in code
7.8.2. Messaging
The messaging flow must be documented by annotations as well. There are diagramms automatically generated. See documentation messaging overview for further information.
7.8.3. Use cases
The usecases and their steps have to be
documented inside code by using a dedicated
annotation which itself is tagged with an @UseCaseDefinition annotation.
See existing examples in SecHub code.
Tag relevant entrypoints as dedicated usecase step so
other developers can easily find them by their IDE (in eclipse
for example you can use CTRL + g to find all references of the
selected usecase annotation class
|
The UseCaseModelAsciiDocGenerator will automatically
generate asciidoc file gen_usecases.adoc which will
contain all the data from the code and linked
adoc files. Also all REST API documentation for usecases having a @UseCaseRestDoc association will be automatically generated.
See also Usecase documentation
7.8.4. Tests
In genereal unit tests which are testing a dedicated class MUST have same package as tested classes. So it’s easier to find and also possible to use package private fields for mocking etc.
7.8.4.1. Unit tests
7.8.4.1.1. Fields
We prefer fields to local variables, fields have to be rebuild by an @Before method.
7.8.4.1.2. Junit versions
Our integration tests and most of the "normal" existing unit tests do currently use Junit4 as testframework and not Junit5. Because having some special Junit4 Rules for integration testing, those tests will be still written in Junit 4, but for new "normal" unit tests you should prefer to use Junit5.
| It is planned to migrate existing tests to Junit5 in future, because of some benefits. But unfortunately some method signatures have changed (e.g. "Assert.assertEquals(…) - especially for the message string) so this will take some time. |
7.8.4.1.3. Maintainable tests
Structure For a better maintenance and reading of tests, we insist on comments dividing a
-
prepare
setup of mocks, creation of objects etc. -
check preconditions (optional)
if necessary check that precondition is fulfilled before test is started -
execute
Execute the part / method which shall be tested -
test
Except when test code is just a one liner this would be ridiculous..
Naming and creation of fields
We do
-
use a before method to create the instance to test, so "fresh" on every test.
-
setup mocks general behaviour in before method, special parts inside test methods
-
the part to test shall be named like
${name}toTest- e.g.analyzerToTest -
create mocks inside before method - so no side effects
-
provide mocks to services by package private methods (easy to inject + test)
-
use simple names for normal mockito mocks, use
mocked${name}inside MockMVC tests where we have injected spring mockito objects. -
test methods do normally not start with
testbecause with Junit4 this become absolete and we try to avoid duplication (it’s clear this is a test method when@Testannotation is at method…)
| Just refer to existing tests when you start a new one. |
@Rule
public void ExpectedException expected = ExpectedException.none();
@Before
public void before(){
/* mocks */
validator = mock(SimpleUIserIdValidator.class);
mailService = mock(SimpleMailService.class);
/* setup */
serviceToTest = new MyServiceToTest();
serviceToTest.valdiator = validator;
serviceToTest.mailService = mailService;
}
@Test
public void mailservice_is_called(){
/* execute */
boolean mailSent = serviceToTest.informUser("user1");
/* test */
verify(mailService).sendMail("user1");
assertTrue(mailSent);
}
@Test
public void inform_user_calls_validator_and_throws_validator_exception(){
/* test */
expected.expect(IllegalArgumentException.class);
expected.expectMessage("wrong user");
/* prepare */
doThrow(new IllegalArgumentException("wrong user")).when(validator.validate(eq("user1"));
/* execute */
serviceToTest.informUser("user1");
}When a precondition check is really necessary we add also /* check preconditions */ segment:
public void testMe(){
/* prepare */
.....
/* check preconditions */
...
/* execute */
...
/* test */
...
}7.8.4.1.4. Naming of mocks and test targets
-
Creating a mock field for e.g. a service
UserServicewill be named asuserService. We do NOT add something like amockpost or prefix! -
The test target field - e.g.
MailServicewill be called something like….ToTest. For exampleserviceToTest
7.8.4.1.5. Naming of unit tests
"Normal" Junit tests will simply called ${nameOfClassToTest}Test.java They have no dependency to spring
7.8.4.1.6. Using json in unit tests versus production code
org.json.JSONxxyz will make problems because test implementation is using a lightweight variant with other api.
There were some obscure problems with this situation. So inside the adapter framework the context has got a dedicated json support which is using only jackson parts and has a fluent api.
Use only those for communication. It also has an automated support for deep tracing with product identification
7.8.4.2. Unit tests (with spring context)
Junit needing a running spring boot container will be called ${nameOfClassToTest}SpringBootTest.java
They use @SpringBootTest inside and have access to dependency
injection etc.
| Prefer normal junit tests to spring boot tests, as they are much faster and often sufficient. |
7.8.4.3. Mocked RestController/MVC Tests (with spring context)
Those tests will also be called ${name}MockTest.java - will e.g. use use Spring annotation @WebMvcTest
7.8.4.4. WireMock tests
When we have to use wire mock - e.g. to mock up product servers, we
call them ${name}WireMockTest.java
7.8.4.5. DB integration tests
Those tests will be called ${name}DBTest.java - and will use Spring annotation @DataJpaTest
For an example look into JobRepositoryDBTest
|
7.8.4.6. Integration tests
In project sechub-integrationtest full integration tests are settled.
The project needs a running server in profile integrationtest.
7.8.4.6.1. Example for an integration test
import static com.mercedesbenz.sechub.integrationtest.api.TestAPI.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import com.mercedesbenz.sechub.integrationtest.api.IntegrationTestExtension;
import com.mercedesbenz.sechub.integrationtest.api.WithTestScenario;
@ExtendWith(IntegrationTestExtension.class)(1)
@WithTestScenario(Scenario6.class)(2)
public class ExampleIntTest {
@Test
void example_doing_some_test_stuff(){
// now use the TestAPI methods to test your wanted stuff
}
}| 1 | Annotation used to mark this test as a SecHub Integration Test |
| 2 | Annotation used to select the scenario to use inside the integration test. (Scenarios are predefined and use an automated setup with test data which will be always cleaned up and provided automatically) |
|
For more details about those tests inspect existing tests. You can also read the |
|
There are old existing integration tests which are not using the Junit5 extension New integration tests shall always use the new Junit5 annotations. New assert methods created for TestAPI shall use Junit5 only as well. |
These tests will be called ${name}Scenario${n}IntTest.java
7.8.4.6.2. Integration tests using SecHubClient
Some integration tests do need a build SecHub client and execute the client.
If these tests are failing, please check you have called gradlew buildGo before,
otherwise no SecHub client is available for testing…
|
7.8.4.6.3. Integration tests generating event trace information
We wanted to have an overview about events happening when a usecase is executed and do this by special integration tests where event tracing is enabled. At the end of the test we write JSON files containing event trace information .
We use ${name}EventTraceScenario${n}IntTest.java as naming convention for those tests.
See also Usecase event overview for more information.
7.8.4.7. RestDOC tests
In project sechub-doc there are RESTDOC tests settled. Those tests are annotated with
UseCaseRestDoc and associated with dedicated UseCase.
The tests will automatically create REST api documentation by using Spring REST DOC.
(See also REST Doc tooling.)
The tests MUST be settled here because gradle support classpath runtime information only at current project, so to prevent
heavy changeds on build logic, we simply setup those tests inside sechub-doc project itself.
| As a side effect it is very much easier for developers to see what parts are rest doc tested at one glance. |
7.8.4.7.1. What is the difference between a MockTest and a RestDocTest?
RestDoc tests are designed to check fields, params and results described in documentations are really as is. There is no logic testing inside those tests. They are more or less just for documentation. On the other hand the MockTest pendants are only for logic testing, so also destructive variants and more technical parts are tested here.
7.8.4.7.2. How can I ensure that I do not forget to describe necessary REST API parts?
Every call to REST API must be described as a part for use cases . So there is
a usecase annotation used at the restcontroller method which should have a method with an @Step result. At the @Step
annotation there is a field needsRestDoc which is per default set to false. For steps doing rest operations and
needs to be documented, just set needsRestDoc to true. When you have done this you cannot forget to document, because
there is an automated test which fail when you got not RestDoc tests annotated with @UseCaseRestDoc for the use case…
It will not break the build, but produce a failing test. There is also an opposite check that you got no @UseCaseRestDoc
tests without corrsponding set of steps having needsRestDoc enabled.
You can also find easily restDoc relevant parts by search caller hierarchy of needsRestDoc inside your code.
So you get a list of all controller methods having documented API…
|
7.8.4.7.3. Naming
We use ${restControllerClassName}RestDocTest.java as name pattern to find RestDoc tests easier.
restControllerClassname is just the java class name of the controller were the rest call is made
(normally the @Step annotation must have there the needRestAPI='true' setup )
Having always the Controllers and also the necessary @MockBean annotations as spring test
dependency this will reduce the boilerplate code to one location…
|
7.8.4.8. System tests
System tests are tests which test the entire application.
7.8.4.8.1. Naming
The name pattern ${nameOfClassToTest}SystemTest.java is used to find system tests.
7.9. Updates
7.9.1. Updating Spring Boot version
7.9.1.1. Update build.gradle
As first we update the spring boot version inside ${rootFolder}/build.gradle.
As an example we upgrade from version 3.2.2 to 3.2.4:
The existing code in ${rootFolder}/build.gradle
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.2.2' apply falsewill be replaced by
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.2.4' apply false7.9.1.2. Generate spring_boot_dependagen.gradle
We have some projects which do not have any Spring dependencies (e.g. sechub-commons-core).
But these projects are used in different SecHub Spring boot applications as dependencies and also
often use the same libraries which are used in Spring as well.
Here we could have version conflicts and it is pretty hard to handle this manually.
This is the reason why we use https://github.com/de-jcup/dependagen to create the
file spring_boot_dependagen.gradle.
7.9.1.2.1. Howto use DependaGen
|
If not already done, clone the For example: After this you can import the dependagen project into your Eclipse IDE and it is ready to use. |
Change the spring boot template to wanted version
vim ./dependagen/gradle-templates/spring-boot/template_build.gradleChange the spring boot version (and if necessary also the version for spring dependency management plugin)
// ...
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.2.4'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.4'
id 'org.asciidoctor.convert' version '1.5.8'
id 'java'
}
// ...Generate files
Execute DependaGenApplication with generate as argument.
Copy the generated output/
Please copy
dependagen/gen/gradle-templates/springboot/spring_boot_dependagen.gradle
to
sechub/gradle/spring_boot_dependagen.gradle
After this regenerate your IDE setup - e.g. for eclipse: ./gradlew cleanEclipse eclipse.
Check there are no compile issues. If no problems appear you can commit and push and the update
is done.
8. Documentation
8.1. Documentation types
8.1.1. Markdown
Simple technical information - e.g. about the content of an folder
- should be written in a README.md with markdown syntax.
8.1.2. Asciidoc
When a full scaled documentation is needed it should be done with Asciidoc.
The documentation sources are inside the sechub-doc/src folder.
| You can use the Asciidoc user manual or look into Asciidoc quick reference for more information |
8.2. Documentation in code
8.2.1. Automated description of important code part
There exists an annotation @MustBeDocumented , which is not
only used as a marker for important code parts but also is used by an automatic
generation of an .adoc file which are included in asciidoc documentation.
8.2.2. Automated description of configurations
With usage of @MustBeDocumented at Spring annotation @Value or @ConfigurationProperties
the infrastructure properties will be documented
automatically.
|
Do not forget to annotate configuration parts - otherwise they will NOT appear inside documentation! |
8.2.2.1. Example for SpringBoot @Value annotation
@Value("${sechub.demo.autodoc.field1:default-field1}")
@MustBeDocumented(value = "The description for field1", scope = "Test scope1")
private string field1;
@Value("${sechub.demo.autodoc.field2}")
@MustBeDocumented(value = "The description for field2", scope = "Test scope1")
private string someField2;The AsciidocGenerator will generate following something similar like this for system properties:
Table with id test_scope1 :
| Key | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.demo.autodoc.field1 |
default-field1 |
The description for field1 |
sechub.demo.autodoc.some-field2 |
The description for field2 |
| Look into existing code for further examples |
8.2.2.2. Example for SpringBoot @ConfigurationProperties annotation
@MustBeDocumented(scope=“Test scope2”)
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix=PREFIX)
public class ExampleProperties{
private static final String PREFIX = “sechub.demo.autodoc.example”;
public ExampleProperties(
@Description("Description of parameter name...")
String name,
@Description("Description of postal code parameter...")
Integer postalCode,
Details details) {
// implementation...
}
)
public static class Details {
public Details(
@Description("If true, the person loves dogs")
Boolean lovesDogs,
@Description("If true the person loves cats")
Boolean lovesCats){
// implementation...
}
}
}The AsciidocGenerator will generate following something like this for system properties:
Table with id test_scope2 :
| Key | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
sechub.demo.autodoc.example.name |
Description of parameter name… |
|
sechub.demo.autodoc.example.postal-code |
Description of postal code parameter… |
|
sechub.demo.autodoc.example.details |
||
sechub.demo.autodoc.example.details.loves-dogs |
If true, the person loves dogs |
|
sechub.demo.autodoc.example.details.loves-dogs |
If true the person loves cats |
Look into existing code for further examples - e.g. SecHubSecurityProperties
|
8.2.3. Automated description of use cases
With usage of special usecase annotations which itself are marked with @UseCaseDefintion it’s possible
to create an automated use case description. It contains also generated
Usecase event trace overview diagrams.
8.2.4. How to test documentation generation
Some documentation generators needs existing data - e.g. from integration test runs. But the complete documentation gradle build takes a long time - this would make it cumbersome to test something when maintaining documentation generators or checking if new configuration setup works with documentation build.
To handle this, we have a special manual test: AsciidocGeneratorManualTest.
Start the test with system property sechub.manual.test.by.developer=true and after 2 seconds (
when using IDE internal builds) all generated documentation output is available inside the folder:
sechub-doc/src/docs/asciidoc/documents/gen/
|
The test will execute the complete generation by |
8.2.5. Automated Diagrams
8.2.5.1. Domain messaging overview
Using Annotations, which are itself tagged with @DomainMessaging annotation, those parts will automatically
listed inside generated messaging diagram(s) gen_domain_messaging_overview.plantuml :
Click to reveal the diagram
For an example look into @IsReceivingAsyncMessage and look also for its references.
|
8.2.5.2. Usecase event overview diagrams
For some usecases we got event trace information (from special integration tests). With this information additional diagrams are generated and included at usecase description level. They show the events happening after a usecase has been triggered.
But not every usecase has got such a diagram: Either there are no events (can happen) or just no integration test for this case has been created.
8.3. Documentation generation
By calling gradlew documentation the AsciidocGenerator is build and used. This generator will automatically
generate documentation areas like System properties or Scheduling which will
be rendered by Asciidoctor afterwards.
8.4. Prerequisites
To have Usecase event overview generated, the integrationtests must have run before! Otherwise this information will not be shown inside the asciidoc output! This was optional to seperate documentation and integration tests. But even tracing can only be done at runtime - so it’s necessary to execute integration tests and then create documentation.
Build server and GitHub action do this automatically.
8.5. Generation of SecHub pages
With each release, the github pages documents are being updated automatically by the release action workflow.
9. Build
9.1. About build technology
Leading entry point/technology is always gradle. So if you want to build something, please look at the
corresponding gradle tasks.
We use github-actions for CI which gives us a quick response at
github.com. For automated deployment or S3 storage testing etc. Jenkins can
be used by defined pipeline scripts.
9.2. Jenkins auto deployment
When you want to build and automate deployment of SecHub by Jenkins you can use a preconfigured pipeline script.
Your Jenkins server should be at minimum: Jenkins ver. 2.176.1.
|
The described Jenkins auto deployment is now relying on the GitHub actions build - see GitHub workflows folder. Deployment artifacts are available at after gradle workflow has been done. In future the artifacts will be automatically available in github packages so you can use those for your autodeployment process and just use it as a maven repository. In the meantime you must deploy manually. Why still a jenkins file then?
|
9.2.1. Continous integration build
This setup builds all branches except master (master is always build by next
job…). The multibranch pipeline build is for continous integration
builds - means to get fast feedback.
Please setup CI by…
-
Jenkins → Manage → Manage Credentials
-
add
sechub-servercontaining the SecHub server url -
add
sechub-useridcontaining the SecHub user id -
add
sechub-api-tokencontaining the api token for sechub-userid
-
-
Jenkins → create new Item →
Multibranch pipeline, name:sechub-open-source-ci -
Branch sources:
Git+-
Project repository:
https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub.git -
Behaviours:
-
Discover branches
-
Filter by name (with wildcards):
-
-
Include: *
Exclude: master
-
Build configuration:
-
Mode
by jenkinsfile -
Script path:
continous-integration-multibranch-pipeline.jenkins
-
-
Scan Multibranch Pipeline Triggers
-
Periodically if not otherwise run
-
Interval
5 minutes
-
-
Save …
9.2.2. Release build
Release builds are only done at master branch and do also publish
artifacts to maven repository when commit has been tagged.
The tags are starting with a v then be followed
by major.minor.hotfix, a hyphen and then the type.
A server could be released by a tag like
v1.1.0-server, a new client by v1.2.0-client for example.
For setup release build please do following:
-
Jenkins > create new Item →
Pipeline, name:sechub-open-source-release -
Build triggers :
Poll SCM
Schedule:
# every five minutes H/5 * * * *
-
Pipeline:
Pipeline script from SCM-
SCM: Git
-
Repository URL:
https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub.git -
Branches to build:
*/master -
Script Path:
release-pipeline.jenkins
-
-
Save …
Don’t use accidently a multibranch pipeline here but only
a pipeline job!
Otherwise the algorithm for automatical calling for
sechub-serer-released and sechub-client-released jobs
does not work. Reason: multibranch pipelines handle tags special
and will not fetch tags - what is necessary for release.
|
9.2.3. Special client and server release trigger jobs
If there are new versions of client or server available - means tagged with
client or server versions (e.g. v1.1.0-server or v1.2.0-client) the former
created release job will automatically publish client and server artifacts (includes
documentation, spring boot jars, binaries etc.) to dedicated maven repository
and after this calls one/or two of the following jobs:
sechub-server-released with parameter SERVERVERSION as 1.1.0
sechub-client-released with parameter CLIENTVERSION as 1.2.0
So you have to add these additional Pipeline jobs.
| The client and server release jobs has to be stored in another git repository containing your specific deployment parts etc. |
9.2.3.1. Examples
Here are some simple examples - easy to adopt:
sechub-server-released job// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pipeline {
agent any
parameters {
string(
name: 'SERVERVERSION',
defaultValue: '0.0.0',
// OSS build does enter this automatically!
description: 'New server version...'
)
}
stages {
stage('Handle new server released') {
steps {
echo "Implement me: deploy server :${params.SERVERVERSION}"
}
}
}
}sechub-client-released job// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pipeline {
agent any
parameters {
string(
name: 'CLIENTVERSION',
defaultValue: '0.0.0',
// OSS build does enter this automatically!
description: 'New client version...'
)
}
stages {
stage('Handle new client released') {
steps {
echo "Implement me: upload client :${params.CLIENTVERSION}"
}
}
}
}9.2.3.2. Eclipse
When you execute ./gradlew eclipse at command line the eclipse files for those projects will be generated.
As next step import the additionally created projects manually into Eclipse ("Import → existing projects").
If you are using the Eclipse standard Gradle integration (Eclipse Buildship), the manual import step is probably necessary as well.
Another option is to use the EGradle plugin - it uses also
./gradlew eclipse and does the import automatically.
9.2.3.3. IntelliJ
For IntelliJ - similar to the steps for Eclipse - you can use the gradle idea task
./gradlew idea -Dsechub.build.stage=all
9.3. Gradle build commands overview
9.3.1. Build Server
Just call
./gradlew build
9.3.2. Build Client
Just call
./gradlew buildGo
9.3.3. Execute integration tests
Start the integration test server
./gradlew startIntegrationTestServer
Execute tests
./gradlew integrationtest
Optionally shut down the integration test server
./gradlew stopIntegrationTestServer
9.3.4. Build Documentation
Just call
./gradlew documentation
9.4. Publishing artifacts / development naming convention
Artifacts are being published automatically when a release workflow runs on github.com.
If you publish artifacts while developing and testing then make sure that the versioning tag contains "-SNAPSHOT" behind the product version.
Examples (SecHub server 1.10.0 development):
- 1.10.0_alpine-SNAPSHOT
- 1.10.0_alpine-SNAPSHOT1
- 1.10.0_alpine-SNAPSHOT-2024-11-30
10. Concepts
10.1. Security tools
10.1.1. Modules and module groups
10.1.1.1. Modules
Security tools are categorized into modules. Each module performs a different security testing method:
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
codeScan |
Scans the code for potential vulnerabilities (weaknesses). Also known as SAST or static source code analysis |
webScan |
Scans a deployed web application for vulnerabilities. Also known as DAST. |
infraScan |
Scans infrastructure for vulnerabilities. |
licenseScan |
Scans code or artifacts for license information |
secretScan |
Scans code or artifacts for secrets |
iacScan |
Scans infrastruture as code for potential vulnerabilities (weaknesses). |
Internally a module is represented by a dedicated ScanType.
|
10.1.1.2. Module groups
Every module belongs to exact one module group:
| Module | Module group |
|---|---|
codeScan |
static |
webScan |
dynamic |
infraScan |
network |
licenseScan |
static |
secretScan |
static |
iacScan |
static |
Every module group contains at least one module:
| Module group | Contained modules |
|---|---|
static |
codeScan, licenseScan, secretScan, iacScan |
dynamic |
webScan |
network |
infraScan |
Inside a SecHub configuration file the user defines which modules shall be executed by the SecHub job. But only modules which are in same module group can be run as part of the same job.
|
As an example: Inside one SecHub job configuration file, it is
|
10.2. Domain Driven Design
To have loose coupling we decided to have an simple DDD approach (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain-driven_design). To avoid too much complexity but keep the domains clearly separated following was done:
-
Domains do only communicate between each other via EventBus with explicit Domain Messages. (see also domain communication constraints )
-
Every domain has got it’s own data pool. We currently use only ONE database. But every domain has got it’s own Tables! The tables names starting with a string describing domain (for example
AUTH_USERwould represent user data for domain authorization…) -
The "Event Bus" is currently - SecHub is a self contained system at the moment - just a simple Spring injection based publish/subscribe system done simply by implementing Observer pattern.
If it becomes necessary to separate SecHub into different deployment units we must use a "real" event bus - e.g.KAFKAand do some refactorings.
|
Developers are able to define meta information inside code to obtain full generated messaging diagrams. See Technical documentation for details about documentation generation and how to
use annotations to establish results.
|
10.3. Resilience
We do currently not use Hystrix or another framework to handle resilience, but use a simple own approach:
A resilient action executor can be used to execute a dedicated
action. Implementation of ResilienctConsultant will give
dedicated proposals how to handle an error.
There are currently two different ways:
-
Retry
In this case the failed action will be retried some times before the exception is thrown -
Fall through
Here the failure is recognized as a situation which will be happen very often because a fix will take some time and so to fail fast for a given time period instead of blocking
10.4. Job restarts
The next diagram shows the involved classes and the program flow when PDS is used for communication - but if no PDS adapter is used for the product execution the behavior is similar: Each adapter is able to store meta data for the current job via callback but is also responsible to handle existing meta data on restarts.
The event REQUEST_RESTART_JOB is also triggered when the batch trigger services
resumes suspended jobs.
|
It is always a good idea to use PDS instead of direct product handling (via dedicated adapters) because PDS (via the PDS adapter) provides relaunch /restart meta data handling out of the box! |
10.5. Deployment without scheduler stop
Before this concept, for new deployments of SecHub server instances, administrators had to stop the scheduler and wait for running jobs to finish. After no jobs were running any longer, the deployment was triggered and after this the scheduler was enabled again and job processing started again.
This works always, but has a catch: If there are many running jobs it can take a while until all of those running jobs are done. And also in the mean time no new jobs are started. This means that, if we have a great count of running jobs, the time gap between deployment and start of new jobs increases.
CI/CD builds or any other use of SecHub takes longer in the meantime, which can be unpleasant / a bad user experience.
10.5.1. Stop job processing when SIGTERM received
K8s and other systems will send a SIGTERM signal to give application the possibility to shutdown
gracefully.
On a SIGTERM signal a SecHub server instance temporarily suspends a job, allowing its PDS
instances to continue processing it in the background.
All running SecHub jobs on terminating instance will be interrupted, marked with execution state
SUSPENDED and set ENDED time stamp as shown in next figure:
See also UC-079
|
The next new SecHub server will resume the suspended job and proceeds with the results from the PDS instances (or wait for them if still not already available). |
10.5.2. Resume suspended jobs
The batch trigger service does trigger the resume operation which leads to REQUEST_RESTART_JOB event
which restarts the job.
To prevent too fast restarts, the ENDED timestamp of SecHub job will be inspected on suspended jobs
and only fetched as next job when the time gap is greater than a defined (configurable) time period.
See also UC-080
10.6. Mappings
SecHub needed a way to configure simple configuration values and also provide a mapping from project names to adapter specific values (see Scan config )
10.6.1. Structure
To provide this in a very generic way SecHub does use the mappings means
a simple setup of
-
pattern
(simple key or a regular expression) -
replacement
(just the value) -
comment (describes what this mapping is used for - just for information)
10.6.2. Domain handling
10.6.2.1. Global mappings
The Administration domain will know every global mapping (e.g. scan configuration) and provide the
corresponding REST API for administrators.
Changes of global mappings will be sent from administration domain to other domains via event bus and a message with ID: MAPPING_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED.
Dedicated message handlers inside other domains will recognize wanted parts and store information when necessary.
10.6.2.2. Product executor parameter mappings
This will not lead to any domain event. The product executors will inspect the mapping information always again before a job has been started. The mapping data is stored inside executor configurations, which is always available inside a job execution, so there is no need of any domain events.
10.7. PDS with SecHub
With the Product Delegation Server (PDS) the SecHub server can simply integrate different products in a very convenient, scalable and resilient way.
|
This documentation only gives an overview how and why SecHub uses PDS. Please look into the dedicated PDS documentation for architecture and also technical details! |
10.7.1. General
10.7.1.1. PDS In an nutshell
There are many open source clients available having no server component inside so lacking:
-
REST access
-
queuing
-
status requests
-
scalable
-
… more
So when we want to adapt them in SecHub style (the product does the work and we ask for result) we
need to provide a ProductDelegationServer (in short form PDS).
PDS is
-
a spring boot application which uses a network DB for providing cluster possibility
-
a complete standalone application without runtime dependencies to SecHub server (or its shared kernel)
-
provides REST access
-
a very simple priviledge model with just two users (
tech user+admin user), basic auth viaTLS, credentials are simply defined by environment entries on startup -
provides jobs, queing, monitoring etc.
-
can execute single files (e.g. a bash script), where job parameters are available as environment variables at runtime
-
a standard way to integrate any product into SecHub in a scalable and easy way
10.7.1.2. Handling of resources
-
PDS server provides
auto unzippingof uploaded resources when configured - see PDS server configuration file -
When a PDS job fails or is done the resources inside job workspace location are automatically removed
10.7.1.3. Communication between SecHub and PDS
The communication between SecHub server and PDS is very similar to the communication between SecHub client and SecHub server.
The PDS adapter will do following steps from SecHub side - as a client of PDS:
-
creates a PDS job
-
(Optional: Only necessary when PDS does not resuse SecHub storage) uploads sources and/or binaries to PDS
-
approves PDS job
-
waits until PDS job has finished
-
downloads PDS report data
As shown in next figure:
10.7.2. Details about PDS
For more details please refer to the <<https://mercedes-benz.github.io/sechub/latest/sechub-product-delegation-server.html,PDS documentation>> available at
10.8. Archive extraction
The data structure concept does need an automated archive
extraction. The main java class is ArchiveSupport.
The next figure gives an overview about the involved classes:
10.9. False-positive handling
SecHub must be able to handle false positives of used products.
10.9.1. General
10.9.1.1. How can false positives be handled across multiple security products?
10.9.1.1.1. Problem
-
Missing API
Most commercial security products are able to mark false positives, but maybe not every tool has a dedicated API for this feature. In addition, many FOSS security tools do not support false positive handling.
10.9.1.1.2. Solution
Instead of configuring false positives for each product (e.g. by calling a REST API) we do the filtering of false positives always at SecHub side only!
The involved product just returns all it’s findings without any false positive marking on the product side. SecHub will store the product results in the database without any filtering.
Only when it comes to report generation at the end, SecHub will filter the false positives from the result. This makes it easy to debug - the original information from the product is still available and problems on false positive marking can be reproduced and fixed.
10.9.1.2. Different kinds of false-positive filtering
Some people prefer code/API-centric way to define false positives, some prefer a WebUI.
10.9.1.2.1. API centric
Defining false positives is done by declaring false positive information in a JSON file
-
by referencing job results from former SecHub job UUID and the corresponding finding entry (by id) and/or
-
by specifying a project data section where specific patterns that match false positive findings are declared
and post it to the SecHub server REST API.
|
The |
|
The Each entry can be updated or removed by the given |
Example JSON using job results
{
"apiVersion": "1.0", (1)
"type": "falsePositiveDataList", (2)
"jobData": [ (3)
{
"jobUUID": "6cfa2ccf-da13-4dee-b529-0225ed9661bd", (4)
"findingId": 1, (5)
"comment": "Can be ignored because not in deployment" (6)
},
{
"jobUUID": "6cfa2ccf-da13-4dee-b529-0225ed9661bd",
"findingId": 15
}
]
}| 1 | apiVersion (mandatory) - API version |
| 2 | type (mandatory) - must be falsePositiveDataList |
| 3 | jobData - List of job data that is used to mark a single finding as a false positive |
| 4 | jobData.jobUUID (mandatory) SecHub Job-UUID of the report where the finding was |
| 5 | jobData.findingId (mandatory) Finding ID which shall be marked as false positive |
| 6 | jobData.comment (optional) A comment describing the reason why this is a false positive |
Example JSON using project data
{
"apiVersion": "1.0", (1)
"type": "falsePositiveDataList", (2)
"projectData": [ (3)
{
"id": "unique-id", (4)
"comment": "It was verified that there is no SQL-injection",
"webScan": { (5)
"cweId": 89, (6)
"urlPattern": "https://*.example.com/rest/products/search?*", (7)
"methods": [ "GET", "DELETE" ] (8)
}
}
]
}| 1 | apiVersion (mandatory) - API version |
| 2 | type (mandatory) - must be falsePositiveDataList |
| 3 | projectData - List that can be used to mark more than a single finding as a false positive. Currently only available for web scans. |
| 4 | projectData.id that identifies this entry. If the same id is used again,
the existing false positive entry will be overwritten. The id is also mandatory to unmark this entry. |
| 5 | projectData.webScan (optional) section can be used to define false positive patterns for web scans (DAST). It provides more possibilities to the user than above jobData. |
| 6 | projectData.webScan.cweId is used to mark a certain type of finding as false positive.When handling web scan project data this will be treated as a mandatory field. Please insert here the cweId from the original report. If there was no cweId in the original report, then it must be omitted or set to zero "cweId": 0. |
| 7 | projectData.webScan.urlPattern (mandatory) specifies an URL pattern to identify a false positive.
Asterisks can be used as wildcards e.g. if you have different environments like DEV, INT, PROD or you have variable parts like in API calls or query paramaters https://.example.com/rest//search?*. |
| 8 | projectData.webScan.methods (optional) Can be used to further restrict the false positive matching, to specific request methods protocols, like GET, POST, etc. |
Important information on the wildcard approach in projectData, regarding web scans:
- To be marked as a false positive a finding must match the given cweId and the urlPattern
- Wildcards (*) can be used inside urlPattern.
- Wildcards match anything until the next NON-wildcard character.
- Multiple wildcards can be used in one urlPattern.
- An optional list of (HTTP) methods can be specified to limit the false positive entry to certain methods, e.g if you specify "methods": [ "GET", "DELETE" ] like in the example above that means even if the cweId and the urlPattern are matching, if the finding was found with a POST request it would not be a false positive. When leaving methods out, this false positive entry apply to any method.
- An urlPattern which contains only wildcards (*) is not allowed.
10.9.1.2.2. Web UI
Just uses the API centric approach (by using given REST API,) over UI.
10.9.1.2.3. Code centric
Inside source code / deployment scripts etc. users can define comments to define false positive handling - this is only possible for situations where we have access to source code - means SAST (static application security testing)
|
Currently this is not supported! The detection algorithm is already implemented inside |
10.9.2. Technical details about false positive handling
There are two different kind of phases:
-
User definition of false positive definitions
-
Job execution / runtime
10.9.2.1. Definition phase
When a user has a SecHub report with some findings - the user can define false positives in two different ways. By the report UUID and the finding id which represents the false positive or by providing additional information like patterns to identify a false positive.
The configuration is described at how to define false positives by API.
|
When using the first approach by providing report UUID and the finding id, the user only gives information about which finding in an existing report is seen as a false positive. While a new false positive is created, SecHub inspects the report and fetches all necessary meta data internally - depending on the scan type. These meta data will be stored independently from the report. So even if the report will be deleted afterwards, the false-positive handling will still work! When using the second approach the user provides additional data that helps identifying a false positive or even a specific group of false positives. This approach requires more effort from a user to provide the data which identify the wanted false positives. But it can be very helpful especially for web scans, where some finding parts dynamically change, like scanner payloads in query parameters or URL paths. |
At this phase duplicate checks are done for tuples of report UUID and finding id for the first approach. For the projectData approach duplicates are detect by the id the user provided!
Meta data is only collected in definition phase, but NOT inspected! !
|
Here a simple example for better understanding. On the first approach with finding id and report UUID:
On the second approach with the additional data for the project:
|
10.9.2.1.1. Overview
The next figure shows a simplified UML diagram (shows only relevant parts). Below the figure you will find sub chapters with more information.
10.9.2.1.2. Used storage mechanism
For every SecHub project a project scan config entry for false positives exists.
The entry does contain a FalsePositiveProjectConfiguration object as JSON.
10.9.2.1.3. Data structure
The FalsePositiveProjectConfiguration object contains a list of FalsePositiveEntry objects.
Every FalsePositveEntry object contains either FalsePositiveJobData with FalsePositiveMetaData or FalsePositiveProjectData,
but never both in one FalsePositveEntry.
-
FalsePositiveJobData
contains job uuid, finding id and comment - this information is provided by user. -
FalsePositiveMetaData
contains meta information about findings - this information is gathered and calculated by SecHub internally when a user has marked a report finding as a false positive. So the meta information is independent (so when a reoprt has been deleted, we still have the false positive meta information).-
It contains many meta information - e.g. a
cweId- but alsoFalsePositiveCodeMetaDatafor code scans details.
-
-
FalsePositiveProjectData
contains information to identify a finding or a group of findings as false positives. Currently it can only be used for web scans. In how to define false positives by API the example shows all mandatory and optional parameters.
10.9.2.1.4. Definition by user
A user does define a FalsePositiveDataList object which contains a list of FalsePositiveJobData or FalsePositiveProjectData. Such a list will
be used to add false positives.
To remove a FalsePositiveJobData entry from the FalsePositiveProjectConfiguration, the user has to provide the job UUID and finding id already used to define this entry.
To remove a FalsePositiveProjectData entry from the FalsePositiveProjectConfiguration, the user has to provide the id defined with the corresponding entry.
10.9.2.1.5. Merging
When a user adds or removes false positive definitions, the FalsePositiveProjectConfiguration will be updated by
FalsePositiveDataConfigMerger.
10.9.2.2. Job execution phase
Here Sereco is in charge, which does inspect each FalsePositveEntry and use either the meta data or the project data depending on the entry.
10.9.2.2.1. Overview
10.9.3. Code scan
10.9.3.1. API centric
see general concept
10.9.3.1.1. How to identify same vulnerability on code changes?
-
We inspect source and sink and use
-
Location
-
relevant part - this is absolutely necessary.
-
-
Line numbers must always be irrelevant!
|
Very important for Sereco: If no relevant part is available we must at least create a pseudo one by given source snippet - in a whitespace reduced form! We will compress the source content, so adding new lines, spaces, tabs etc. would not matter. So if a product does not support "relevant part" detection we must create the "relevant
part" inside |
10.9.3.2. Web UI
see general concept
10.9.3.3. Code centric
|
This approach is currently not enabled/full supported! Details:
|
Inside source code the developers will be able to mark their code, marked as vulnerable, as being a false positive by using comments. After the push to repository it’s inside history who was defining the vulnerability as a false positive.
We use following tags:
NOSECHUB
and
NOSECHUB-END
|
In future we could provide additional identifiers for E.g. |
10.9.3.3.1. Java
We will provide single comments (//)
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
public class FalsePositiveJavaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// NOSECHUB (1)
falsePositiveCall(); //NOSECHUB-END (2)
}
}| 1 | marks start |
| 2 | marks end |
All between those tags will be ignored by SecHub.
10.9.4. Web scan
10.9.4.1. Code centric
Not possible
10.9.4.2. API centric
see general concept
10.9.4.3. Web UI
see general concept
10.9.5. Infra scan
10.9.5.1. Code centric
Not possible
10.9.5.2. API centric
see general concept
|
The identification of similarity is done here by
For infrastructure scans a false positive detection is currently not implemented. |
10.9.5.3. Web UI
see general concept
10.10. Product execution profiles and executor configuration
To have the possibility of using dedicated security products for different projects, to disable/enable products on demand without server restart or just to test new products in one evaluation project but not for all other projects a runtime configuration is necessary.
This is provided by execution profiles and and executor configurations.
10.10.1. Overview
10.10.2. Executor configuration
An executor configuration represents a runtime configuration for product executors. The configuration has an enabled state. So it is possible to enable/disable product execution.
10.10.3. Execution profile
An execution profile can contain multiple executor configurations. The configurations can be shared between multiple profiles. E.g. a config with name "pds-gosec-1" can be used in profiles "profileA" and also "profileB" at the same time.
Additionally a profile can be assigned to a project (but technically we assign a projectId to a profile, because
in domain scan we only know projectIds but no the Project entity…).
The profile has also an enabled state - like executors.
10.10.4. How execution process uses profiles and configurations
ScanService is called by SecHub batch operation from scheduler and contains the project id for the
project to scan for.
When it comes to execution, ProductExectionStoreService fetches all enabled profiles related to the given
project id and executes all enabled product executors for the wanted scan job - e.g. code scan product executors
10.10.4.1. Results handling done by configured report executor or fallback
All of the results returned by the dedicated product executors are stored in database. After this has been done,
the configured report product executor(s) is (are) executed (if none has been defined in at least one profile, the
fallback will automatically use Sereco product executor version 1, which is embedded)
10.11. Product results
Product results can be either from security products or from reporting products.
For a job different security products can be executed, depending on the execution configuration.
After this the results will be stored in database as dedicated ProductResult entries.
Afterwards reporting products will be executed to collect the former stored reports and merge them together.
The report product merge result will be stored as a ProductResult as well in database for the job.
When no report collector is configured/available the embedded report product Sereco ("SecHub report collector") will be used .
|
10.11.1. Product messages inside product result
Every product can add custom messages which shall be available to user.
10.11.1.1. Storing product messages
The product adapter fetches the information from the product and delivers it to
the product executor, who stores the SecHub messages inside the ProductResult entity.
10.11.1.2. Read and delivery of report data to end user
SerecoProductExecutor collects all SecHub messages from other job results and combines them
inside its own data as SerecoAnnotation. The annotations will be inspected on report creation
by SerecoResultTransformer.
Further details for report creation can be found at report data flow.
10.11.2. Report data flow
10.11.2.1. Report model
Here a reduced class model of the report data model:
10.11.2.2. Creation of ScanReport entities
Here a graphical overview how the report data is created by the ScanService and
finally written as ScanReport entity into the database:
10.11.2.3. Read and delivery of report data to end user
When the user downloads the report, the result inside the persisted scan report entity will be used.
10.12. Job status
After a SecHub job has been created, it has a status which will change at the different process steps. Some of these steps are described here.
10.12.1. Job status fetching
10.12.2. Job status data flow
10.12.2.1. Job execution done, final Job status update
10.13. SecHub job cancellation
An administrator is able to cancel a running SecHub job. This is done across different domains and there are multiple events involved. The next diagram shall bring an overview.
10.14. Auto cleanup
To prevent full hard drives there is an option to automatically remove old data.
It also cleans up old encryption settings when it comes to encryption rotation.
|
See also |
10.14.1. Configuration
Administrators can configure the auto cleanup configuration by uploading a json configuration via REST (see REST API for UC_065-Admin updates auto cleanup configuration ).
{
"cleanupTime" : {
"unit" : "months", (1)
"amount" : 3 (2)
}
}| 1 | The time unit to use. Can be
|
| 2 | Amount of time. When 0 is defined, the auto cleanup is deactivated, all other positive values are time
unit related. Negative values are not allowed. |
10.14.2. Execution
The execution is automatically done by SecHub.
10.14.3. Cleaned data
All data which is older than the defined time period is removed from:
-
Scan product results
-
Scan project log
-
Schedule job entries
-
Administration job information
|
Scan report data is currently NOT deleted. So it can be used for statistics. In a later feature there will be specialized statistic tables - when this has been implemented, the auto cleanup will be extended to drop old scan report data as well. |
10.15. PDS solutions
It is easy to integrate security products, even command line tools without a network API, into
SecHub via PDS (Product delegation server).
A PDS solution is a ready-made package for SecHub in which a PDS and the necessary security products are already pre-installed and can be used directly without additional adjustments.
| The PDS solutions can be found at https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub/tree/develop/sechub-pds-solutions. |
10.15.1. Checkmarx PDS solution
The checkmarx PDS solution uses sechub-wrapper-checkmarx which is a standalone Spring Boot application.
If started in non production mode, the data will be mocked when inside IDE.
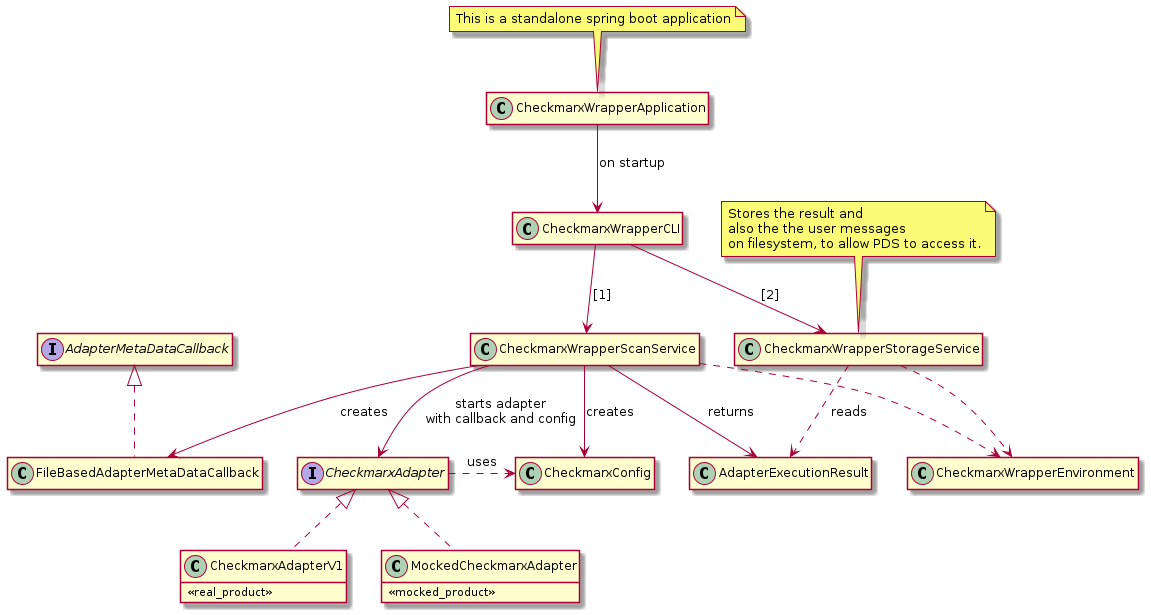
10.15.2. PDS code scan executor Configuration
| Job parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
pds.checkmarx.user |
Mandatory |
The user name used to communicate with Checkmarx. You can use env:$YOUR_USER_VARIABLENAME to use environment variables instead of real credentials. |
pds.checkmarx.password |
Mandatory |
The password used to communicate with Checkmarx. You can use env:$YOUR_PWD_VARIABLENAME to use environment variables instead of real credentials. |
pds.checkmarx.baseurl |
Mandatory |
The base URL of the Checkmarx server. |
pds.checkmarx.engine.configuration.name |
Optional |
The engine to use - when empty, the default engine will be used. |
pds.checkmarx.always.fullscan.enabled |
Optional |
When 'true', Checkmarx will do a full scan and not a delta scan. |
pds.checkmarx.result.check.period.milliseconds |
Optional |
The time period in milliseconds when the next check for Checkmarx resuls will be done. An example: If you define |
pds.checkmarx.result.check.timeout.minutes |
Optional |
The maximum time in minutes when the checkmarx communication does time out and the connection will be terminated. |
pds.checkmarx.mocking.enabled |
Optional |
When 'true' than, instead of the real Checkmarx adapter, a mock adapter will be used. This is only necessary for tests. |
checkmarx.newproject.teamid.mapping |
Mandatory |
Can be either defined directly as job parameter (json mapping), or we can send it automatically by reusing an existing SecHub mapping. As an example: 'pds.config.use.sechub.mappings=checkmarx.newproject.teamid.mapping,checkmarx.newproject.presetid.mapping' |
checkmarx.newproject.presetid.mapping |
Optional |
If not the default preset Id shall be used, it can be either defined directly as job paramter (json mapping), or we can send it automatically by reusing an existing SecHub mapping. As an example: 'pds.config.use.sechub.mappings=checkmarx.newproject.teamid.mapping,checkmarx.newproject.presetid.mapping' |
pds.checkmarx.resilience.badrequest.max.retries |
Optional |
Maximum amounts of retries for bad request handling |
pds.checkmarx.resilience.badrequest.retry.wait.milliseconds |
Optional |
Time in milliseconds to wait before next retry when a bad request happend |
pds.checkmarx.resilience.servererror.max.retries |
Optional |
Maximum amounts of retries for internal server error handling |
pds.checkmarx.resilience.servererror.retry.wait.milliseconds |
Optional |
Time in milliseconds to wait before next retry when an internal server error happend |
pds.checkmarx.resilience.networkerror.max.retries |
Optional |
Maximum amounts of retries for network error handling |
pds.checkmarx.resilience.networkerror.retry.wait.milliseconds |
Optional |
Time in milliseconds to wait before next retry when a network error happend |
10.16. Analytics
SecHub can be configured to analyze a scan situation at the beginning to improve runtime behavior or to create statistic data. This is done before all other scans.
|
As usual, different products can be used to provide the analytic data. The analytic scan products can be configured as any other product by defining a executor configuration and add it to a execution profile which can be assigned to SecHub projects. |
The AnalyticsProductExecutionService inside the scan domain does not only execute and store the product results, but
also creates an analytic data model after the analytic scan products have been executed.
This data model can be used at runtime by other product executors inside the scan domain but also in other domains via domain messaging.
|
Currently the information is not used at runtime by other product executors but only inside statistic domain. |
10.17. Statistics
For statistic data handling exists an own domain statistic. The data is collected in
dedicated statistic SQL tables.
|
Statistic data is NOT auto cleaned. |
Every data which shall be stored as statistic data is send from other domains via domain message bus.
Here an short overview about the involved event locations:
|
Inside the entity model we use a very loose coupling (no constraints). |
10.18. Data encryption
10.18.1. General
We want
-
Data consistency
-
It shall not be possible that we loose data by encryption in any way.
It must be ensured that the servers are always able to read and write data.
-
-
Full automated cipher rotation
There is no need for manual interaction - means it is not necessary to create any cron jobs or something else to convert non encrypted data to encrypted data or to rotate a password or to use a new encryption method. -
Data protection /Privacy policy
-
Even for administrators it shall not be possible to fetch the information directly
(of course a person who knows the encryption password and has access to the database will always be able to calculate values - but we separate here between administration and operation inside this concept, so protection is fully possible) -
The data must not be accidentally made available in decrypted form - for example through a REST call in which the data object is passed along unencrypted.
-
-
Easy encryption administration
-
It shall be possible for an administrator to configure a new cipher entry via REST
-
-
Secure storage of encryption passwords
-
Encryption passwords are always provided via environment entries, we store always the environment variable name to use inside the database but never plain values!
-
10.18.2. Server startup
A SecHub server will stop on startup phase when one of the entries inside the cipher pool cannot be handled by this server.
This ensures that every new started server is able to handle all of them / is always readable.
10.18.3. Administration
10.18.3.1. Encryption rotation
An administrator is able to start encryption rotation via REST. This will
-
use new encryption setup for all new data
-
automatically convert existing encrypted data with new encryption setup in background
10.18.3.2. Encryption status
An administrator is able to fetch encryption status from SecHub server. All domains which are doing data encryption add their current status information into result.
10.18.3.3. Cleanup old encryption setup
Auto Cleanup automatically removes old information. This means that old encrypted information that cannot be updated for some reason may eventually disappear and old encryption configurations are then no longer needed and can be removed.
To fully automate this, after the respective Auto Cleanup, the domains are always checked for encryption configurations that are no longer used and these are then automatically removed (except for the most recent encryption configuration).
|
If you have setup auto cleanup to 0 days, the auto cleanup is disabled completely and unused encryption setup will also not be removed. |
10.18.4. Scheduler
Inside the schedule domain, the sensitive information is the sechub job configuration.
10.18.4.1. Database
10.18.4.1.1. Table
We store the cipher information inside table: SCHEDULE_CIPHER_POOL_DATA.
|
Why in schedule domain and only there? Because it is the responsible domain for the storage. All other
domains may NEVER persist this information (for |
Here an an overview of the table (names can be different in database):
| id | algorithm | password_source_type | password_source_data | encoding | test_text | test_initial_vector | test_encrypted | creation_timestamp | created_from |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
NO_ENCRYPTION |
PLAIN_TEXT |
PLAIN |
no-encryption |
no-encryption |
2024-06-24_10:00:01 |
null |
||
1 |
AES_GCM_SIV_128 |
ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE |
SECHUB_CRYPTO_P0 |
PLAIN |
SecHub |
easdfa313334 |
53d$125666eeffeded |
2024-06-24_10:05:34 |
Admin1 |
2 |
AES_GCM_SIV_256 |
ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE |
SECHUB_CRYPTO_P1 |
PLAIN |
Apfel |
fxadsfeec33s |
13x313412124$rfewd |
2024-06-24_11:02:14 |
Admin2 |
algorithm
Algorithm to use in encryption - currently we provide:
-
NONE (means not encrypted!)
-
AES_GCM_SIV_128
-
AES_GCM_SIV_256
password_source_type
Currently supported password source types are
-
ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
Here we provide environment variables, the password source data is the name of the environment variable -
NONE
No password - only allowed forNONEalgorithm
We separated source type and source data to be able to provide additional source - e.g. a password fault for the future.
password_source_data
Depends on the source
-
If source is
envthan this is the name of the environment variable which holds the secret
10.18.4.1.2. Usage inside rows
Inside the encrypted rows we will persist the pool id together with an initial vector
initial vector
Some algorithm like AES_GCM_SIV do need an initial vector to encrypt secure. The value here is
auto generated by SecHub and is dependent on the algorithm.
SecHub will always auto generate a dedicate value when it comes to encryption and the vector will be stored together with the encrypted data. If the initial vector is changed, the row cannot be decrypted, even when the secret key is known!
10.18.4.2. Constraints on scheduling
The only situation we need to access the encrypted job configuration is the point, when it comes to job execution. At all other situations it does not matter if the configuration can be decrypted or not.
This means that it may not be possible that an scheduler instance executes a job which is not supported by the current encryption pool!
10.18.5. Handling server updates
10.18.5.1. SecHub server 1.x to 2.x
Old server versions do not have the encryption field inside the scheduler job table or the cipher pool table.
Our SQL migration scripts will initialize scheduler cipher pool table on creation time with a
NONE entry (pool id = 0). This is encryption setup (meaning no encryption) will be added
to all existing jobs.
We want to have zero downtime and rolling updates with k8s and SecHub. To provide this,
it must be ensured, that there is no old server running which creates new jobs with
plain text configurations while update is running. To prevent such a situation
the column name inside schedule_sechub_job have been renamed from configuration to unencrypted_configuration.
If there appears any race conditions, old servers would no longer be able to write data and a
SQL error would happen.
10.18.6. Handling server downgrade
10.18.6.1. SecHub server 2.x to 1.x
For a downgrade from SecHub server V2.x to V1.x it is necessary to ensure, that all data is
encrypted with NONE cipher type (can be done by encryption rotation). When ensured that everything
is "encrypted" with this cipher type, the old server version can be deployed/used and migration
is automatically done as usual.
10.18.7. Handling sensitive data at runtime
JVM crash dumps contain string information. Classes containing sensitive information shall store such information inside sealed objects.
10.18.8. Handling metadata from job configuration
The SecHub configuration is encrypted, because it can contain sensitive data. E.g. when defining a remote data section.
There exists a REST endpoint which gives users the possiblity to fetch job information, together with the meta data defined inside the SecHub configuration.
To obtain this information, the configuration will be decrypted temporary at runtime and the meta data are resolved and returned.
Because meta data shall not contain any sensitive information, this will not be audit logged.
10.18.9. Diagrams
10.18.9.1. Usage of encryption commons
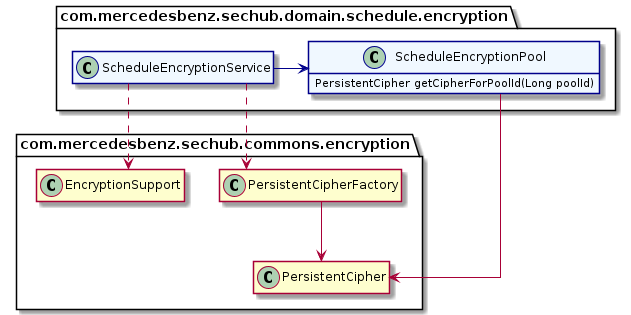
10.18.9.2. Encryption rotation overview
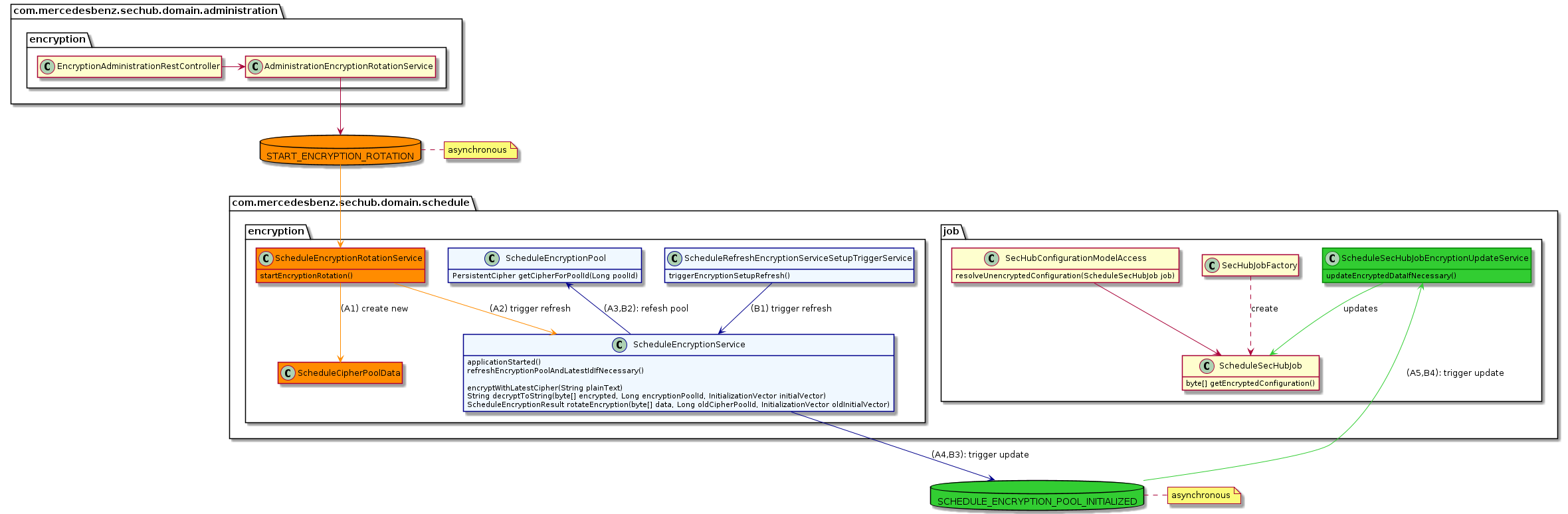
10.19. Oauth2
Because there was a need to configure OAuth2 handling very dynamically, we introduced an
own data structure for setup, see class SecHubSecurityProperties.
The configuration and the description can be found in keys below sechub.security.login at
Login and resource server configuration
10.19.1. JWT handling
Standard Spring Boot way except the configuration keys which are SecHub specific (see link above).
10.19.2. Opaque token handling
Standard Spring Boot way except the configuration keys which are SecHub specific (see link above) but also with a cache mechanism for repsonse tokens.
10.19.2.1. Opaque token cache mechanism
The opaque token handling is cached by two different caches:
First level cache is a fast in memory cache - which is persisted by InMemoryCachePersistence.
This cache is only available on a JVM instance and exists only a short time (e.g. 10 seconds).
If the first level cache does not contain the opaque token response data, the second level (cluster) cache from cluster persistence is fetched and stored again in first cache.
If the second level cache also does not contain the opaque token response data, the IDP will be called to fetch the opaque token response data.
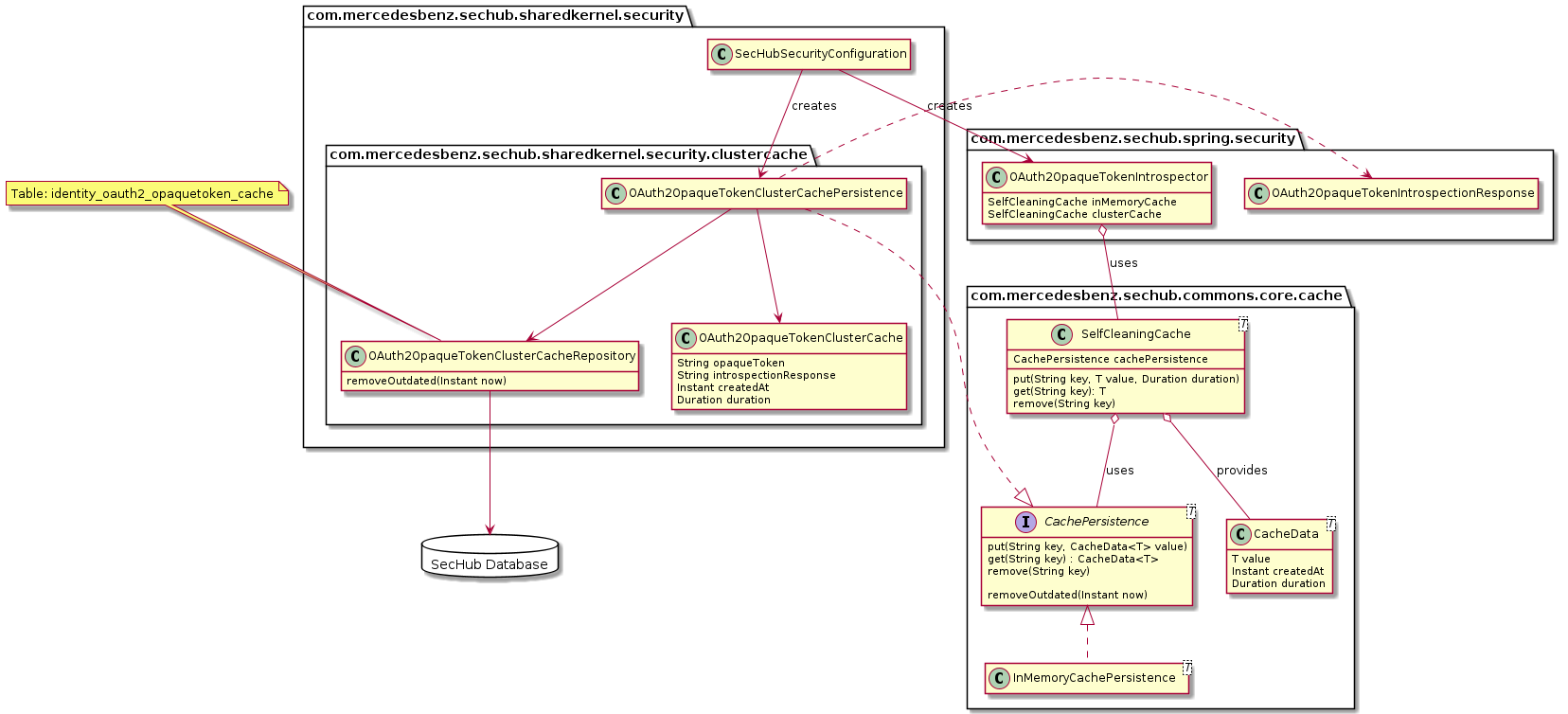
10.20. Use cases
The complete documentation about use cases is generated. If you want to change content, please search for
@UseCaseDefinition references in source code and make necessary changes inside code!
|
10.20.1. Overview about usecase groups
10.20.1.1. Anonymous
All these usecases handling anonymous access.
10.20.1.2. User administration
Usecases handling administration of users
10.20.1.3. Project administration
Usecases for project administration
10.20.1.4. User self service
User actions belonging to their user identity
10.20.1.5. Sechub execution
Execution of SecHub -either by CLI or direct with REST api call
10.20.1.6. Sign up
All these usecases are handling user sign up (part of user self registration process)
10.20.1.7. Job administration
Usecases about job administration
10.20.1.8. Technical
Usecases about technical operations being executed by sechub itself
10.20.1.9. Testing
Some use cases for testing
10.20.1.10. Configuration
Usecases for configuration parts
10.20.1.11. Encryption
Usecases for encryption parts
10.20.1.12. Other
All other use cases
10.20.2. UC_001-User self registration
The self registration can be done by anonymous users.
If a user is not already inside the system and there exists not already a self registration the signup is persisted.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.UseCaseUserSignup
Event overview
|
Involved messages |
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest API call |
2 |
Rest api called to register user. Normally done by user itself This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Persistence |
3 |
Valid self registration input will be persisted to database. This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Email to user |
4 |
A notification is send per email to user that a new user signup has been created and waits for acceptance. This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Email to admin |
A notification is send per email to admins that a new user signup has been created and waits for acceptance. This step is defined at method |
10.20.3. UC_002-Admin lists open user signups
In this usecase the administrator will list the currently unapplied user self registrations/signups.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.signup.UseCaseAdminListsOpenUserSignups
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
All self registrations are returned as json This step is defined at method |
10.20.4. UC_003-Admin applies self registration
In this usecase the administrator will accept the self registration done by an user.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.signup.UseCaseAdminAcceptsSignup
Event overview
|
Involved messages |
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator accepts a persisted self registration entry by calling rest api This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Create user and send events |
3, 4 |
The service will create the user a one time token for api token generation and triggers asynchronous events. It will also remove the existing user signup because no longer necessary. This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Email to user |
A notification is send per email to user that a new api token was requested. The mail contains a link for getting the secure API token This step is defined at method |
||
4 |
Give user access |
Authorization layer is informed about new user and gives access to sechub. But without any project information This step is defined at method |
10.20.5. UC_004-Admin lists all users
An administrator downloads a json file containing all user ids
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminListsAllUsers
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
All userids of sechub users are returned as json This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
All userids of sechub users are returned as json This step is defined at method |
10.20.6. UC_005-User creates a new sechub job
A user wants to create a new sechub job.
| This will not directly start the job. Please refer to User approves job. |
As a result the user will have created a new SecHub job and have a job UUID as result.
After this the user is able to
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserCreatesNewJob
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Authenticated REST call |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Persistence and result |
3 |
Persist a new job entry and return Job UUID This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Store admin job info |
Fetches event about created job and store info in admin domain. This step is defined at method |
10.20.7. UC_006-User uploads source code
A user wants to upload sourcecode for a former created sechub job.
The source code must be a valid zipfile.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserUploadsSourceCode
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Authenticated REST call |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Try to find project and upload sourcecode as zipfile |
When project is found and user has access and job is initializing the sourcecode file will be uploaded This step is defined at method |
10.20.8. UC_007-User approves sechub job
A user wants to approve a former created sechub job.
This means the user has done all necessary preparations - e.g. uploading source code for code scanning - and wants the job marked as ready for execution
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserApprovesJob
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Authenticated REST call |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Try to find job annd update execution state |
When job is found and user has access job will be marked as ready for execution This step is defined at method |
10.20.9. UC_008-Sechub scheduler starts job
Scheduler service starts next SchedulerJob. Before a user has only created and approved a job which was lead only to database persistence of JobData.
The work itself is triggered/executed here by asynchronous batch operation.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.job.UseCaseSchedulerStartsJob
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Scheduling |
2 |
Fetches next schedule job from queue and trigger execution. This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Execution |
3, 4 |
Triggers job execution - done parallel, but with synchronous domain communication (to wait for result). This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Runnable calls execution services |
4 |
The job execution runnable creates the execution context and calls dedicated execution services (preparation, analytics, product execution, storage and reporting) synchronously for the job. It is also responsible for cancelation and supsension of jobs. This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Store admin job info |
5 |
Fetches event about started job and store info in admin domain. This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
Update admin job info |
Deletes store info in admin domain when job is done. This step is defined at method |
10.20.10. UC_009-User checks sechub job state
User wants to get the state of the current running job.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserChecksJobStatus
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Authenticated REST call |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Try to find project and fail or return job status |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.11. UC_010-User downloads sechub job report
A user wants to download a SecHub report for an executed job
by its given job UUID.
The report standard format is a human and machine readable JSON format. Additionally, there is the option to download the report as HTML file.
Both, the HTML and the JSON file have a reduced view of the scan results. Code snippets etc. can be found on the real security products.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserDownloadsJobReport
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to get JSON report |
3 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
REST API call to get HTML report |
3 |
This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Resolve scan report result |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.12. UC_011-User starts scan by client
Sechub has got it’s own client, written in go. The client is available for Linux and Windows and can be downloaded at https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub .
The client encapsulated and simplifies the necessary steps to do a scan to one single step only
It does automate following usecases:
If the scan report traffic light is RED the build client will return an System exit code greater than zero so build will break.
More information about the client can be found inside the user documentation.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserStartsSynchronousScanByClient
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
create new job |
2, 3 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
upload sourcecode |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
upload binaries |
3 |
This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
approve job |
4 |
This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
download job report and traffic light |
4 |
This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
get job status |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.13. UC_012-User clicks link to get new api token
The user has to open the received email and click there on the contained link with a onetimetoken api which is another usecase.
This use case is either triggered by when a new user was initial registered or a new API token was requested by user.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.UseCaseUserClicksLinkToGetNewAPIToken
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
User opens url by browser This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Validation and update |
3, 4 |
When its a valid one time token a new api token is generated and persisted hashed to user. The token itself is returned. When not valid an emtpy string is the result … This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Update auth data |
This step is defined at method |
||
4 |
Inform user about api token change done |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.14. UC_013-Admin creates a project
Administrator creates a project inside SecHub.
A Project is the main entry point for every SecHub operation!
For example a user must have a project assigned to be able to scan on it!
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseAdminCreatesProject
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator creates a new project by calling rest api This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Create project |
The service will create the project when not already existing with such name. This step is defined at method |
10.20.15. UC_014-Admin lists all projects
An administrator downloads a json file containing all project ids
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseAdminListsAllProjects
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
All project ids of sechub are returned as json This step is defined at method |
10.20.16. UC_015-Admin or owner assigns user to project
An administrator or project owner assigns an user to an existing sechub project.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminOrOwnerAssignsUserToProject
Event overview
|
Involved messages |
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator does call rest API to assign user This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Update schedule authorization parts |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Assign user |
3 |
The service will add the user to the project. If user does not have ROLE_USER it will obtain it This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Update scan authorization parts |
4 |
This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Roles changed in auth |
Authorization layer adds ROLE_USER This step is defined at method |
10.20.17. UC_016-Admin or owner unassigns user from project
An administrator or owner unassigns an user from a sechub project.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminOrOwnerUnassignsUserFromProject
Event overview
|
Involved messages |
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator does call rest API to unassign user This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Update authorization parts |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Update authorization parts |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Unassign user |
4 |
The service will remove the user to the project. If users has no longer access to projects ROLE_USER will be removed This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Roles changed in auth |
Authorization layer removes ROLE_USER This step is defined at method |
10.20.18. UC_017-Admin shows user details
An administrator downloads a json file containing json containing user details
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminShowsUserDetails
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Json returned containing details about user and her/his projects This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service fetches user details. |
The service will fetch user details for given user id This step is defined at method |
10.20.19. UC_018-Admin deletes a user
An administrator deletes an user. All associations etc. are removed as well.
|
If the user is still a project owner the delete will not work and an error message will appear that this is not acceptable and that the ownership must be moved before User delete is possible. |
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminDeletesUser
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
User will be deleted This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service deletes user. |
3, 4 |
The service will delete the user with dependencies and triggers asynchronous events This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
revoke user from schedule access |
3 |
This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
revoke user from schedule access |
4 |
This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Delete user access |
Authorization layer is informed about user deltete and removes access to sechub. But without any project information This step is defined at method |
||
5 |
Inform user that the account has been deleted by administrator |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.20. UC_019-Admin deletes user signup
In this usecase the administrator will not accept the self registration done by an user but delete the entry.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.signup.UseCaseAdminDeletesSignup
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest API call |
2 |
Rest api called to remove user signup This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Persistence |
Existing signup will be deleted This step is defined at method |
10.20.21. UC_020-Admin deletes a project
Administrator deletes a project from SecHub.
A Project is the main entry point for every SecHub operation and deleting this will result in:
-
Terminate all running jobs for this project
-
Remove project administration setup
-
User to project association
-
All existing project report results
| Albert Tregnaghi, 2018-08-03: This is currently not full implemented! |
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseAdminDeleteProject
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Project will be deleted This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service deletes projects. |
3, 4, 5, 6, 7 |
The service will delete the project with dependencies and triggers asynchronous events This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Inform sechub admins that project has been deleted |
4 |
This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform project owner that the project has been deleted |
5 |
This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
Inform users that the project has been deleted |
6 |
This step is defined at method |
|
6 |
Update authorization parts - remove entries for deleted project |
7 |
This step is defined at method |
|
7 |
revoke any scan access from project |
8 |
This step is defined at method |
|
8 |
delete all project scan data |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.22. UC_021-Admin shows project details
An administrator downloads a json file containing json with project details
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseAdminShowsProjectDetails
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Json returned containing details about project This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service fetches project details. |
The service will fetch project details This step is defined at method |
10.20.23. UC_022-Update project whitelist
Administrator creates a project inside SecHub.
A Project is the main entry point for every SecHub operation!
For example a user must have a project assigned to be able to scan on it!
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseUpdateProjectWhitelist
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
White list will be updated This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Update project |
The service will update the Project whitelist. This step is defined at method |
10.20.24. UC_023-Admin lists all running jobs
Administrator lists all running jobs inside SecHub.
The list entries do contain
-
jobUUID
-
project id
-
owner of job (id of user who executed job)
-
status
-
since time stamp
-
configuration
These entries are only available at running jobs
This is an important action to get info about current treshold in sechub.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.job.UseCaseAdminListsAllRunningJobs
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator lists all running jobs by calling rest api This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Fetchjob information from database |
Fetches stored job information from administration database. This step is defined at method |
10.20.25. UC_024-User requests new API token
It shall be possible to achieve this by calling REST API and also by just visiting static sechub website and entering email address and post request by simple web form.
When user exists a new one time token will be created and sent to user per email - so same way as done when a new user signup is accepted by admin.
The user has to open the received email.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.UseCaseUserRequestsNewApiToken
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest API call |
Rest api called to request new user api token. Normally done by user itself This step is defined at method |
10.20.26. UC_025-Admin shows scan logs for project
An admin downloads a json file containing log for scans of project
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseAdminShowsScanLogsForProject
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to get JSON list |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.27. UC_026-Admin downloads all details about a scan job
An administrator downloads a ZIP file containing full details of a scan. Main reason for this use case is for debugging when there are problems with security products. Another reason is for developers to adopt new security products easier.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseAdminDownloadsFullScanDataForJob
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to zip file containing full scan data |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Collect all scan data |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.28. UC_027-Admin grants admin rights to user
An administrator grants admin rights to another user. So this user will become also an administrator.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminGrantsAdminRightsToUser
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
User will be granted admin rights This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service grants user admin rights. |
3, 4 |
The service will grant user admin rights and triggers asynchronous events This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Inform user that he/she became administrator |
4 |
This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform SecHub admins that another user became administrator |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.29. UC_028-Admin revokes admin rights from an admin
An administrator revokes existing admin rights from another administrator.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminRevokesAdminRightsFromAdmin
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Admin rights will be revoked from admin This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service revokes user admin rights. |
3, 4 |
The service will revoke user admin righs and triggers asynchronous events This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Inform user about loosing administrator rights |
4 |
This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform SecHub admins that another admin is no longer admin |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.30. UC_029-Admin lists all admins
An administrator downloads a json file containing all names of SecHub admins
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminListsAllAdmins
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
All userids of sechub administrators are returned as json This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
All userids of sechub administrators are returned as json This step is defined at method |
10.20.31. UC_030-Admin disables job processing in scheduler
An administrator disables scheduler job processing. This can be a preparation for system wide update - when scheduling is stoped, user can ask for new SecHub Jobs etc. But as long as scheduler is stopped nothing is executed - so JVMs/PODs can be updated in cluster
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.schedule.UseCaseAdminDisablesSchedulerJobProcessing
Event overview
|
Involved messages |
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator wants to stop (pause) scheduler job processing This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
2 |
Sends request to scheduler domain to disable scheduler job processing This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
3 |
Sends request to scheduler to send updates about current status. This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Disable processing |
4 |
Disables job processing inside scheduler database This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform SecHub admins that scheduler job processing has been disabled |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.32. UC_031-Admin enables scheduler job processing
An administrator starts scheduler job processing. This can be a necessary step after a system wide update where processing of jobs was stoped before.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.schedule.UseCaseAdminEnablesSchedulerJobProcessing
Event overview
|
Involved messages |
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator wants to start (unpause) scheduler job processing This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
3 |
Sends request to scheduler domain to enable scheduler job processing This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Enable processing |
4 |
Enables job processing inside scheduler database This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform SecHub admins that scheduler job processing has been enabled |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.33. UC_032-Admin get scheduler status
An administrator wants to update information about scheduler status
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.schedule.UseCaseAdminTriggersRefreshOfSchedulerStatus
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
Administrator wants to trigger a refresh of scheduler status. Will update information about running, waiting and all jobs in scheduler etc. etc. This step is defined at method |
10.20.34. UC_033-Admin lists status information
An administrator fetches current known status information about sechub
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.status.UseCaseAdminListsStatusInformation
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
Administrator wants to list status information about sechub This step is defined at method |
10.20.35. UC_034-Admin cancels a job
Administrator does cancel a job by its Job UUID
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.job.UseCaseAdminCancelsJob
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Triggers job cancellation request, owners of project will be informed This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Cancel job |
3 |
Will trigger event that job cancel requested This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Try to find job and mark as being canceled |
4 |
When job is found and user has access the state will be updated and marked as canceled This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform user that her/his job has been canceled |
5 |
This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
start cancel operation thread |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.36. UC_035-User defines mock data configuration for project
User retrieves project mockdata - see define project mockdata
|
SecHub must be started with |
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.UseCaseUserDefinesProjectMockdata
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to define mock configuration byJSON data |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call to store mock configuration |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.37. UC_036-User retrieves mock data configuration for project
When other systems integrate sechub into their live cylce (this means not a build server integration,
but an integration from another product…)
they also want to integrate into their integration tests as well - so a special environment is
necessary an INT environment.
When using commercial security products it can happen that integration tests will lead to additional
license costs. To prevent this the INT environment can be setup to use mocked adapters. These
adapters will not communicate with the real security products but instead return mocked product
results. All logic, every behaviour inside SecHub is exactly the same except the communication with
the security product. This technique is used by SecHub for integration testing itself.
|
SecHub must be started with |
Tests/Testers have the possibility to setup wanted traffic-light result on their SecHub
projects by REST API.
-
green will contain only green results,
-
yellow shall contain green and yellow results and
-
red will contain green, yellow and red ones.
{
"codeScan" : {
"result" : "RED"
},
"webScan" : {
"result" : "YELLOW"
},
"infraScan" : {
"result" : "GREEN"
}
}Of course you can reduce mock to wanted parts only:
{
"codeScan" : {
"result" : "YELLOW"
}
}Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.UseCaseUserRetrievesProjectMockdata
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to get JSON data |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call to get JSON data |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.38. UC_037-Admin updates mapping configuration
An administrator changes mapping configuration. Mappings represents a generic mechanism to replace a given string, matched by configured regular expression pattern with a replacement string. Some of the mappings are used for adapter behaviour.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdmiUpdatesMappingConfiguration
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator wants to update a mapping configuration This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
3 |
Services updates data in database and sends event This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Event handler |
4 |
Receives mapping configuration change event This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Service call |
5 |
Updates scan mapping in DB This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
Trigger service |
6 |
Checks periodically for updates in scan configuration This step is defined at method |
|
6 |
Service call |
Checks if current mappings in DB lead to a new scan configuration. This step is defined at method |
10.20.39. UC_038-Admin fetches mapping configuration
An administrator fetches mapping configuration by its ID.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesMappingConfiguration
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator wants to fetch a mapping configuration This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Services fetches data from database, if not set an empty mapping data result will be returned This step is defined at method |
10.20.40. UC_039-Check if the server is alive and running.
An anonymous user or system wants to know if the server is alive and running.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.anonymous.UseCaseAnonymousCheckAlive
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call |
An anonymous user checks if the server is alive and running using the REST API This step is defined at method |
10.20.41. UC_040-Admin fetches server runtime data
An administrator fetches the current SecHub server runtime data. Only administrators are allowed to do this because it contains the server version and knowing the exact server version makes it easier for penetration tester or attacker to attack the system.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.status.UseCaseAdminFetchesServerRuntimeData
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API Call |
Administrator wants to fetch server runtime data. This data contains for example the server version This step is defined at method |
10.20.42. UC_041-Admin restarts a job
Administrator restarts job
When a JVM (or POD) crashes with running SecHub job, the job process execution has been
terminated without resetting the scheduler state.
If this has happened, somebody or a build server who/which is waiting for sechub job result will wait infinite and without hope of having a status refresh.
So the admin must be able to restart a job.
|
The restart will be intransparent for end user so they will just keep on waiting but get the result as soon as possible. |
The restart will
-
first of all write an audit log enry
-
be canceled, when job does not exist in scheduler
-
be canceled, when execution already finished
-
check for running batch jobs with SecHub job UUID.
If there are existing batch operations, those will be stopped -
new scan will be restarted immediately without scheduling, will try to reuse existing results
E.g. when a static code scan job is triggered to a product and scan ID is wellknown, no new scan will be started, but state of this scan is refetched by the ID, etc. etc. But exact resilience behaviour depends on adapter implementation
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.job.UseCaseAdminRestartsJob
Event overview - variant: accidently restart because job has already finished
Event overview - variant: crashed jvm with product result
|
Involved messages |
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Triggeres job restart (soft) This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Restart job |
3 |
Will trigger event that job restart (soft) requested This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Inform sechub admins when job restart was canceled |
4 |
This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform sechub admins when job has been restarted |
5 |
This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
Inform sechub admins when job results have been purged |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.43. UC_042-Admin restarts a job (hard)
Administrator restarts job the hard way , means it is possible to restart a running (not finished) job and destroy all former results.
|
It is very similar to related use case admin restarts job, but with difference that all former product results and also adapter meta data is removed. |
|
We do NOT allow restarts of former finished jobs because finalization does destroy interim data - e.g. uploaded source code etc. - and is no longer restartable. Also we cannot ensure that a client has not already downloaded the existing results, so we we keep them as is! The term "hard" is only because we destroy former meta data and product results! So the restart is like from "scratch". |
The restart will
-
first of all write an audit log enry
-
be canceled, when job does not exist in scheduler
-
be canceled, when execution already finished
-
delete all former product results and also adapter meta data
-
check for running batch jobs with SecHub job UUID.
If there are existing batch operations, those will be stopped -
new scan will be restarted immediately without scheduling, will not try to reuse existing results because such information was formerly deleted
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.job.UseCaseAdminRestartsJobHard
Event overview - variant: accidently restart because job has already finished
Event overview - variant: crashed jvm with product result
Event overview
|
Involved messages |
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Triggeres job restart (hard) This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Restart job |
3 |
Will trigger event that job restart (hard) requested This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Try to restart job |
3 |
When job is found and job is not already finsihed, a restart will be triggered. Existing batch jobs will be terminated This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Try to rstart job (hard) |
3 |
When job is found, a restart will be triggered. Existing batch jobs will be terminated This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Inform sechub admins when job restart was canceled |
4 |
This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform sechub admins when job has been restarted |
5 |
This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
Inform sechub admins when job results have been purged |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.44. UC_043-Admin receives notification about start of a new scheduler instance
Administrators receive notification about start of a new scheduler instance.
The notification will contain also information about potential zombie jobs - just show all started but not finished jobs before scheduler start.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.status.UseCaseAdminReceivesNotificationAboutNewchedulerInstanceStart
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
send domain message that new scheduler instance has been started and information about potential zombie jobs |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Inform sechub admins that new scheduler job has been started |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.45. UC_044-User marks false positives
A user wants to mark false positives either for a finished job or with project data not necessarily connected to a finished job.
To mark false positives using job data the job must have been executed, finished without failure and job NOT been deleted. The user will be able to mark former job results by their given id as false positives.
To mark false positives using project data no job must have been run, but it will help identify findings as false positives of course. The project data are not related to any job information.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserMarksFalsePositives
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to define false positives by JSON data containing identifiers for existing jobs or false positive project data |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.46. UC_045-User unmarks existing false positive definitons
A user wants to unmark existing false positives This means the false positives has been marked before.
| This will NOT change any former job report where the false positive to unmark has been filtered! |
After next scan job the former false positive is no longer filtering the finding.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserUnmarksFalsePositiveByJobData
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to remove existing false positive definition |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.47. UC_046-User fetches false positive configuration of project
A user wants to fetch false positive configuration of project.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserFetchesFalsePositiveConfigurationOfProject
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to fetch existing false positive configuration of project |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.48. UC_047-Admin creates an executor configuration
An administrator creates an executor a new configuration entry.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminCreatesExecutorConfiguration
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator adds a new product executor configuration by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Service creates a new product executor configuration This step is defined at method |
10.20.49. UC_048-Admin deletes executor configuration
An administrator deletes an executor by removing the configuration entry identified by its uuid
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminDeletesExecutorConfiguration
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator deletes an existing product executor configuration by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Service deletes an existing product executor configuration by its UUID This step is defined at method |
10.20.50. UC_049-Admin fetches executor configuration list
An administrator fetches executor configuration list which contains all executor configurations
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesExecutorConfigurationList
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator fetches list of existing product executor configurations by calling REST API, will not contain setup information This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Service fetches data and creates a list containing all executor configurations This step is defined at method |
10.20.51. UC_050-Admin fetches executor configuration
An administrator fetches one explicit executor configuration by its uuid.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesExecutorConfiguration
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator fetches setup of an existing product executor configuration by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Service reads setup information for an existing product executor configuration This step is defined at method |
10.20.52. UC_051-Admin updates executor configuration setup
An administrator updateds dedicated executor configuration. The update does change description, enabled state and also used executors, but Will NOT change any associations between profile and projects.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminUpdatesExecutorConfig
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator updates setup for an existing product executor configuration by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
2 |
Service updates existing executor configuration This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Service updates existing executor configuration This step is defined at method |
10.20.53. UC_052-Admin creates an execution profile
An administrator creates an execution profile
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminCreatesExecutionProfile
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator adds a new product execution profile by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Service creates a new product executor configuration This step is defined at method |
10.20.54. UC_053-Admin deletes execution profile
An administrator deletes execution profile
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminDeletesExecutionProfile
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator deletes an existing product execution profile by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Service deletes an existing product execution profile by its profile id This step is defined at method |
10.20.55. UC_054-Admin updates execution profile
An administrator updateds dedicated execution profile
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminUpdatesExecutionProfile
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
Administrator updates existing profile by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
10.20.56. UC_055-Admin fetches execution profile
An administrator fetches details about an execution profile
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesExecutionProfile
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator fetches setup of an existing product executor configuration by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Service reads setup information for an existing product executor configuration This step is defined at method |
10.20.57. UC_056-Admin fetches execution profile list
An administrator fetches execution profile list
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesExecutionProfileList
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator fetches lsit of all available execution profiles by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Service fetches data and creates a list containing all executor profiles This step is defined at method |
10.20.58. UC_057-Admin assigns execution profile to project
An administrator assigns an execution profile to an existing project
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminAssignsExecutionProfileToProject
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator adds profile relation to project by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Services creates a new association between project id and profile This step is defined at method |
10.20.59. UC_058-Admin unassigns execution profile from project
An administrator unassigns an execution profile from a projects.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminUnassignsExecutionProfileFromProject
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator removes profile relation to project by calling REST API This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
Services deletes an existing association between project id and profile This step is defined at method |
10.20.60. UC_059-Update project metadata
Administrator updates project meta data inside SecHub.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseUpdateProjectMetaData
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
MetaData will be updated This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Update project |
The service will update the Project metadata. This step is defined at method |
10.20.61. UC_060-Admin or owner changes owner of a project
An administrator or the current project owner changes the ownership of an existing SecHub project. If the new owner is not already assigned to the project, the new owner will be assigned automatically. The old owner will still be assigned to the project, but can be removed later by the owner if necessary.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminOrOwnerChangesProjectOwner
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator does call rest API to set new project owner This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Change project owner |
4 |
The service will set the given user as the owner of the project. If the user does not already has the the role ROLE_OWNER it will obtain it. The old owner will loose the project ownership. This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform new and previous project owners that the project owner ship has changed |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.62. UC_061-Admin changes project description
An administrator changes the project description
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseAdminChangesProjectDescription
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Changes project description. Json returned containing details about changed project This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service changes project description. |
The service will change project description. This step is defined at method |
10.20.63. UC_062-Admin changes project access level
An administrator is able to change the access level of a project.
Project access levels do constraint possible user operations for a project - e.g. restrict to read only operations. The details of different restrictions are described below.
A project access level none will make it also for administrators
impossible to fetch reports from the project. Only
special administrator REST API calls are not restricted.
|
10.20.63.1. Levels
-
full
no restrictions -
read_only
users can download their reports, get job status, but cannot trigger any project jobs -
none
users have no access to reports, jobs and cannot trigger any jobs for the project
10.20.63.2. Conststraints
10.20.63.2.1. Full
When a project has access level full any read or write user operation
is possible:
-
a new scan can be triggered, so user can
-
create job
-
approve job
-
upload job data
-
-
scheduling is active for the project new jobs are processed
-
user can check status for a job in their project
-
user can download their former reports
10.20.63.2.2. Read only
When a project has access level read_only only read user operations
are possible:
-
a new scan is not possible, HTTP 403: Forbidden will be sent for
-
create job
-
approve job
-
upload job data
-
-
running jobs are still running
-
already scheduled jobs will be scheduled
-
user are still able to check status for a job in their project
-
user can still download their former reports
10.20.63.2.3. None
When a project has access level none no user operation is possible:
-
a new scan is not possible, HTTP 403: Forbidden will be sent for
-
create job
-
approve job
-
upload job data
-
-
running jobs are still running
-
already scheduled jobs will be scheduled
-
user are NOT able to check status for a job in their project, HTTP 403: Forbidden will be sent
-
user can NOT download their former reports, HTTP 403: Forbidden will be sent
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.project.UseCaseAdminChangesProjectAccessLevel
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Admin does call REST API to change project access level This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Change access level |
3 |
The service will change the project access level inside administration domain and trigger a change event to inform recipients about the new situation. This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Event handler |
4 |
Receives change project access level event This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Event handler |
Receives change project access level event This step is defined at method |
10.20.64. UC_063-Admin updates user email address
An administrator update the email address of an user. After the change an email will be sent to the old email-address to inform the user about the change. In addition, a new mail to the new email address will be sent as well.
|
When the new email address is the same as before, the action will be rejected. |
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminUpdatesUserEmailAddress
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
User emaill address will be changed This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service updates user email address. |
3 |
The service will update the user email address and also trigger events. This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Inform user that the email address has been changed |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.65. UC_064-Admin fetches auto cleanup configuration
An administrator feches current auto cleanup configuration.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesAutoCleanupConfiguration
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator fetches auto cleanup configuration This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Fetches auto cleanup config |
Fetches auto cleanup configuration from database This step is defined at method |
10.20.66. UC_065-Admin updates auto cleanup configuration
An administrator changes auto cleanup configuration.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminUpdatesAutoCleanupConfiguration
Event overview
|
Involved messages |
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Administrator changes auto cleanup configuration This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Updates auto cleanup config |
3, 4, 5 |
Updates auto cleanup configuration as JSON in database and sends event This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Administration domain receives auto cleanup event |
4 |
Received event in administration domain about auto cleanup configuration change. Stores data, so available for next auto clean execution This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Schedule domain receives auto cleanup event |
5 |
Received event in schedule domain about auto cleanup configuration change. Stores data, so available for next auto clean execution This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
Scan domain receives auto cleanup event |
Received event in scan domain about auto cleanup configuration change. Stores data, so available for next auto clean execution This step is defined at method |
10.20.67. UC_066-Sechub administration domain auto cleanup
The administration domain does auto cleanup old data. This is done periodically. The time period is defined by auto cleanup configuration.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.autocleanup.UseCaseAdministrationAutoCleanExecution
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Scheduling |
2 |
Checks for parts to auto clean. This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Delete old data |
deletes old job information This step is defined at method |
10.20.68. UC_067-Sechub scan domain auto cleanup
The scan domain does auto cleanup old data. This is done periodically. The time period is defined by auto cleanup configuration.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.autocleanup.UseCaseScanAutoCleanExecution
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Scheduling |
2 |
Checks for parts to auto clean. This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Delete old data |
deletes old job information This step is defined at method |
10.20.69. UC_068-Sechub schedule domain auto cleanup
The schedule domain does auto cleanup old data. This is done periodically. The time period is defined by auto cleanup configuration.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.autocleanup.UseCaseScheduleAutoCleanExecution
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Scheduling |
2 |
Checks for parts to auto clean. This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Delete old data |
3 |
deletes old job information This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Schedule cipher pool data cleanup |
Removes cipher pool data entries from database which are no longer used by any job This step is defined at method |
10.20.70. UC_069-User uploads binaries
A user wants to upload binaries for a former created SecHub job.
The binaries must be inside a valid tar file.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserUploadsBinaries
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Authenticated REST call |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Try to find project and upload binaries as tar |
When project is found and user has access and job is initializing the binaries file will be uploaded This step is defined at method |
10.20.71. UC_070-User downloads job report in SPDX format
A user wants to download a SPDX report for a finished SecHub job
using the job UUID.
Only SPDX JSON is supported.
In case, there is no SPDX JSON result for a given job an error will be thrown.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserDownloadsSpdxJobReport
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to get SPDX JSON report |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.72. UC_071-User lists jobs for project
User fetches a list containing information about jobs of a SecHub project. Per default only the last created job is returned, but it is possible to define a limit and fetch more than one. In this case the returned entries are ordered by creation date.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.job.UseCaseUserListsJobsForProject
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
get pageable list of jobs in project |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Assert access by service and fetch job information for user |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.73. UC_072-Admin shows user details for email address
An administrator fetches user details for an email address.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAdminShowsUserDetailsForEmailAddress
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Json returned containing details about user and her/his projects This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service fetches user details. |
The service will fetch user details for given user email address This step is defined at method |
10.20.74. UC_073-Admin starts encryption rotation
An administrator starts encryption rotation.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.encryption.UseCaseAdminStartsEncryptionRotation
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Admin triggers rotation of encryption via REST This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service call |
3 |
Triggers rotation of encryption via domain message This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Service call |
4 |
Forces new cipher pool entry creation and triggers encryption service pool refresh This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Service call |
5 |
Creates new cipher pool entry in database in own transaction This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
Refresh encryption pool |
6 |
Encryption pool is refreshed (necessary because pool changed before this method call) This step is defined at method |
|
6 |
Update encrypted data |
Encrypted data is updated (a direct pool refresh was triggered by admin action) This step is defined at method |
10.20.75. UC_074-Scheduler encryption pool refresh
The scheduler refreshes its encryption pool data to handle new setup
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.encryption.UseCaseScheduleEncryptionPoolRefresh
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Init encryption pool |
3 |
Encryption pool is created on startup This step is defined at method |
|
1 |
Encryption pool data refresh trigger |
2 |
Scheduler instance will check if encryption pool is in sync with the database definitions. If not, the instance will try to create new encryption pool object and provide the new setup. This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Refresh encryption pool |
3 |
Encryption pool is refreshed (if necessary) This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Update encrypted data |
Encrypted data is updated (all other cluster members) This step is defined at method |
10.20.76. UC_075-Scheduler rotates data encryption
The scheduler checks for old encrypted data and will encrypt with latest cipher
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.encryption.UseCaseScheduleRotateDataEncryption
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Update encrypted data |
Final update of encrypted job data. Will update all SecHub jobs having a pool id which is lower than latest from encryption pool This step is defined at method |
10.20.77. UC_076-Admin fetches encryption status
An administrator fetches encryption status from all domains where encryption is used.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.encryption.UseCaseAdminFetchesEncryptionStatus
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Service call |
1 |
Services collects encryption status from domains via event bus This step is defined at method |
|
1 |
Rest call |
Admin fetches encryption status from domains via REST This step is defined at method |
10.20.78. UC_077-SecHub does cleanup encryption
Secub does an ecnryption cleanup.
Inside relevant domains the encryption situation will be checked and old encryption setup, which is no longer necessary, will be dropped.
For example: When encryption was done with formerly via ENV variable
SECRET_1_AES_256 and the new one setup is using SECRET_2_AES_256 and
all jobs have been migrated to the new encryption, the cipher setup
using SECRET_1_AES_256 will become obsolete and will be automatically
removed. After the remove is done, there is no longer a need to
start the server with SECRET_1_AES_256, but only with SECRET_2_AES_256 …
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.encryption.UseCaseEncryptionCleanup
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Schedule cipher pool data cleanup |
Removes cipher pool data entries from database which are no longer used by any job This step is defined at method |
10.20.79. UC_078-User unmarks existing false positive project data definitons
A user wants to unmark existing false positives This means the false positives has been marked before.
| This will NOT change any former job report where the false positive to unmark has been filtered! |
After next scan job the former false positive is no longer filtering the finding.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.user.execute.UseCaseUserUnmarksFalsePositiveByProjectData
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to remove existing false positive project data definition by id |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.80. UC_079-System suspends running jobs on SIGTERM
When a SecHub instance is receiving a SIGTERM signal from OS, the server instance must block further job processing (on this instance) and suspend all of its running jobs. Because after some time the job will be resumed by another instance, this process will not stop any running PDS jobs.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.other.UseCaseSystemSuspendsJobsWhenSigTermReceived
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Scheduler terminates |
2 |
Scheduler instance is terminating. Will stop processing new jobs and inform job executor to suspend This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Scheduler job executor suspends current jobs |
3 |
Scheduler instance is terminating. Will mark current running jobs of this instance as SUSPENDED This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Scheduler job executor suspends current jobs |
4 |
Scheduler instance is terminating. Will mark current running jobs of this instance as SUSPENDED This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Scan job executor stops suspended jobs |
5 |
Scheduler instance has marked jobs as suspended. Will stop execution of scans of these jobs This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
Scan job executable handles SUSPEND state |
6 |
Scan job executable stops execution because suspended This step is defined at method |
|
6 |
Inform listeners |
7 |
Inform listeners about job suspension This step is defined at method |
|
7 |
Administration handles suspended job |
Administration domain removes suspended job from its running job list This step is defined at method |
10.20.81. UC_080-System resumes suspended jobs
SecHub jobs which have been suspended a minimum duration time will be restarted automatically.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.other.UseCaseSystemResumesSuspendedJobs
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Schedule suspended jobs |
2 |
Scheduler checks not only for new jobs but also for resumed ones. This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Resolve next job |
3 |
Resolves UUID of job which shall be executed at next time. If there is a suspended job and shall be resumed this job will be returned. Otherwise the selected schedule strategy will be used to determine next job uuid. Remark: A suspended job shall only be executed when the minium duration time has been reached. The time period can be configured and prevents side effects at deployments. This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Mark next job to execute |
4 |
When a suspended job is the next one, the job execution state will be changed to RESUMING This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Resume job |
The SecHub job will be resumed. This is done by triggering a soft restart request for the job. You can read Admin restarts a job for the steps which are
done at restart process. The steps are the same, except there is no audit logging
and the event is not triggered from This step is defined at method |
10.20.82. UC_081-get assigned project data
User, Owner or Admin fetches a list containing information about assigned and/ or owned projects.
The Project data contains the following information:
-
Project ID
-
Owner
-
is owned
-
assigned users (can only be viewed by owner or admin)
A project user can see only projects he is assigned to. A project owner can see all projects he owns and the assigned users. A project admin can see assigned or owned projects and all assigned users.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.project.UseCaseGetAssignedProjectDataList
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest API call to get Projects with information |
2 |
Rest api call to get projects with details This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Fetch enabled profiles for project |
Event handling at scan domain to collect enabled profiles for projects This step is defined at method |
10.20.83. UC_082-Admin creates or updates a template
An administrator creates or updates a template
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminCreatesOrUpdatesTemplate
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to create or update template |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service creates or updates template |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.84. UC_083-Admin deletes a template
An administrator deletes a template. Will also remove any association between projects and this template
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminDeletesTemplate
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to delete a template |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service removes all assignments and deletes template completely |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.85. UC_084-Admin fetches template
An administrator fetches template data by its id
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesTemplate
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to fetch template |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service fetches template |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.86. UC_085-Admin fetches all template ids
An administrator fetches a list containing all templates ids
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesAllTemplateIds
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to fetch template list |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Services fetches all template ids |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.87. UC_086-Admin assigns template to project
An administrator assigns a template to a project
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminAssignsTemplateToProject
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Admin does call REST API to assign a template to project This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
service assigns template to project |
3 |
The service will request the template assignment in domain 'scan' via synchronous event and updates mapping in domain 'administration' afterwards This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
service assigns project to template in scan domain |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.88. UC_087-Admin unassigns template from project
An administrator unassigns a template from a project
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminUnassignsTemplateFromProject
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Admin does call REST API to unassign a template from project This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
service unassigns template from project |
3 |
The service will request the template unassignment in domain 'scan' via synchronous event and updates mapping in domain 'administration' afterwards This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
service unassigns project from template in scan domain |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.89. UC_088-Admin uploads an asset file
An administrator uploads a file for an asset. If the file already exists, it will be overriden.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminUploadsAssetFile
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to upload a file for an asset |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service tries to upload file for asset |
Uploaded file will be stored in database and in storage This step is defined at method |
10.20.90. UC_089-Admin downloads an asset file
An administrator downloads a file fom an asset.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminDownloadsAssetFile
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to download a file for an asset |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service downloads asset file from database |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.91. UC_090-Admin fetches asset ids
An administrator fetches all available asset ids.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesAssetIds
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to fetch all availbale asset ids |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service fetches all asset ids from database |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.92. UC_091-Admin fetches asset details
An administrator fetches details about an asset. For example: the result will contain names but also checksum of files.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminFetchesAssetDetails
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to fetch details about asset |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service fetches asset details for given asset id |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.93. UC_092-Admin deletes an asset file
An administrator deletes a file fom an asset.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminDeletesOneFileFromAsset
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to delete an asset file |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Services deletes file from asset |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.94. UC_093-Admin deletes asset comletely
An administrator deletes an asset completely.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminDeletesAssetCompletely
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to delete complete asset |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Services deletes all asset parts |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.95. UC_094-User cancels a job
User does cancel a job by its Job UUID
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.job.UseCaseUserCancelsJob
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Triggers job cancellation request, owners of project will be informed This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Cancel job |
3 |
Will trigger event that job cancel requested This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Try to find job and mark as being canceled |
4 |
When job is found and user has access the state will be updated and marked as canceled This step is defined at method |
|
4 |
Inform user that her/his job has been canceled |
5 |
This step is defined at method |
|
5 |
start cancel operation thread |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.96. UC_095-User fetches his user details
The authenticated user fetches his user details
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseUserFetchesUserDetailInformation
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
Json response containing details about the authenticated user This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service fetches user details for the authenticated user. |
The service will fetch user details for the authenticated user This step is defined at method |
10.20.97. UC_096-Admin executes templates healthcheck or updates a template
An administrator creates or updates a template
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.config.UseCaseAdminExecutesTemplatesHealthcheck
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to create or update template |
2 |
This step is defined at method |
10.20.98. UC_097-User updates his own email address
The authenticated user updates his own email address
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseUserUpdatesEmailAddress
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
User request to update their email address This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service checks user mail address and sends approval mail |
3 |
The service will check the user input and send a mail to verify This step is defined at method |
|
3 |
Send mail to verify |
The service will send a mail to the new email address to verify the change request. This step is defined at method |
10.20.99. UC_098-Anonymous user verifies new email address
The unauthenticated user verifies his new email address by link containing JWT token.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.usecases.admin.user.UseCaseAnonymousUserVerifiesEmailAddress
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Rest call |
2 |
User verifies his new email address This step is defined at method |
|
2 |
Service verifies user mail address |
3 |
The service will verify the token and update the user email address This step is defined at method |
10.20.100. UC_099-User requests finding explanation
In this usecase the user requests an explanation for a finding.
Technical information
You will find relevant code parts by searching for references of @com.mercedesbenz.sechub.sharedkernel.assistant.UseCaseUserRequestFindingExplanation
Steps
| Nr | Title | Role(s) | Next | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
REST API call to get an explanation for the given finding. |
This step is defined at method |
10.21. Domain driven design
10.21.1. Domain Message Bus
The domain message bus represents an abstraction layer for communication between different domains. It shall be the ONLY way to communicate between the different domains. Purpose: In future maybe the domains will be separate spring boot applications and be also autark deployable!
Currently SecHub contains of ONE deployable spring boot application. But to prevent the "Big ball of mud" this abstraction must be always used when one domain calls another one.
10.21.2. Domain communication and actions
10.21.2.1. Overview
10.21.2.1.1. Diagram
10.21.2.1.2. List of all messages
10.21.2.2. Message ANALYZE_SCAN_RESULTS_AVAILABLE
10.21.2.3. Message ASSIGN_OWNER_AS_USER_TO_PROJECT
10.21.2.4. Message AUTO_CLEANUP_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.5. Message BINARY_UPLOAD_DONE
10.21.2.6. Message GET_ENCRYPTION_STATUS_SCHEDULE_DOMAIN
10.21.2.7. Message JOB_CANCELLATION_RUNNING
10.21.2.8. Message JOB_CREATED
10.21.2.9. Message JOB_DONE
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.10. Message JOB_EXECUTION_STARTING
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.11. Message JOB_FAILED
10.21.2.12. Message JOB_RESTART_CANCELED
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.13. Message JOB_RESTART_TRIGGERED
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.14. Message JOB_RESULTS_PURGED
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.15. Message JOB_RESULT_PURGE_DONE
10.21.2.16. Message JOB_RESULT_PURGE_FAILED
10.21.2.17. Message JOB_STARTED
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.18. Message JOB_SUSPENDED
10.21.2.19. Message MAPPING_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED
10.21.2.20. Message PRODUCT_EXECUTOR_CANCEL_OPERATIONS_DONE
10.21.2.21. Message PROJECT_ACCESS_LEVEL_CHANGED
10.21.2.22. Message PROJECT_CREATED
10.21.2.23. Message PROJECT_DELETED
10.21.2.24. Message PROJECT_OWNER_CHANGED
10.21.2.25. Message PROJECT_WHITELIST_UPDATED
10.21.2.26. Message REQUEST_ASSIGN_TEMPLATE_TO_PROJECT
10.21.2.27. Message REQUEST_DETAILS_FOR_JOB_FINDING
10.21.2.28. Message REQUEST_ENABLED_PROFILE_IDS_FOR_PROJECTS
10.21.2.29. Message REQUEST_FULL_CONFIGURATION_VALIDATION
10.21.2.30. Message REQUEST_JOB_CANCELLATION
10.21.2.32. Message REQUEST_JOB_RESTART_HARD
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.33. Message REQUEST_PURGE_JOB_RESULTS
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.34. Message REQUEST_SCHEDULER_DISABLE_JOB_PROCESSING
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.35. Message REQUEST_SCHEDULER_ENABLE_JOB_PROCESSING
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.36. Message REQUEST_SCHEDULER_JOB_STATUS
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.37. Message REQUEST_SCHEDULER_STATUS_UPDATE
10.21.2.38. Message REQUEST_UNASSIGN_TEMPLATE_FROM_PROJECT
10.21.2.39. Message REQUEST_USER_ROLE_RECALCULATION
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.40. Message RESULT_ASSIGN_TEMPLATE_TO_PROJECT
10.21.2.41. Message RESULT_DETAILS_FOR_JOB_FINDING
10.21.2.42. Message RESULT_ENABLED_PROFILE_IDS_FOR_PROJECTS
10.21.2.43. Message RESULT_ENCRYPTION_STATUS_SCHEDULE_DOMAIN
10.21.2.44. Message RESULT_FULL_CONFIGURATION_VALIDATION
10.21.2.45. Message RESULT_UNASSIGN_TEMPLATE_FROM_PROJECT
10.21.2.46. Message SCAN_DONE
10.21.2.47. Message SCAN_FAILED
10.21.2.48. Message SCAN_SUSPENDED
10.21.2.49. Message SCHEDULER_JOB_PROCESSING_DISABLED
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.50. Message SCHEDULER_JOB_PROCESSING_ENABLED
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.51. Message SCHEDULER_JOB_STATUS
10.21.2.52. Message SCHEDULER_STARTED
10.21.2.53. Message SCHEDULER_STATUS_UPDATE
10.21.2.54. Message SCHEDULE_ENCRYPTION_POOL_INITIALIZED
10.21.2.55. Message SOURCE_UPLOAD_DONE
10.21.2.56. Message START_ENCRYPTION_ROTATION
10.21.2.57. Message START_SCAN
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.58. Message TEMPLATE_DELETED
10.21.2.59. Message UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION
10.21.2.60. Message USER_ADDED_TO_PROJECT
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.61. Message USER_API_TOKEN_CHANGED
10.21.2.62. Message USER_BECOMES_SUPERADMIN
10.21.2.64. Message USER_DELETED
10.21.2.65. Message USER_EMAIL_ADDRESS_CHANGED
10.21.2.66. Message USER_EMAIL_ADDRESS_CHANGE_REQUEST
10.21.2.67. Message USER_NEW_API_TOKEN_REQUESTED
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.68. Message USER_NO_LONGER_SUPERADMIN
10.21.2.69. Message USER_REMOVED_FROM_PROJECT
|
Use cases related to this message |
10.21.2.70. Message USER_ROLES_CHANGED
|
Use cases related to this message |
11. Configurations
11.1. Execution profiles
An execution profile can contain multiple executor configurations. The configurations can be shared between multiple profiles.
|
As an example: a config with name "pds-gosec-1" can be used in profiles "profileA" and also "profileB" at the same time. |
When a profile is assigned to a project and the profile is enabled, all of its enabled executor configurations are executed for the project when suitable for code scan type.
Technically we assign a projectId to a profile, because in domain scan we only know projectIds but not Project entity…
|
|
To have a scan job running, at least one executor configuration must match - otherwise you will have always a "green" scan result. |
Following usecases are supported:
11.2. Executor configuration
SecHub uses product executors to call security products by dedicated product adapters.
Each used security product has at least one executor configuration.
Inside such a configuration, we can define properties and parameters which are used when it comes to SecHub job execution. The data is evaluated and used by product executors at runtime and no server restart is necessary.
So for example you can easily change a base URL of a product location and it will automatically be used by next job execution.
|
At the moment They ignore
You still have to configure the ignored parts by system environment variables (or system properties) in a global way and you can’t change these settings at runtime. |
11.2.1. Data structure
11.2.1.1. Name
Just the name of the executor configuration. Can be changed.
11.2.1.2. Enabled
Only when the executor configuration is enabled, it will be used (of course it has also be added to an enabled profile and this to a project).
11.2.1.3. UUID
Unmodifiaable unique ID of an executor configuration. Cannot be changed.
11.2.1.4. Product identifier
The product identifier for the product executor to use. Examples are:
-
PDS_CODESCAN -
PDS_WEBSCAN -
PDS_INFRASCAN -
PDS_LICENSESCAN
11.2.1.5. Executor version
At the moment all product executors exists only in version 1 and as long as there is no
breaking change the exisitng product executor will be extended and the existing version will be kept.
When there are breaking changes - e.g. the communication between SecHub and a new version of the security product becomes completely different, or parameters have a complete other meaning, an additional product executor with another version will be available.
11.2.1.6. Product base URL
Here we define the base URL to the security product including port number.
As an example: https://checkmarx.example.org:6011
11.2.1.7. Product credentials
To use a security product, we always need login credentials. These credentials must be defined inside the configuration.
11.2.1.7.1. Environment variable references
To store no real credentials in SecHub database, you can reference SecHub server environment
variables instead - just use the pattern env:${variableName}.
SecHub server will store the given pattern in database, but the content of the environment variable will be used at runtime when it comes to authentication.
|
Example for an environment variable reference: Let’s assume a have a running PDS server which accepts "exampleToken" as API token for technical user. You would add export PDS_CODESCAN1_APITOKEN=exampleToken at the beginning of your start script for SecHub server. In your executor configuration you would set the API token field to |
11.2.1.7.2. User
The user name used by SecHub to authenticate at security product.
11.2.1.7.3. Password or API token
The password or API token used by SecHub to authenticate at security product.
| It is strongly recommended to use environment variable references environment variable references here instead of plain text. |
11.2.1.8. Parameters
Parameters are used at job execution runtime to setup product adapters and to change security product behaviours.
11.2.1.8.1. Mappings
Some product executors do need special mappings - e.g for new project creations. Please look at mapping for more details about the concept and the format.
11.2.1.8.2. Key values
It is also possible to provide just dedicated key value parameters.
11.2.2. Usecases
Following usecases are supported:
11.2.3. Product specific details
11.2.3.1. PDS
For PDS we have a set of predefined configuration parameters (see next table) and the possibility to define custom parameters.
Some of the predefined parameters are generated. In this case the user cannot define them in the executor configuration, but they are listed here for the sake of completeness.
| Key | Description | Additional info |
|---|---|---|
sechub.productexecutor.pds.forbidden.targettype.internet |
When this key is set to true, then this PDS instance does not scan INTERNET! |
|
sechub.productexecutor.pds.forbidden.targettype.intranet |
When this key is set to true, then this PDS instance does not scan INTRANET! |
|
sechub.productexecutor.pds.timetowait.nextcheck.milliseconds |
When this is set, the value will be used to wait for next check on PDS server. If not, the default from PDS install set up is used instead. |
|
sechub.productexecutor.pds.timeout.minutes |
When this is set, the value will be used to wait before timeout happens when no communication with PDS server is possible. If not, the default from PDS install set up is used instead. |
|
sechub.productexecutor.pds.trustall.certificates |
When 'true' then all certificates are accepted. Do not use this in production! |
|
sechub.productexecutor.pds.adapter.resilience.retry.max |
Maximum amount of retries to handle resilience. When not defined or smaller than 0 the default will be: 3 |
|
sechub.productexecutor.pds.adapter.resilience.retry.wait.milliseconds |
Amount of milliseconds the PDS adapter shall wait before doing a next retry to handle resilience. When not defined or smaller than 1 the default will be: 10000 |
|
pds.config.productidentifier |
Contains the product identifier, so PDS knows which part is to call on it's side. |
|
pds.scan.target.type |
Contains the target type (depending on scan type) and will be just an additional information for PDS from SecHub. |
|
pds.config.use.sechub.storage |
When 'true' the SecHub storage will be reused by the PDS server. In this case SecHub will not upload job data to PDS. But it's crucial to have the same root storage setup on the PDS server side (e.g. same s3 bucket for S3 storage, or same NFS base for shared volumes). When not 'true' or not defined, PDS will use its own storage locations |
|
pds.config.use.sechub.mappings |
Contains a comma separated list of mappping ids. Each defined mapping will be fetched from SecHub DB as JSON and sent as job parameter with the mapping id as name to the PDS. |
|
pds.config.sechub.storage.path |
This contains the sechub storage location when sechub storage shall be used. So PDS knows location - in combination with sechub job UUID reuse is possible |
|
pds.config.filefilter.includes |
This contains a comma separated list of path patterns for file includes. These patterns can contain wildcards. Matching will be done case insensitive! Every file which is matched by one of the patterns will be included - except those which are explicitly excluded. When nothing is defined, then every content is accepted for include. For example: '*.go,*.html, test1.txt' would include every Go file, every HTML file and files named 'test1.txt'. |
|
pds.config.script.trustall.certificates.enabled |
When 'true' the PDS adapter script used by the job will have the information and can use this information when it comes to remote operations. |
|
pds.config.supported.datatypes |
Can be SOURCE, BINARY, NONE or a combination as a comma separated list. This data should normally not be defined via a default value of an optional PDS configuration parameter. |
|
pds.config.jobstorage.read.resilience.retries.max |
Defines the maximum amount of retries done when a job storage read access is failing |
|
pds.config.jobstorage.read.resilience.retry.wait.seconds |
Defines the time to wait in seconds before the next retry is done (when it comes to storage READ problems) |
|
pds.config.product.timeout.minutes |
Maximum allowed time in minutes, before a product will time out - this means that the launcher script is automatically canceled by PDS |
|
pds.config.filefilter.excludes |
This contains a comma separated list of path patterns for file excludes. These patterns can contain wildcards. Matching will be done case insensitive! When empty, then nothing will be excluded. The exclude operation will be done AFTER the include file filtering. For example: '*.go,*.html, test1.txt' would exclude every Go file, every HTML file and files named 'test1.txt'. |
|
pds.scan.target.url |
This contains the target URL for the current scan (i.e. webscan). Will not be set in all scan types. E.g. for a code scan this environment variable will not be available |
|
pds.debug.enabled |
When 'true', the PDS instance will show up some debug information on scan time. The output level of debugging information differs on PDS solutions/launcher scripts. |
|
pds.wrapper.remote.debugging.enabled |
Additional information will be always sent to launcher scripts. Interesting to debug wrapper applications remote. |
|
pds.add.scriptlog.to.pdslog.enabled |
When 'true', the PDS instance will add the complete log output from launcher script (and wrapper calls) to PDS log after the PDS launcher script has finished. |
|
pds.scan.configuration |
This contains the SecHub configuration as JSON object (but reduced to current scan type, so e.g. a web scan will have no code scan configuration data available |
|
pds.config.cancel.event.checkinterval.milliseconds |
This is the maximum time the launcher script process will be kept alive after a cancellation event is sent. This gives the launcher script process a chance to recognize the cancel event and do some final cancel parts and exit gracefully. |
|
pds.config.cancel.maximum.waittime.seconds |
The time in seconds PDS will check again if the launcher script process is alive or not when the process shall be canceled. When nothing defined, the default value is:0. If the value is 0 the process will be terminated without waiting. |
|
pds.mocking.disabled |
When 'true' any PDS adapter call will use real PDS adapter and not a mocked variant. |
|
pds.config.template.metadata.list |
Contains a list of template meta data entries (json). |
|
11.2.3.2. Checkmarx
11.2.3.2.1. Mapping teams and presets for new projects
When a user starts a scan and a checkmarx project does not already exist, it will be created.
In some cases, however, it should not be created with the default Checkmarx "preset" but a dedicated one. And when creating many projects we do not want to assign all other presetIds manually to the project (a preset is something like a profile in Checkmarx where scope of scan can be defined at project level).
Also there should be an automated assignment to dedicated teams when the project is newly created.
This can be done by name pattern providers checkmarx.newproject.presetid.mapping and checkmarx.newproject.teamid.mapping
as shown in following example:
An example parameter configuration:
Define mapping for key checkmarx.newproject.presetid.mapping
{
"entries": [
{
"pattern": "my-java-project-.*",
"replacement": "100021",
"comment":"java projects"
},
{
"pattern": "a-go-project-.*",
"replacement": "100031",
"comment":"go projects"
},
{
"pattern": ".*",
"replacement": "100001",
"comment":"others"
}
]
}
}Define mapping for key checkmarx.newproject.teamid.mapping
{
"entries": [
{
"pattern": "my-java-project-.*",
"replacement": "1",
"comment":"team id for java projects"
},
{
"pattern": "a-go-project-.*",
"replacement": "2",
"comment":"team id for go projects"
},
{
"pattern": ".*",
"replacement": "3",
"comment":"team id for other projects"
}
]
}On lazy project creation time, depending on project name in sechub, after checkmarx project creation the project will automatically be assigned to the pattern specific presetId.
For example:
-
project named in SecHub with
my-java-project-marvelous1will have preset id100021and teamId1. -
project named in SecHub with
a-go-project-super-cliwill have preset id100031and teamId2. -
project named in SecHub with
something-else`will have preset id `100001and teamId3
|
First matching part will be used! So ordering is important! |
======= Technical details
Checkmarx install setup does use a dedicated configuration support to provide presetId and teamId
to adapter. Adapter will use presetId (if defined) and teamId (mandatory as before) when
project creation is necessary
11.2.3.2.2. How to obtain preset id
Unfortunately the preset ID is necessary for REST calls, but not visible at Checkmarx UI.
You can either directly access the DB or inspect the web page by web tools in you browser (e.g. enable network monitoring and change preset id at UI…)
11.2.3.2.3. How to obtain team id
Unfortunately the team ID is necessary for REST calls, but not visible at Checkmarx UI.
You can either directly access the DB or inspect the web page by web tools in you browser (e.g. enable network monitoring and change team at UI…)
11.2.4. Examples
| As long as there is no dedicated Web UI for administration we use the Developer Admin UI for example screenshots: |
For every example you have either to create a new executor configuration or edit an an existing one.
To edit an existing one, select main menu entry "Edit executor configuration" as shown in next figure:
This will result in a selection dialog.
11.2.4.1. Checkmarx configuration
At the configuration editor dialog you can change the data structure. Parameters are inside a simple text field. But there exists also a button "Edit parameters".
|
If you edit directly inside the |
When you press the "Edit parameters" button, a dedicated parameter editor will appear:
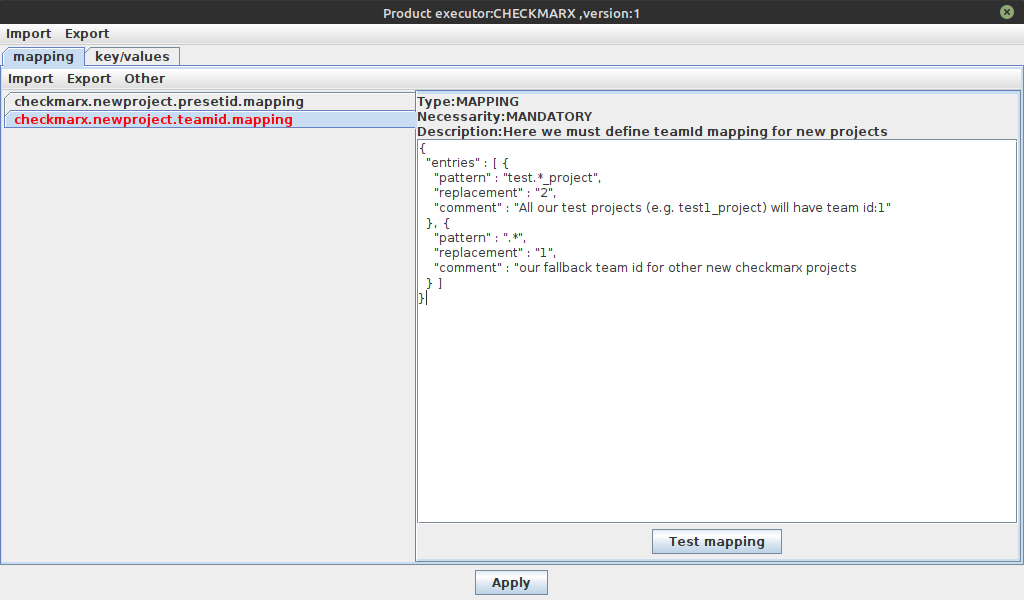
On last figure the type, the necessarity and a short description of the parameters are shown above the text component. This makes it easier to configure values.
At the mapping tab pane you can edit the JSON data. With "Test mapping" button you can also check if the naming pattern are correct and the expected values are resulting.
For the "normal" key value pairs we got the "key/values" tab pane. Here the content is normally
only simple text. For example checkmarx.fullscan.always could contain
like "true" or "false" or simply nothing.
After pressing the Apply button the changed data is set inside executor configuration in correct
format.
11.2.4.2. PDS code scan configuration
Here we got an example for a configuration with selected product identifier PDS_CODESCAN:
The pds.config.productidentifier which is an mandatory value is marked red because it must be
sent to PDS server to identify which product shall be used on the other side.
Optional, but wellknown PDS key value pairs are shown in black - the parameters example.key1 and
example.key2 are marked yellow. Reason: Those keys are unknown by
SecHub and so normally custom parameters.
11.2.4.3. Sereco configuration
Sereco is the only product which needs no configuration at all, because it is an embedded "product".
It also needs no profile setup or something else - as long as there is no other reporting product
available/configured for a SecHub job, an automated fallback will always call Sereco at the end to ensure a report
result is created.
But Sereco is the one and only exception!
11.3. Scan configuration
Sometimes it is necessary to provide special scan configuration setup, e.g. when initializing scan operations at server side.
This can be done by a special scan configuration which is defined as JSON.
Please don’t be confused this configuration with SecHub configuration which is always on client side.
| The scan configuration feature was established before the runtime configuration by profiles and executor configurations was introduced. It is a global configuration for scanning. |
11.3.1. General
11.3.1.1. Name pattern ID providers
Currently only namePatternIdProviders are provided, which contain an id and mappings from name patterns
to identifiers. By this very generic approach dedicated adapters can fetch identifiers for specific name setups.
11.3.2. Mapping
Scan configuration can be changed by SecHub mapping - look at mapping for more information.
Just use the provider ID as mapping ID.
|
11.3.2.1. Technical details
Usage
A caller can use the ScanMappingConfigurationService to fetch an NamePatternIdprovider which is able to provide
an ID for a given name. This is a very generic approach and callers must only use unique IDs to
have dedicated, name based id mappings.
An ID can be any string. Given regular expressions are handled by JAVA regular expression Pattern
Cluster handling
Synchronization inside cluster is done over database and a special scheduler service:
ScanMappingConfigurationRefreshTriggerService . This servcie checks periodically if current scan configuration
has been changed by administrators. If so the name pattern provider will be rebuild.
A ScanProjectConfigService provides access to ScanProjectConfig entities for a given
ScanProjectConfigID key for a dedicated project.
We currently store the following types of data through this mechanism:
-
Mock configuration
-
False positive configuration false positive configuration
-
Project access level
You can look into ScanProjectConfigID and check call hierarchy to get more details.
|
12. API
12.1. Rest API documentation
The complete documentation about REST API is generated. If you want to change content, please search for
@UseCaseRestDoc references in source code and make necessary changes inside code!
|
12.1.1. Overview
12.1.1.1. Anonymous
All these usecases handling anonymous access.
12.1.1.2. User administration
Usecases handling administration of users
-
REST API for UC_016-Admin or owner unassigns user from project
-
REST API for UC_026-Admin downloads all details about a scan job
-
REST API for UC_028-Admin revokes admin rights from an admin
-
REST API for UC_060-Admin or owner changes owner of a project
-
REST API for UC_072-Admin shows user details for email address
12.1.1.3. Project administration
Usecases for project administration
12.1.1.4. User self service
User actions belonging to their user identity
12.1.1.5. Sechub execution
Execution of SecHub -either by CLI or direct with REST api call
12.1.1.6. Sign up
All these usecases are handling user sign up (part of user self registration process)
12.1.1.7. Job administration
Usecases about job administration
12.1.1.8. Testing
Some use cases for testing
12.1.1.9. Configuration
Usecases for configuration parts
-
REST API for UC_049-Admin fetches executor configuration list
-
REST API for UC_051-Admin updates executor configuration setup
-
REST API for UC_057-Admin assigns execution profile to project
-
REST API for UC_058-Admin unassigns execution profile from project
-
REST API for UC_064-Admin fetches auto cleanup configuration
-
REST API for UC_065-Admin updates auto cleanup configuration
12.1.1.10. Encryption
Usecases for encryption parts
12.1.1.11. Other
All other use cases
12.1.2. Check if the server is alive and running.
REST API for usecase UC_039-Check if the server is alive and running.
12.1.2.1. HEAD variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/anonymous/check/alive |
Method |
HEAD |
Status code |
200 OK |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/anonymous/check/alive' -i -X HEADResponse body
(empty)
12.1.2.2. GET variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/anonymous/check/alive |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/anonymous/check/alive' -i -X GETResponse body
(empty)
12.1.3. Admin lists all users
REST API for usecase UC_004-Admin lists all users
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/users |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
List of user Ids |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/users' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GETResponse body
["user1","user2","admin1"]12.1.4. Admin or owner assigns user to project
REST API for usecase UC_015-Admin or owner assigns user to project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/management/project/{projectId}/membership/{userId} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
The user id of the user to assign to project |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/management/project/projectId1/membership/userId1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.5. Admin or owner unassigns user from project
REST API for usecase UC_016-Admin or owner unassigns user from project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/management/project/{projectId}/membership/{userId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
The user id of the user to unassign from project |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/management/project/userId1/membership/projectId1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETE \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.6. Admin shows user details
REST API for usecase UC_017-Admin shows user details
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/user/{userId} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user id of user to show details for |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The name of the user |
|
|
The email address of the user |
|
|
True, when this user is a super administrator |
|
|
The projects the user has access to |
|
|
The projects the user is owner of |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/user/user1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GETResponse body
{"userId":"user1","email":"user1@example.org","superAdmin":false,"projects":["project1"],"ownedProjects":[]}12.1.7. Admin deletes a user
REST API for usecase UC_018-Admin deletes a user
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/user/{userId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The userId of the user who shall be deleted |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/user/USER_ID' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETEResponse body
(empty)
12.1.8. Admin shows project details
REST API for usecase UC_021-Admin shows project details
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project/{projectId} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id to show details for |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The name of the project |
|
|
A list of all users having access to the project |
|
|
Username of the owner of this project. An owner is the person in charge. |
|
|
A list of all whitelisted URIs. Only these ones can be scanned for the project! |
|
|
A list of all templates assigned to the project |
|
|
An JSON object containing metadata key-value pairs defined for this project. |
|
|
An arbitrary metadata key |
|
|
The project access level |
|
|
The project description. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project/projectId1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"projectId":"projectId1","users":["name1","name2"],"templateIds":[],"metaData":{"key1":"value1"},"owner":"name1","description":"description","accessLevel":"full","whiteList":["http://www.sechub.example.org","http://www.sechub.example.com"]}12.1.9. Admin downloads all details about a scan job
REST API for usecase UC_026-Admin downloads all details about a scan job
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/scan/download/{jobUUID} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The job UUID |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/scan/download/06ab1d77-a8a2-4dc4-9beb-04e421ea396c' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'12.1.10. Admin grants admin rights to user
REST API for usecase UC_027-Admin grants admin rights to user
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/user/{userId}/grant/superadmin |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The userId of the user who becomes admin |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/user/USER_ID/grant/superadmin' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POSTResponse body
(empty)
12.1.11. Admin revokes admin rights from an admin
REST API for usecase UC_028-Admin revokes admin rights from an admin
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/user/{userId}/revoke/superadmin |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The userId of the user who becomes admin |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/user/USER_ID/revoke/superadmin' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POSTResponse body
(empty)
12.1.12. Admin lists all admins
REST API for usecase UC_029-Admin lists all admins
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/admins |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
List of admin Ids |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/admins' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GETResponse body
["admin1","admin2"]12.1.13. Admin or owner changes owner of a project
REST API for usecase UC_060-Admin or owner changes owner of a project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/management/project/{projectId}/owner/{userId} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
The user id of the user to assign to project as the owner |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/management/project/projectId1/owner/userId1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.14. Admin updates user email address
REST API for usecase UC_063-Admin updates user email address
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/user/{userId}/email/{emailAddress} |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The userId of the user whose email address will be changed |
|
The new email address |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/user/USER_ID/email/EMAIL_ADDRESS' -i -u 'user:secret' -X PUTResponse body
(empty)
12.1.15. Admin shows user details for email address
REST API for usecase UC_072-Admin shows user details for email address
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/user-by-email/{emailAddress} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The email address of user to show details for |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Basic authentication credentials |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The name of the user |
|
|
The mail address of the user |
|
|
True, when this user is a super administrator |
|
|
The projects the user has access to |
|
|
The projects the user is owner of |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/user-by-email/user1@example.org' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GETResponse body
{"userId":"user1","email":"user1@example.org","superAdmin":false,"projects":["project1"],"ownedProjects":[]}12.1.16. Admin creates a project
REST API for usecase UC_013-Admin creates a project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
201 CREATED |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Name of the project to create. Is also used as a unique ID! |
|
|
The description of the project. |
|
|
Username of the owner of this project. An owner is the person in charge |
|
|
All URIs used now for whitelisting. Former parts will be replaced completely! |
|
|
An JSON object containing metadata key-value pairs defined for this project |
|
|
An arbitrary metadata key-value pair |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"apiVersion":"1.0", "name":"projectId", "description":"A description of the project.", "owner":"ownerName1", "whiteList":{"uris":["192.168.1.1","https://my.special.server.com/myapp1/"]}, "metaData":{"key1":"value1", "key2":"value2"}}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.17. Admin lists all projects
REST API for usecase UC_014-Admin lists all projects
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/projects |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
List of project Ids |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/projects' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
["project1","project2"]12.1.18. Admin deletes a project
REST API for usecase UC_020-Admin deletes a project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project/{projectId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id to delete |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project/projectId1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETE \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.19. Update project whitelist
REST API for usecase UC_022-Update project whitelist
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project/{projectId}/whitelist |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The id of the project for which whitelist shall be updated |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
All URIS used now for whitelisting. Former parts will be replaced completely! |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project/projectId1/whitelist' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"apiVersion":"1.0", "whiteList":{"uris":["192.168.1.1","https://my.special.server.com/myapp1/"]}}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.20. Admin shows scan logs for project
REST API for usecase UC_025-Admin shows scan logs for project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project/{projectId}/scan/logs |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project Id |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
An array of scan log summary entries |
|
|
The user id of the user which executed the scan |
|
|
The timestamp when the scan was started |
|
|
The timestamp when the scan was ended |
|
|
A status field about scan situation |
|
|
The uuid of corresponding sechub Job. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project/project1/scan/logs' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
[{"sechubJobUUID":"16713175-97ae-431d-97ac-cbfcdfdfb914","executedBy":"spartakus","started":"2025-08-31T14:50:14.824693193","ended":"2025-09-01T14:50:14.824735482","status":"OK"}]12.1.21. Update project metadata
REST API for usecase UC_059-Update project metadata
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project/{projectId}/metadata |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The id of the project for which metadata shall be updated |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Metadata object. Contains key-value pairs. |
|
|
An arbitrary metadata key. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project/projectId1/metadata' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"apiVersion":"1.0", "metaData":{"key1":"value1"}}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.22. Admin changes project description
REST API for usecase UC_061-Admin changes project description
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project/{projectId} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id to change details for |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The name of the project. |
|
|
A list of all users having access to the project. |
|
|
Username of the owner of this project. An owner is the person in charge. |
|
|
A list of all whitelisted URIs. Only these ones can be scanned for the project! |
|
|
A list of all templates assigned to the project |
|
|
An JSON object containing metadata key-value pairs defined for this project. |
|
|
An arbitrary metadata key |
|
|
The project access level |
|
|
The project access level |
|
|
The project description. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project/projectId1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{
"description" : "new description"
}'Response body
{"projectId":"projectId1","users":["name1","name2"],"templateIds":[],"metaData":{"key1":"value1"},"owner":"name1","description":"description","accessLevel":"full","whiteList":["http://www.sechub.example.org"]}12.1.23. Admin changes project access level
REST API for usecase UC_062-Admin changes project access level
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project/{projectId}/accesslevel/{projectAccessLevel} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
The new project access level. Accepted values: full(Full access to project, no restrictions), read_only(Users have only read access to existing data, No new jobs possible), none(Users have no access at all.) |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project/projectId1/accesslevel/read_only' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.24. get assigned project data
REST API for usecase UC_081-get assigned project data
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/projects |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Project ID |
|
|
Owner of the Project |
|
|
Name of owner |
|
|
Email address of owner |
|
|
If caller is owner of the project |
|
|
Optional: Assigned users (only viewable by owner or admin) |
|
|
Name of assigned user |
|
|
Email address of assigned user |
|
|
List of profile IDs assigned to the project. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/projects' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
[{"projectId":"project1","owner":{"userId":"user1","emailAddress":"user1@example.org"},"assignedUsers":[{"userId":"user1","emailAddress":"user1@example.org"},{"userId":"user2","emailAddress":"user2@example.org"}],"enabledProfileIds":["profile1","profile2"],"isOwned":true}]12.1.25. User fetches his user details
REST API for usecase UC_095-User fetches his user details
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/management/user |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/management/user' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GETResponse body
(empty)
12.1.26. User updates his own email address
REST API for usecase UC_097-User updates his own email address
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/management/user/email/{emailAddress} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
204 NO_CONTENT |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/management/user/email/new.user1@email.com' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POSTResponse body
(empty)
12.1.27. Anonymous user verifies new email address
REST API for usecase UC_098-Anonymous user verifies new email address
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/anonymous/email/verify/{oneTimeToken} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
204 NO_CONTENT |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/anonymous/email/verify/token1' -i -X GETResponse body
(empty)
12.1.28. User requests finding explanation
REST API for usecase UC_099-User requests finding explanation
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/assistant/explanation/project/{projectId}/job/{jobUUID}/finding/{findingId} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The projectId of the project the job of the finding the user requests a explanation |
|
The jobUUID of the job of the finding the user requests a explanation |
|
The findingId of the finding the user requests a explanation |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The explanation of the security finding |
|
|
The title of the explanation section |
|
|
The text content of the explanation section |
|
|
The potential impact of the security finding |
|
|
The title of the potential impact section |
|
|
The text content of the potential impact section |
|
|
A list of recommendations on how to handle the security finding |
|
|
The title of a recommendation on how to handle the security finding |
|
|
The content of a recommendation on how to handle the security finding |
|
|
Vulnerable and secure code snippets of the security finding with an explanation |
|
|
Vulnerable code snippet of the security finding |
|
|
Secure code snippet of the security finding |
|
|
Explanation of the code snippet related to the security finding |
|
|
The title of the explanation of the code snippet related to the security finding |
|
|
The content of the explanation of the code snippet related to the security finding |
|
|
References for further reading on the security finding |
|
|
The title of the reference for the security finding |
|
|
The URL of the reference for the security finding |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/assistant/explanation/project/project1/job/f1d02a9d-5e1b-4f52-99e5-401854ccf936/finding/42' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GETResponse body
{"findingExplanation":{"title":"Absolute Path Traversal Vulnerability","content":"This finding indicates an 'Absolute Path Traversal' vulnerability in the `AsciidocGenerator.java` file. The application constructs a file path using user-supplied input (`args[0]`) without proper validation. An attacker could provide an absolute path (e.g., `/etc/passwd` on Linux or `C:\\Windows\\System32\\drivers\\etc\\hosts` on Windows) as input, allowing them to access arbitrary files on the system, potentially bypassing intended security restrictions [3, 7]."},"potentialImpact":{"title":"Potential Impact","content":"If exploited, this vulnerability could allow an attacker to read sensitive files on the server, including configuration files, source code, or even password files. This could lead to information disclosure, privilege escalation, or other malicious activities [1, 5]."},"recommendations":[{"title":"Validate and Sanitize User Input","content":"Always validate and sanitize user-supplied input before using it to construct file paths. In this case, ensure that the `path` variable does not contain an absolute path. You can check if the path starts with a drive letter (e.g., `C:\\`) on Windows or a forward slash (`/`) on Unix-like systems [1]."},{"title":"Use Relative Paths and a Base Directory","content":"Instead of allowing absolute paths, restrict user input to relative paths within a designated base directory. Construct the full file path by combining the base directory with the user-provided relative path. This limits the attacker's ability to access files outside the intended directory [1]."},{"title":"Normalize the Path","content":"Normalize the constructed file path to remove any directory traversal sequences (e.g., `../`). This can be achieved using the `java.nio.file.Path.normalize()` method. After normalization, verify that the path still resides within the allowed base directory [1, 6]."}],"codeExample":{"vulnerableExample":"public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {\n String path = args[0];\n File documentsGenFolder = new File(path);\n //Potentially dangerous operation with documentsGenFolder\n}","secureExample":"public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {\n String basePath = \"/safe/base/directory\";\n String userPath = args[0];\n\n // Validate that userPath is not an absolute path\n if (new File(userPath).isAbsolute()) {\n System.err.println(\"Error: Absolute paths are not allowed.\");\n return;\n }\n\n Path combinedPath = Paths.get(basePath, userPath).normalize();\n\n // Ensure the combined path is still within the base directory\n if (!combinedPath.startsWith(basePath)) {\n System.err.println(\"Error: Path traversal detected.\");\n return;\n }\n\n File documentsGenFolder = combinedPath.toFile();\n //Safe operation with documentsGenFolder\n}","explanation":{"title":"Code Example Explanation","content":"The vulnerable example directly uses user-provided input to create a `File` object, allowing an attacker to specify an arbitrary file path. The secure example first defines a base directory and combines it with the user-provided path using `Paths.get()`. It then normalizes the path and verifies that it remains within the base directory before creating the `File` object. This prevents path traversal attacks by ensuring that the application only accesses files within the intended directory [2, 6]."}},"references":[{"title":"OWASP Path Traversal","url":"https://owasp.org/www-community/attacks/Path_Traversal"},{"title":"CWE-22: Improper Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory ('Path Traversal')","url":"https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/22.html"},{"title":"Snyk Path Traversal","url":"https://snyk.io/learn/path-traversal/"}]}12.1.29. User creates a new sechub job
REST API for usecase UC_005-User creates a new sechub job
12.1.29.1. Code Scan variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Code scan configuration block |
|
|
Referenced data configuration objects by their unique names |
|
|
Code scan sources from given file system folders |
|
|
Code scan sources from given file system files |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"codeScan":{"fileSystem":{"files":[],"folders":["testproject1/src/main/java","testproject2/src/main/java"]},"use":[]},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"b9435416-727a-4e00-abba-d919f91eb790"}12.1.29.2. Code Scan using data section variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Code scan configuration block |
|
|
Referenced data configuration objects by their unique names |
|
|
Unique reference name |
|
|
Sources from given file system folders |
|
|
Sources from given file system files |
|
|
Unique reference name |
|
|
Binaries from given file system folders |
|
|
Binaries from given file system files |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"codeScan":{"use":["source-ref-name","bin-ref-name"]},"data":{"sources":[{"fileSystem":{"files":["testproject1/src/other/example/php-example.php"],"folders":["testproject1/src/main/java","testproject2/src/main/java"]},"name":"source-ref-name"}],"binaries":[{"fileSystem":{"files":["testproject1/build/other/native.dll"],"folders":["testproject1/build/kotlin","testproject1/build/kotlin"]},"name":"bin-ref-name"}]},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"0b5b1bf9-c024-41f6-8582-125d87ac3ea4"}12.1.29.3. Secret scan variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Secret scan configuration block |
|
|
Referenced data configuration objects by their unique names |
|
|
Unique reference name |
|
|
Unique reference name |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"data":{"sources":[{"name":"source-ref-name"}],"binaries":[{"name":"bin-ref-name"}]},"secretScan":{"use":["source-ref-name","bin-ref-name"]},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"476b3c00-3340-43b8-bb67-9f1bff8b53b8"}12.1.29.4. License scan variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
License scan configuration block |
|
|
Referenced data configuration objects by their unique names |
|
|
Unique reference name |
|
|
Unique reference name |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"data":{"sources":[{"name":"source-ref-name"}],"binaries":[{"name":"bin-ref-name"}]},"licenseScan":{"use":["source-ref-name","bin-ref-name"]},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"bb25c4e5-0d34-40c1-8004-be5a2f2dd13f"}12.1.29.5. Infrastructure scan variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Infrastructure configuration block |
|
|
Infrastructure URIs to scan for |
|
|
Infrastructure IPs to scan for |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"infraScan":{"uris":["https://localhost"],"ips":["127.0.0.1"]},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"cb63e588-936a-4aaa-b8b0-39fd6f6d874d"}12.1.29.6. Web scan anonymous variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Webscan configuration block |
|
|
Webscan URI to scan for |
|
|
Duration of the scan as integer |
|
|
Unit of the duration. Possible values are: millisecond(s), second(s), minute(s), hour(s), day(s) |
|
|
Include URL sub-paths to scan. Example: /hidden |
|
|
Exclude URL sub-paths to scan. Example: /admin |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"webScan":{"maxScanDuration":{"duration":1,"unit":"HOUR"},"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp/login","includes":["/admin","/hidden","/admin.html"],"excludes":["/public/media","/static","/contaxt.html"]},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"3edc710e-b3ff-4ab0-a7f7-3ef60df9b374"}12.1.29.7. Web scan with api definition variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Webscan configuration block |
|
|
Webscan URI to scan for |
|
|
Type of the API definition files that will be provided |
|
|
Reference to the data section containing the API definition files. Always use 'sources' with 'files' instead 'folders'. |
|
|
Specifies an URL to read the API definition from. |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"webScan":{"api":{"type":"OPEN_API","apiDefinitionUrl":"https://www.example.org/api/v1/swagger/","use":["openApi-file-reference"]},"url":"https://www.example.org/"},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"e298db69-0609-4276-b70e-c20d73df63d5"}12.1.29.8. Web scan with client certificate definition variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Webscan configuration block |
|
|
Webscan URI to scan for |
|
|
Password the client certificate file is protected with |
|
|
Reference to the data section containing the client certificate definition file. Always use 'sources' with a single 'file' instead 'folders'. |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"webScan":{"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp","clientCertificate":{"password":"example-cert-password","use":["client-certificate-file-reference"]}},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"e21a3661-cb19-4aa8-8c56-765bb6d788a4"}12.1.29.9. Web Scan login basic variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Webscan configuration block |
|
|
Webscan URI to scan for |
|
|
Webscan login definition |
|
|
Login URL |
|
|
basic login definition |
|
|
username |
|
|
password |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"webScan":{"login":{"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp/login","basic":{"user":"username1","password":"password1"}},"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp"},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"a22a6bc4-4475-4cd7-b412-ff7e437ef6d5"}12.1.29.10. Web Scan login form scripted variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Webscan configuration block |
|
|
Webscan URI to scan for |
|
|
Webscan login definition |
|
|
Optional TOTP configuration as an additional authentication factor. |
|
|
The seed/secret for the TOTP generation. If TOTP is configured this parameter is mandatory. |
|
|
The time in seconds the generated TOTP is valid. In most cases nothing is specified and the default of '30' seconds is used. |
|
|
The length of the generated TOTP. In most cases nothing is specified and the default length '6' is used. |
|
|
The hash algorithm to generate the TOTP. In most cases nothing is specified and the default hash algorithm 'HMAC_SHA1' is used. Currently available values are: 'HMAC_SHA1', 'HMAC_SHA256', 'HMAC_SHA512' |
|
|
The encoding type of the 'seed'. The default value is 'AUTODETECT'. Currently available values are: 'BASE64', 'BASE32', 'HEX', 'PLAIN', 'AUTODETECT' |
|
|
Login URL |
|
|
form login definition |
|
|
script |
|
|
action type: username, password, input, click, wait |
|
|
css selector |
|
|
value |
|
|
description |
|
|
the time unit to wait: millisecond, second, minute, hour, day. |
|
|
Webscan 'logout' section to avoid logout for webscans of a frontend. |
|
|
xpathto locate the element to avoid on the frontend. |
|
|
'htmlElement' to locate the element to avoid on the frontend. |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"webScan":{"login":{"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp/login","form":{"script":{"pages":[{"actions":[{"type":"USERNAME","selector":"#example_login_userid","value":"username1","description":"the username field"},{"type":"INPUT","selector":"#example_login_email_id","value":"user@example.com","description":"The email id field."}]},{"actions":[{"type":"WAIT","value":"2345","unit":"MILLISECOND"},{"type":"PASSWORD","selector":"#example_login_pwd","value":"Super$ecret234!"},{"type":"CLICK","selector":"#example_login_button"}]}]}},"totp":{"seed":"example-seed","validityInSeconds":30,"tokenLength":6,"hashAlgorithm":"HMAC_SHA1","encodingType":"BASE32"}},"logout":{"xpath":"/html/body/div","htmlElement":"div"},"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp"},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"f3a524a7-1fb3-44d1-a6a5-984318b7ff44"}12.1.29.11. Web Scan login basic with login verification variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Webscan configuration block |
|
|
Webscan URI to scan for |
|
|
Webscan login definition |
|
|
Login URL |
|
|
login verification definition |
|
|
Verification URL |
|
|
Expected HTTP status code |
|
|
basic login definition |
|
|
username |
|
|
password |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"webScan":{"login":{"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp/login","basic":{"user":"username1","password":"password1"},"verification":{"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp/verification","responseCode":204}},"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp"},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"1ec9b501-5c2f-440e-a9a2-22bf59f4dd07"}12.1.29.12. Web Scan headers variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique id of the project id where a new sechub job shall be created |
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Webscan configuration block |
|
|
Webscan URI to scan for |
|
|
List of HTTP headers. Can be used for authentication or anything else. |
|
|
Name of the defined HTTP header. |
|
|
Value of the defined HTTP header. Either specify the header value directly here or reference a data section with 'use' e.g. if the value is to big, but never specify both. |
|
|
Reference to the data section containing a file with the value for this header, e.g if the value is to big for the sechub configuration. Always use 'sources' with a single 'file' instead 'folders'. |
|
|
Optional list of URLs this header shall be used for like: https://mywebapp.com/path/. Can contain wildcards like: https://mywebapp.com/path/<*>/with/wildcard |
|
|
Defines header masking. If 'true' the header value will be replaced with '**' inside the report, 'false' will show the value as is. Default is set to 'true'. |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique job id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"webScan":{"url":"https://localhost/mywebapp","headers":[{"name":"api-token","value":"secret","onlyForUrls":["https://localhost/mywebapp/admin","https://localhost/mywebapp/<*>/profile","https://localhost/mywebapp/blog/<*>"],"sensitive":true,"use":["header-value-file-ref-for-big-tokens"]}]},"apiVersion":"1.0"}'Response body
{"jobId":"cb69cc33-d2bb-4476-bf9d-dda750ce71df"}12.1.30. User uploads source code
REST API for usecase UC_006-User uploads source code
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job/{jobUUID}/sourcecode |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The id of the project where sourcecode shall be uploaded for |
|
The SecHub jobUUID. During the job creation this unique job identifier is automatically generated by SecHub. |
Query parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
A sha256 checksum for file upload validation |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job/f8d5f0dc-7310-4346-85c0-7deb676cd20d/sourcecode?checkSum=checkSumValue' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: multipart/form-data;charset=UTF-8' \
-F 'file=PK
�<M test1.txtPK ?
�<M $ test1.txt
��IW� ��IW� ��IW� PK [ ' 'Response body
(empty)
12.1.31. User approves sechub job
REST API for usecase UC_007-User approves sechub job
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job/{jobUUID}/approve |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The id of the project where sechub job shall be approved |
|
The SecHub jobUUID. During the job creation this unique job identifier is automatically generated by SecHub. |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job/194fdb53-bb82-41e7-85bf-dbc683238425/approve' -i -X PUT \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.32. User checks sechub job state
REST API for usecase UC_009-User checks sechub job state
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job/{jobUUID} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The id of the project where sechub job was started for |
|
The SecHub jobUUID. During the job creation this unique job identifier is automatically generated by SecHub. |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The job uuid |
|
|
Creation timestamp of job |
|
|
Start timestamp of job execution |
|
|
End timestamp of job execution |
|
|
Owner / initiator of job |
|
|
State of job |
|
|
Result of job |
|
|
Trafficlight of job - but only available when job has been done. Possible states are GREEN, YELLOW, RED, OFF |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job/fa874268-87e6-438e-9dbf-8ca76c138d3d' -i -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"jobUUID":"fa874268-87e6-438e-9dbf-8ca76c138d3d","owner":"CREATOR1","created":"","started":"2025-09-01T14:35:10.218841474","ended":"2025-09-01T14:50:10.218871951","state":"ENDED","result":"OK","trafficLight":"GREEN"}12.1.33. User downloads sechub job report
REST API for usecase UC_010-User downloads sechub job report
12.1.33.1. JSON variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/report/{jobUUID} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project Id |
|
The job UUID |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/report/b290da61-6563-428a-89d8-c1099ce2d65f' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'12.1.33.2. HTML variant
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/report/{jobUUID} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project Id |
|
The job UUID |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/report/9fc90c10-1f59-4799-9cf7-b3a48d2071b0' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-H 'Accept: application/xhtml+xml'12.1.34. User marks false positives
REST API for usecase UC_044-User marks false positives
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/false-positives |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The projectId of the project where users adds false positives for |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
The type of the json content. Currently only accepted value is 'falsePositiveDataList' but we also still accept the deprecated type 'falsePositiveJobDataList'. |
|
|
Job data list containing false positive setup based on former jobs |
|
|
SecHub job uuid where finding was |
|
|
SecHub finding identifier - identifies problem inside the job which shall be markeda as a false positive. |
|
|
A comment describing why this is a false positive |
|
|
Project data list containing false positive setup for the project |
|
|
Identifier which is used to update or remove the respective false positive entry. |
|
|
A comment describing why this is a false positive. |
|
|
Defines a section for false positives which occur during webscans. |
|
|
Defines a url pattern for false positives which occur during webscans. Can be used with wildcards like '.host.com'. Each entry must contain more than just wildcards, '..' or '*' are not allowed. |
|
|
Defines a list of (HTTP) methods for false positives which occur during webscans. This is optional and if nothing is specified, the entry applies to all methods. |
|
|
Defines a CWE ID for false positives which occur during webscans. This is mandatory, but can be empty. If it is not specified it matches the findings with no CWE IDs. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/false-positives' -i -u 'user:secret' -X PUT \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"apiVersion":"1.0","type":"falsePositiveDataList","jobData":[{"jobUUID":"f1d02a9d-5e1b-4f52-99e5-401854ccf936","findingId":42,"comment":"an optional comment why this is a false positive..."}],"projectData":[{"id":"unique-identifier","webScan":{"cweId":564,"urlPattern":"https://*.example.com/api/*/search","methods":["GET","POST"]},"comment":"an optional comment for this false positive project entry"}]}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.35. User unmarks existing false positive definitons
REST API for usecase UC_045-User unmarks existing false positive definitons
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/false-positive/{jobUUID}/{findingId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
Job uuid |
|
Finding id - in combination with job UUID this defines the false positive to remove |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/false-positive/f1d02a9d-5e1b-4f52-99e5-401854ccf936/42' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETEResponse body
(empty)
12.1.36. User fetches false positive configuration of project
REST API for usecase UC_046-User fetches false positive configuration of project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/false-positives |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Job data list containing false positive setup based on former jobs |
|
|
User id of author who created false positive |
|
|
Creation timestamp |
|
|
Meta data for this false positive |
|
|
Scan type - e.g. codeScan |
|
|
Name of origin finding marked as false positive |
|
|
CWE (common weakness enumeration). For code scans this is always set. |
|
|
CVE (common vulnerability and exposures). For infra scans this is always set. |
|
|
OWASP At least this field must be set for web scans when no cwe identifier is defined. |
|
|
Severity of origin report entry marked as false positive |
|
|
Code part. Only available for scan type 'codeScan' |
|
|
entry point |
|
|
location of code |
|
|
relevant part of source vulnerability |
|
|
source code |
|
|
end point (sink) |
|
|
location of code |
|
|
relevant part of source vulnerability |
|
|
source code |
|
|
Job data parts, can be used as key to identify false positives |
|
|
SecHub job uuid where finding was |
|
|
SecHub finding identifier - identifies problem inside the job which shall be markeda as a false positive. ATTENTION: at the moment only code scan false positive handling is supported. Infra and web scan findings will lead to a non accepted error! |
|
|
A comment from author describing why this was marked as a false positive |
|
|
Project data list containing false positive setup for the project. |
|
|
Identifier which is used to update or remove the respective false positive entry. |
|
|
A comment describing why this is a false positive. |
|
|
Defines a section for false positives which occur during webscans. |
|
|
Defines a url pattern for false positives which occur during webscans. Can be used with wildcards like '.host.com'. Each entry must contain more than just wildcards, '..' or '*' are not allowed. |
|
|
Defines a list of (HTTP) methods for false positives which occur during webscans. This is optional and if nothing is specified, the entry applies to all methods. |
|
|
Defines a CWE ID for false positives which occur during webscans. This is mandatory, but can be empty. If it is not specified it matches the findings with no CWE IDs. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/false-positives' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GETResponse body
{"falsePositives":[{"jobData":{"jobUUID":"f1d02a9d-5e1b-4f52-99e5-401854ccf936","findingId":42,"comment":"Only used in documentation build not in deployment"},"author":"developer1","metaData":{"scanType":"codeScan","name":"Absolute Path Traversal","severity":"MEDIUM","code":{"start":{"location":"java/com/mercedesbenz/sechub/docgen/AsciidocGenerator.java","relevantPart":"args","sourceCode":"\tpublic static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {"},"end":{"location":"java/com/mercedesbenz/sechub/docgen/AsciidocGenerator.java","relevantPart":"File","sourceCode":"\t\tFile documentsGenFolder = new File(path);"}},"cweId":36},"projectData":{"id":"unique-identifier","webScan":{"cweId":564,"urlPattern":"https://*.example.com/api/*/search","methods":["GET","POST"]},"comment":"an optional comment for this false positive project entry"},"created":"2020-06-12 11:53:15"}]}12.1.37. User uploads binaries
REST API for usecase UC_069-User uploads binaries
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/job/{jobUUID}/binaries |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The id of the project for which the binaries are uploaded for |
|
The SecHub jobUUID. During the job creation this unique job identifier is automatically generated by SecHub. |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
The file size of the tar-archive to upload in bytes. Needs to be a positive integer value. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/job/31e62318-68f4-471b-bf3c-dcd5b6b509e0/binaries' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: multipart/form-data;charset=UTF-8' \
-H 'x-file-size: 10240' \
-F 'file=test1.txt 0000664 0001750 0001750 00000000000 13353454574 012170 0 ustar albert albert ' \
-F 'checkSum=checkSumValue'Response body
(empty)
12.1.38. User downloads job report in SPDX format
REST API for usecase UC_070-User downloads job report in SPDX format
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/report/spdx/{jobUUID} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project Id |
|
The job UUID |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/report/spdx/48e9ce2c-455b-42c4-83dc-a5c23234770d' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'12.1.39. User unmarks existing false positive project data definitons
REST API for usecase UC_078-User unmarks existing false positive project data definitons
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/false-positive/project-data/{id} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
204 NO_CONTENT |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
Identifier which is used to remove the respective false positive entry. |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/false-positive/project-data/unique-identifier' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETEResponse body
(empty)
12.1.40. User self registration
REST API for usecase UC_001-User self registration
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/anonymous/signup |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The api version, currently only 1.0 is supported |
|
|
Wanted userid, the userid must be lowercase only! |
|
|
Email address |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/anonymous/signup' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"apiVersion":"1.0","userId":"valid_userid","emailAddress":"valid_mailaddress@example.org"}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.41. Admin lists open user signups
REST API for usecase UC_002-Admin lists open user signups
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/signups |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
List of user signups |
|
|
The user id |
|
|
The email address |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/signups' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GETResponse body
[{"userId":"johnsmith","emailAddress":"john.smith@example.com"},{"userId":"janesmith","emailAddress":"jane.smith@example.com"}]12.1.42. Admin applies self registration
REST API for usecase UC_003-Admin applies self registration
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/signup/accept/{userId} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
201 CREATED |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The userId of the signup which shall be accepted |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/signup/accept/user1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POSTResponse body
(empty)
12.1.43. User clicks link to get new api token
REST API for usecase UC_012-User clicks link to get new api token
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/anonymous/apitoken/{oneTimeToken} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
A one time token the user has got by a previous mail from sechub server |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/anonymous/apitoken/oneTimeToken1' -i -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.44. Admin deletes user signup
REST API for usecase UC_019-Admin deletes user signup
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/signup/{userId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The userId of the signup which shall be deleted |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/signup/userId1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETEResponse body
(empty)
12.1.45. User requests new API token
REST API for usecase UC_024-User requests new API token
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/anonymous/refresh/apitoken/{emailAddress} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Email address for user where api token shall be refreshed. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/anonymous/refresh/apitoken/emailAddress@example.com' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.46. Admin lists all running jobs
REST API for usecase UC_023-Admin lists all running jobs
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/jobs/running |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The uuid of the running job |
|
|
The name of the project the job is running for |
|
|
Owner of the job - means user which triggered it |
|
|
A status information |
|
|
Timestamp since when job has been started |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/jobs/running' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
[{"jobUUID":"16cd6158-6735-434b-aaeb-6b2b8111dfb2","projectId":"project-name","owner":"owner-userid","status":"RUNNING","since":"2025-09-01T14:50:19.761025912"}]12.1.47. Admin cancels a job
REST API for usecase UC_034-Admin cancels a job
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/jobs/cancel/{jobUUID} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The job UUID |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/jobs/cancel/af0d72be-6600-4062-8b92-9277b169d0d6' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.48. Admin restarts a job
REST API for usecase UC_041-Admin restarts a job
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/jobs/restart/{jobUUID} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The job UUID |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/jobs/restart/d410be42-bf83-43ab-ac7d-8f4249c68c03' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.49. Admin restarts a job (hard)
REST API for usecase UC_042-Admin restarts a job (hard)
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/jobs/restart-hard/{jobUUID} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The job UUID |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/jobs/restart-hard/e4371737-4cb3-46e4-8342-0e8d3a4b4cac' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.50. User cancels a job
REST API for usecase UC_094-User cancels a job
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/management/jobs/{jobUUID}/cancel |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
204 NO_CONTENT |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The job UUID |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/management/jobs/19d85a19-18d9-4c53-91fd-966c3098abae/cancel' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.51. User defines mock data configuration for project
REST API for usecase UC_035-User defines mock data configuration for project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/mockdata |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/mockdata' -i -u 'user:secret' -X PUT \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-d '{"codeScan":{"result":"RED"},"webScan":{"result":"YELLOW"},"infraScan":{"result":"GREEN"}}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.52. User retrieves mock data configuration for project
REST API for usecase UC_036-User retrieves mock data configuration for project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/mockdata |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/mockdata' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'Response body
{"codeScan":{"result":"RED"},"webScan":{"result":"YELLOW"},"infraScan":{"result":"GREEN"}}12.1.53. Admin updates mapping configuration
REST API for usecase UC_037-Admin updates mapping configuration
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/mapping/{mappingId} |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The mappingID, identifiying which mapping shall be updated |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Pattern |
|
|
Replacement |
|
|
Comment |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/mapping/checkmarx.newproject.teamid.mapping' -i -u 'user:secret' -X PUT \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"entries":[{"pattern":"testproject_*","replacement":"8be4e3d4-6b53-4636-b65a-949a9ebdf6b9","comment":"testproject-team"},{"pattern":".*","replacement":"3be4e3d2-2b55-2336-b65a-949b9ebdf6b9","comment":"default-team"}]}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.54. Admin fetches mapping configuration
REST API for usecase UC_038-Admin fetches mapping configuration
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/mapping/{mappingId} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The mapping Id |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Pattern |
|
|
Replacement |
|
|
Comment |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/mapping/checkmarx.newproject.teamid.mapping' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"entries":[{"pattern":"testproject_*","replacement":"8be4e3d4-6b53-4636-b65a-949a9ebdf6b9","comment":"testproject-team"},{"pattern":".*","replacement":"3be4e3d2-2b55-2336-b65a-949b9ebdf6b9","comment":"default-team"}]}12.1.55. Admin creates an executor configuration
REST API for usecase UC_047-Admin creates an executor configuration
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/executor |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
201 CREATED |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A name for this configuration |
|
|
Executor product identifier |
|
|
Executor version |
|
|
Enabled state of executor, per default false |
|
|
Base URL to the product |
|
|
User name, either plain (not recommended) or with env:VARIABLENAME, in last case the user name will be from environment variable |
|
|
Password, either plain (not recommended) or with env:VARIABLENAME, in last case the password will be from environment variable |
|
|
Job parameter key |
|
|
Job parameter value |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/executor' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"name":"PDS gosec configuration 1","productIdentifier":"PDS_CODESCAN","executorVersion":1,"enabled":false,"setup":{"baseURL":"https://productXYZ.example.com","credentials":{"user":"env:EXAMPLE_USENAME","password":"env:EXAMPLE_PASSWORD"},"jobParameters":[{"key":"example.key1","value":"A value"},{"key":"example.key2","value":"Another value"}]}}'Response body
cdf9a280-6541-4b48-82b6-1391cad018ee12.1.56. Admin deletes executor configuration
REST API for usecase UC_048-Admin deletes executor configuration
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/executor/{uuid} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The configuration uuid |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/executor/17cf8e18-9740-40a5-bb0e-98e93065b66e' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETE \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.57. Admin fetches executor configuration list
REST API for usecase UC_049-Admin fetches executor configuration list
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/executors |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Always |
|
|
The uuid of the configuration |
|
|
The configuration name |
|
|
Enabled state of configuration |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/executors' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"executorConfigurations":[{"uuid":"3533d143-4cac-4923-b57f-5a0e27b1fdbd","name":"example configuration","enabled":true}],"type":"executorConfigurationList"}12.1.58. Admin fetches executor configuration
REST API for usecase UC_050-Admin fetches executor configuration
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/executor/{uuid} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The configuration uuid |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The uuid of this configuration |
|
|
The name of this configuration |
|
|
Executor product identifier |
|
|
Executor version |
|
|
Enabled state of executor |
|
|
Base URL to the product |
|
|
User name, either plain (not recommended) or with env:VARIABLENAME, in last case the user name will be from environment variable |
|
|
Password, either plain (not recommended) or with env:VARIABLENAME, in last case the password will be from environment variable |
|
|
Job parameter key |
|
|
Job parameter value |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/executor/8b28f829-0226-4471-bd78-0998458a889f' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"uuid":"8b28f829-0226-4471-bd78-0998458a889f","name":"New name","productIdentifier":"PDS_CODESCAN","setup":{"baseURL":"https://product.example.com","credentials":{"user":"env:EXAMPLE_USENAME","password":"env:EXAMPLE_PASSWORD"},"jobParameters":[{"key":"example.key1","value":"A value"}]},"executorVersion":1,"enabled":false}12.1.59. Admin updates executor configuration setup
REST API for usecase UC_051-Admin updates executor configuration setup
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/executor/{uuid} |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The configuration uuid |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The name of this configuration |
|
|
Executor product identifier |
|
|
Executor version |
|
|
Enabled state of executor, per default false |
|
|
Base URL to the product |
|
|
User name, either plain (not recommended) or with env:VARIABLENAME, in last case the user name will be from environment variable |
|
|
Password, either plain (not recommended) or with env:VARIABLENAME, in last case the password will be from environment variable |
|
|
Job parameter key |
|
|
Job parameter value |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/executor/741e095b-3f0d-4abb-a906-78ab858ad6bb' -i -u 'user:secret' -X PUT \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"name":"New name","productIdentifier":"PDS_CODESCAN","executorVersion":1,"enabled":false,"setup":{"baseURL":"https://productNew.example.com","credentials":{"user":"env:EXAMPLE_NEW_USENAME","password":"env:EXAMPLE_NEW_PASSWORD"},"jobParameters":[{"key":"example.key1","value":"A value but changed. Remark: the other parameter (example.key2) has been removed by this call"}]}}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.60. Admin creates an execution profile
REST API for usecase UC_052-Admin creates an execution profile
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/execution/profile/{profileId} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
201 CREATED |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The profile id |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A short description for the profile |
|
|
Enabled state of profile, default is false |
|
|
Configurations can be linked at creation time as well - see update description |
|
|
Projects can be linked by their ids at creation time as well - see update description |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/execution/profile/new-profile-1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"description":"a short description for profile","configurations":[],"projectIds":[],"enabled":false}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.61. Admin deletes execution profile
REST API for usecase UC_053-Admin deletes execution profile
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/execution/profile/{profileId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The profile id |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/execution/profile/profile-to-delete-1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETE \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.62. Admin updates execution profile
REST API for usecase UC_054-Admin updates execution profile
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/execution/profile/{profileId} |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The profile id |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A short description for the profile |
|
|
Enabled state of profile, default is false |
|
|
Add uuid for configuration to use here |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/execution/profile/existing-profile-1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X PUT \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"description":"changed description","configurations":[{"uuid":"21de7e85-4772-4901-b317-63d0eccb2da9","executorVersion":0,"enabled":false,"setup":{"credentials":{},"jobParameters":[]}}],"enabled":true}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.63. Admin fetches execution profile
REST API for usecase UC_055-Admin fetches execution profile
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/execution/profile/{profileId} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The profile id |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A short description for the profile |
|
|
Enabled state of profile, default is false |
|
|
uuid of configuration |
|
|
name of configuration |
|
|
enabled state of this configuration |
|
|
executed product |
|
|
executor version |
|
|
Projects can be linked by their ids here |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/execution/profile/existing-profile-1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"description":"a description","enabled":true,"configurations":[{"uuid":"45f38123-c576-48ef-901b-14c1d7dee527","name":"New name","productIdentifier":"PDS_CODESCAN","setup":{"baseURL":"https://product.example.com","credentials":{"user":"env:EXAMPLE_USENAME","password":"env:EXAMPLE_PASSWORD"},"jobParameters":[{"key":"example.key1","value":"A value but changed. Remark: the other parameter (example.key2) has been removed by this call"}]},"executorVersion":1,"enabled":false}],"projectIds":["project-1","project-2"]}12.1.64. Admin fetches execution profile list
REST API for usecase UC_056-Admin fetches execution profile list
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/execution/profiles |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Always |
|
|
The profile id |
|
|
A profile description |
|
|
Enabled state of profile |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/execution/profiles' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"executionProfiles":[{"id":"profile1","description":"A short decription for profile1","enabled":false},{"id":"profile2","description":"A short decription for profile2","enabled":false}],"type":"executionProfileList"}12.1.65. Admin assigns execution profile to project
REST API for usecase UC_057-Admin assigns execution profile to project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/execution/profile/{profileId}/project/{projectId} |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
201 CREATED |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
The profile id |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/execution/profile/profile-1/project/project-1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.66. Admin unassigns execution profile from project
REST API for usecase UC_058-Admin unassigns execution profile from project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/execution/profile/{profileId}/project/{projectId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
The profile id |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/execution/profile/profile-1/project/project-1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETE \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.67. Admin fetches auto cleanup configuration
REST API for usecase UC_064-Admin fetches auto cleanup configuration
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/autoclean |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/autoclean' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"cleanupTime":{"unit":"MONTH","amount":0}}12.1.68. Admin updates auto cleanup configuration
REST API for usecase UC_065-Admin updates auto cleanup configuration
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/config/autoclean |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
202 ACCEPTED |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/config/autoclean' -i -u 'user:secret' -X PUT \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{"cleanupTime":{"unit":"MONTH","amount":0}}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.69. Admin creates or updates a template
REST API for usecase UC_082-Admin creates or updates a template
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/template/{templateId} |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The (unique) template id |
Request fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The template type. Must be be defined when a new template is created. An update will ignore changes of this property because the type is immutable! Currently supported types are: [Lcom.mercedesbenz.sechub.commons.model.template.TemplateType;@73f84c1a |
|
|
The asset id used by the template |
|
|
The variable name |
|
|
Defines if the variable is optional. The default is false |
|
|
Defines a simple validation segment. |
|
|
The minimum content length of this variable |
|
|
The maximum content length of this variable |
|
|
A regular expression which must match to accept the user input inside the variable |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/template/template1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X PUT \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{
"type" : "WEBSCAN_LOGIN",
"variables" : [ {
"name" : "username",
"optional" : false,
"validation" : {
"minLength" : 3,
"maxLength" : 15,
"regularExpression" : "[a-zA-Z0-9_-].*"
}
} ],
"assetId" : "asset-id1"
}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.70. Admin deletes a template
REST API for usecase UC_083-Admin deletes a template
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/template/{templateId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The (unique) template id |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/template/template1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETE \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.71. Admin fetches template
REST API for usecase UC_084-Admin fetches template
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/template/{templateId} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The (unique) template id |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The template type. Currently supported types are: [Lcom.mercedesbenz.sechub.commons.model.template.TemplateType;@3a12b444 |
|
|
The (unique) template id |
|
|
The asset id used by the template |
|
|
The variable name |
|
|
Defines if the variable is optional. The default is false |
|
|
Defines a simple validation segment. |
|
|
The minimum content length of this variable |
|
|
The maximum content length of this variable |
|
|
A regular expression which must match to accept the user input inside the variable |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/template/template1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"id":"template1","type":"WEBSCAN_LOGIN","variables":[{"name":"username","optional":false,"validation":{"minLength":3,"maxLength":15,"regularExpression":"[a-zA-Z0-9_-].*"}}],"assetId":"asset-id1"}12.1.72. Admin fetches all template ids
REST API for usecase UC_085-Admin fetches all template ids
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/templates |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Array contains all existing template identifiers |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/templates' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
["template1","template2"]12.1.73. Admin assigns template to project
REST API for usecase UC_086-Admin assigns template to project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project/{projectId}/template/{templateId} |
Method |
PUT |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
The id of the template to assign to project |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project/projectId1/template/template1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X PUT \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.74. Admin unassigns template from project
REST API for usecase UC_087-Admin unassigns template from project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/project/{projectId}/template/{templateId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The project id |
|
The id of the template to unassign from project |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/project/projectId1/template/template1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETE \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.75. Admin uploads an asset file
REST API for usecase UC_088-Admin uploads an asset file
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/asset/{assetId}/file |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The id of the asset to which the uploaded file belongs to |
Query parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
A sha256 checksum for file upload validation |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/asset/asset-1/file?checkSum=c6965634c4ec8e4f5e72dffd36ea725860e8b485216260264a0973073805e422' -i -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: multipart/form-data;charset=UTF-8' \
-F 'file=PK
�<M test1.txtPK ?
�<M $ test1.txt
��IW� ��IW� ��IW� PK [ ' 'Response body
(empty)
12.1.76. Admin downloads an asset file
REST API for usecase UC_089-Admin downloads an asset file
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/asset/{assetId}/file/{fileName} |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The asset identifier |
|
The name of the file to download from asset |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/asset/asset-1/file/PRODUCT1.zip' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'12.1.77. Admin fetches asset ids
REST API for usecase UC_090-Admin fetches asset ids
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/asset/ids |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Array contains all existing asset identifiers |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/asset/ids' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GETResponse body
["asset-1","asset-2"]12.1.78. Admin fetches asset details
REST API for usecase UC_091-Admin fetches asset details
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/asset/{assetId}/details |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The asset identifier |
|
|
Array containing data about files from asset |
|
|
Name of file |
|
|
Checksum for file |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/asset/asset-1/details' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"assetId":"asset-1","files":[{"fileName":"PRODUCT1.zip","checksum":"c6965634c4ec8e4f5e72dffd36ea725860e8b485216260264a0973073805e422"}]}12.1.79. Admin deletes an asset file
REST API for usecase UC_092-Admin deletes an asset file
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/asset/{assetId}/file/{fileName} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The asset identifier |
|
The name of the file to delete inside the asset |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/asset/asset-1/file/PRODUCT1.zip' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETEResponse body
(empty)
12.1.80. Admin deletes asset comletely
REST API for usecase UC_093-Admin deletes asset comletely
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/asset/{assetId} |
Method |
DELETE |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The asset identifier for the asset which shall be deleted completely |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/asset/asset-1' -i -u 'user:secret' -X DELETE \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.81. Admin starts encryption rotation
REST API for usecase UC_073-Admin starts encryption rotation
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/encryption/rotate |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/encryption/rotate' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \
-d '{
"algorithm" : "AES_GCM_SIV_256",
"passwordSourceType" : "ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE",
"passwordSourceData" : "SECRET_1"
}'Response body
(empty)
12.1.82. Admin fetches encryption status
REST API for usecase UC_076-Admin fetches encryption status
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/encryption/status |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The type description of the json content |
|
|
Name of the domain which will provide this encryption data elements |
|
|
Unique identifier |
|
|
Algorithm used for encryption |
|
|
Type of password source. Can be [NONE, ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE] |
|
|
Data for password source. If type is ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE then it is the the name of the environment variable. |
|
|
Map containing information about usage of this encryption |
|
|
Key value data |
|
|
Creation timestamp |
|
|
User id of admin who created the encryption entry |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/encryption/status' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"type":"encryptionStatus","domains":[{"name":"schedule","data":[{"id":"1","algorithm":"AES_GCM_SIV_256","passwordSource":{"type":"ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE","data":"SECRET_1"},"usage":{"job.state.cancel_requested":4,"job.state.canceled":5,"job.state.ended":8,"job.state.initializing":1,"job.state.ready_to_start":2,"job.state.resuming":7,"job.state.started":3,"job.state.suspended":6},"createdFrom":"admin-username","created":"2024-08-01T09:26:00"}]}]}12.1.83. Admin disables job processing in scheduler
REST API for usecase UC_030-Admin disables job processing in scheduler
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/scheduler/disable/job-processing |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
202 ACCEPTED |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/scheduler/disable/job-processing' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.84. Admin enables scheduler job processing
REST API for usecase UC_031-Admin enables scheduler job processing
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/scheduler/enable/job-processing |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
202 ACCEPTED |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/scheduler/enable/job-processing' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.85. Admin get scheduler status
REST API for usecase UC_032-Admin get scheduler status
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/scheduler/status/refresh |
Method |
POST |
Status code |
202 ACCEPTED |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/scheduler/status/refresh' -i -u 'user:secret' -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
(empty)
12.1.86. Admin lists status information
REST API for usecase UC_033-Admin lists status information
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/status |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Status key identifier |
|
|
Status value |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/status' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
[{"key":"status.scheduler.enabled","value":"true"},{"key":"status.scheduler.jobs.all","value":"100"},{"key":"status.scheduler.jobs.initializing","value":"1"},{"key":"status.scheduler.jobs.ready_to_start","value":"19"},{"key":"status.scheduler.jobs.started","value":"20"},{"key":"status.scheduler.jobs.ended","value":"50"},{"key":"status.scheduler.jobs.cancel_requested","value":"2"},{"key":"status.scheduler.jobs.canceled","value":"8"}]12.1.87. Admin fetches server runtime data
REST API for usecase UC_040-Admin fetches server runtime data
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/info/server |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The sechub server version. |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/info/server' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"serverVersion":"0.12.3"}12.1.88. User lists jobs for project
REST API for usecase UC_071-User lists jobs for project
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/project/{projectId}/jobs |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Path parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The id of the project where job information shall be fetched for |
Query parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
The wanted (maximum) size for the result set. When not defined, the default will be 1. |
|
The wanted page number. When not defined, the default will be 0. |
|
An optional dynamic query parameter to filter jobs by labels. The syntax is 'metadata.labels.${labelKey}=${labelValue}'. It is possible to query for multiple labels (up to 10 ). The filter works as an AND combination: Only jobs having all wanted label key value combinations are returned. |
|
An optional parameter to define if meta data shall be fetched as well. When not defined, the default will be false. |
Request headers
| Name | Description |
|---|
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The page number |
|
|
The total pages available |
|
|
The job uuid |
|
|
Creation timestamp of job |
|
|
Start timestamp of job execution |
|
|
End timestamp of job execution |
|
|
User who initiated the job |
|
|
Execution state of job |
|
|
Execution result of job |
|
|
Trafficlight of job - but only available when job has been done. Possible states are GREEN, YELLOW, RED, OFF |
|
|
Meta data of job - but only contained in result, when query parameter |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/project/project1/jobs?size=1&page=0&withMetaData=true&metadata.labels.stage=testing' -i -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"page":0,"totalPages":1,"content":[{"jobUUID":"3a270fe4-cd4d-490f-8173-0fb642be3466","executedBy":"User1","created":"2025-09-01T14:33:10.670237349","started":"2025-09-01T14:35:10.670266103","ended":"2025-09-01T14:50:10.670276472","executionState":"ENDED","trafficLight":"GREEN","executionResult":"OK","metaData":{"labels":{"stage":"test"}}}]}12.1.89. Admin executes templates healthcheck or updates a template
REST API for usecase UC_096-Admin executes templates healthcheck or updates a template
Definition
| Value | |
|---|---|
Path |
/api/admin/templates/healthcheck |
Method |
GET |
Status code |
200 OK |
Response fields
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Represents overall healthcheck status. Can be one of : [OK, WARNING, ERROR] |
|
|
A list of healthcheck status entries. Each entry represents a problem or an information. |
|
|
Type of this entry. Can be one of : [INFO, WARNING, ERROR] |
|
|
A description about the the entry |
|
|
The template id for the template where the problem/information is related to |
|
|
A list of projects which have the template assigned |
|
|
The uuid of the product executor config where the problem/info is related to (in combination with template) |
|
|
A list of the invovled profiles, means using executor config and being assigned to projects |
|
|
A list of hints which gives additinal information. E.g. A disabled executor configuration which leads to problems will lead to a WARNING, but not to an ERROR. In this case a hint 'At least one executor config is not enabled' would be added. |
|
|
A solution how to fix/resolve the problem |
|
|
The asset identifier which is used to locate the file |
|
|
The name of the file inside the asset |
Example
Curl request
$ curl 'https://sechub.example.com/api/admin/templates/healthcheck' -i -u 'user:secret' -X GET \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8'Response body
{"status":"WARNING","entries":[{"type":"ERROR","description":"The file 'asset-1/pds-product1-id.zip' does not exist!","templateId":"template-1","projects":["project-1"],"executorConfigUUID":"349ea899-e780-4553-bd50-06c12fe96c9e","profiles":["profile-1"],"hints":["At least one combination of executor and profile is enabled.","At least one profile is enabled.","At least one executor config is enabled."],"solution":"Upload a file 'pds-product1-id.zip' to asset folder 'asset-1'","assetId":"asset-1","fileName":"pds-product1-id.zip"},{"type":"WARNING","description":"The file 'asset-1/pds-product2-id.zip' does not exist!","templateId":"template-1","projects":["project-2"],"executorConfigUUID":"2b25b007-f3d2-4591-ba42-409e19d9a5e8","profiles":["profile-2"],"hints":["At least one profile is enabled.","At least one executor config is not enabled."],"solution":"Upload a file 'pds-product2-id.zip' to asset folder 'asset-1'","assetId":"asset-1","fileName":"pds-product2-id.zip"}]}13. Technical debt
13.1. Long running transactions
There could be a problem about long running transactions.
13.2. Domain messaging system
13.2.1. Authorization
At the moment the domain auth is not 100% correct implemented
respectively used more as layer that being a domain having a bounded context.
Explanation:
Inside project sechub-authorizhation spring boot auth handling is
defined. We got our own database table starting with "AUTH_" and
communication is done by events. So far so good. It works very well
at the moment.
But… this works only because we currently have ONE self contained
system. Spring boot uses the UserDetailService defined inside this project.
If we decide to separate SecHub into different deployment
units, we must either use the project as a library for deployed parts
(so more a "layer") or we introduce a possiblitiy for other domains
to get authorization info from this one.
As long as we do not separate and have all contained in ONE application this is not a problem. When separation must be done, we need a concept to change auth handling in adequate way.
13.2.2. Current event bus implementation
Currently the domain messaging is done by a simple observer pattern.
It’s working, is easy to maintain, simple but has some caveats:
-
Domain communication is done only inside ONE cluster member (seen from starting point).
(We got still cluster side working! The scheduling approach handles it correctly. But a job will have communication etc. only inside same JVM - which is maybe even a good thing ? - and reduces complexity)-
What does this include?
-
We got no "cluster communication".
-
We got no fallback handling when e.g. a cluster fails we got no respawning of the handling or queue entry
-
-
| This was a wanted architecture decision to keep things simple on startup. The used wrapper mechanism gives us t the chance to change the implementation when necessary, without too much effort. The benefits of data separation is still there. |
13.2.2.1. Additional information
-
Sending asynchronous messages are really asynchronous
The implementation inDomainMessageServiceuses a spring task executor to provide this in conjunction with observer pattern.
13.2.3. What possibilities do we have to change this in future?
-
Use Queuing System (maybe something more lightweight than KAFKA…)
-
Write another spring application which has got REST API and is installed one time in cluster
-
Problem: Bottleneck, much effort, deployment, etc.
-
-
Keep simple implementation as is but implement resilience
14. HowTos
14.1. Howto integrate a new product
At the beginning of SecHub it was always necessary to implement a new product adapter (in Java), create a new product executor (in Java) and create new product result importer (also in Java).
Those days are gone. Nowadays we are shifting every new product into a PDS (product delegation server) solution. For PDS we have an already existing PDS adapter (the logic to communicate with PDS) which is used always.
|
At the moment we have still some direct product adapters. Some are marked as deprecated and will vanish. Others will be replaced by PDS solutions. In the future there shall be only two products which have dedicated adapter implementations: SERECO and PDS. |
For every existing type of scan there is a dedicated PDS product executor available. When the security product is able to produce SARIF output, we are able to import this already. You can find multiple existing solutions and more details at https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub/tree/develop/sechub-pds-solutions.
|
In the best case scenario there is no need to write anything in Java - we copy an existing pds-solution to a new folder name, make some necessary adjustments, change the caller script and we are done… Only when a product result is not already supported by SERECO (SecHub report collector),
we must write a special |
14.2. Howto configure mock behaviours
14.2.1. Default mock adapter used in SecHub integration tests
The MockedAdapterSetupService reads a JSON configfile from file path.
Default file is located at /sechub-other/mockdata/mockdata_setup.json
If you want to use another location, use system property defined in
MockedAdapterSetupService.java to define another location.
Example:
{
"entries": [
{ (1)
"adapterId": "MockedNetsparkerAdapter",
"combinations": [
{(2)
"target" : "https://vulnerable.demo.example.org", (3)
"throwsAdapterException": false,(4)
"filePath": "./../sechub-other/mockdata/netsparker-mockdata-one-important-vulnerability.xml" (5)
},
{
"target": "https://safe.demo.example.org",
"throwsAdapterException": false,
"filePath": "./../sechub-other/mockdata/netsparker-mockdata-green.xml"
},
{
"target": "{any-other-target}",
"throwsAdapterException": false,
"filePath": "./../sechub-other/mockdata/netsparker-mockdata-green.xml"
}
]
}
]
}| 1 | One Adapter definition for mocking, can be multiple times, but for each adapter only one definition! |
| 2 | A combination for the adapter |
| 3 | Target url definition, for code scanners the file resource folders are the targets
e.g. "../sechub-doc/src/main/java". When using "{any-other-target}" this will the combination
used for all not defined combinations. |
| 4 | Mocked adapter will not throw an exception on execution time, when true defined the adapter will thow an adapter execution. Interesting for tests |
| 5 | Filepath for result file to return by mock when target url of Job starts with defined one |
14.2.2. Project specific mock adapter behaviour
Users can define a mock configuration via REST. This is convenient for integration tests from foreign systems. But there can not be any product specific configuration.
For more details see use case description or look at GitHub issue #141
14.3. Howto start a local development server like in production
In most cases its enough to use mocked adapter variants for development. But sometimes its necessary to start up a local development server using real security products (e.g. full integration testing etc.)
Launch configuration is described at Test/Use real products. You should also use same storage as you use in production! So when you are using a S3 bucket for storage there you should define this as well!
14.4. Howto quickly test a SecHub server release on local machine
For a "quick test" we start the release simply in integrationtest mode.
14.4.1. Get the release
You got different options: You can either download an existing release from https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub/releases , or you build it from scratch.
|
Here an example for a scratch-build: Checked out GIT tag |
14.4.2. Start release on your machine
Open a shell at the folder where your jar (In the next script we use sechub-server-0.19.1.jar) is located. Then
execute the server in integrationtest mode.
java -Dspring.profiles.active=mocked_products,h2,integrationtest -Dsechub.server.debug=false -Dsechub.storage.sharedvolume.upload.dir=temp -Dsechub.targettype.detection.intranet.hostname.endswith=intranet.example.org -Dsechub.config.trigger.nextjob.initialdelay=0 -Dsechub.integrationtest.ignore.missing.serverproject=true -jar sechub-server-0.19.1.jar
14.4.3. Further steps
Use the DAUI (Developer Administration User Interface) to test the server. In integration test mode, you can test nearly all SecHub server features - except the real product communication, because all adapters are mocked.
15. Reporting
This chapter describes the different SecHub report types and how to read them.
Job reports do only contain information of exact one scan job done by SecHub.
15.1. Job reports
Users can download the results of their finished scan jobs. SecHub provides these report formats:
-
HTML
human friendly report variant with less details -
JSON
as an also machine readable format. It can be directly used by the SecHub IDE plugins (Eclipse, IntelliJ, VSCode/Codium) -
SPDX JSON
15.1.1. HTML
The main purpose for the HTML report is to have a human friendly report which gives you a fast overview.
At the top left corner you see a traffic light showing either
-
GREEN
-
YELLOW or
-
RED.
|
You can open the details by clicking on "Open details". This allows you to see the full hierarchy from entry point down to data sink and can help you in analyzing this finding. It also shows a description and a possible solution (if there is one). |
The next picture shows a report which resulted in a red traffic light.
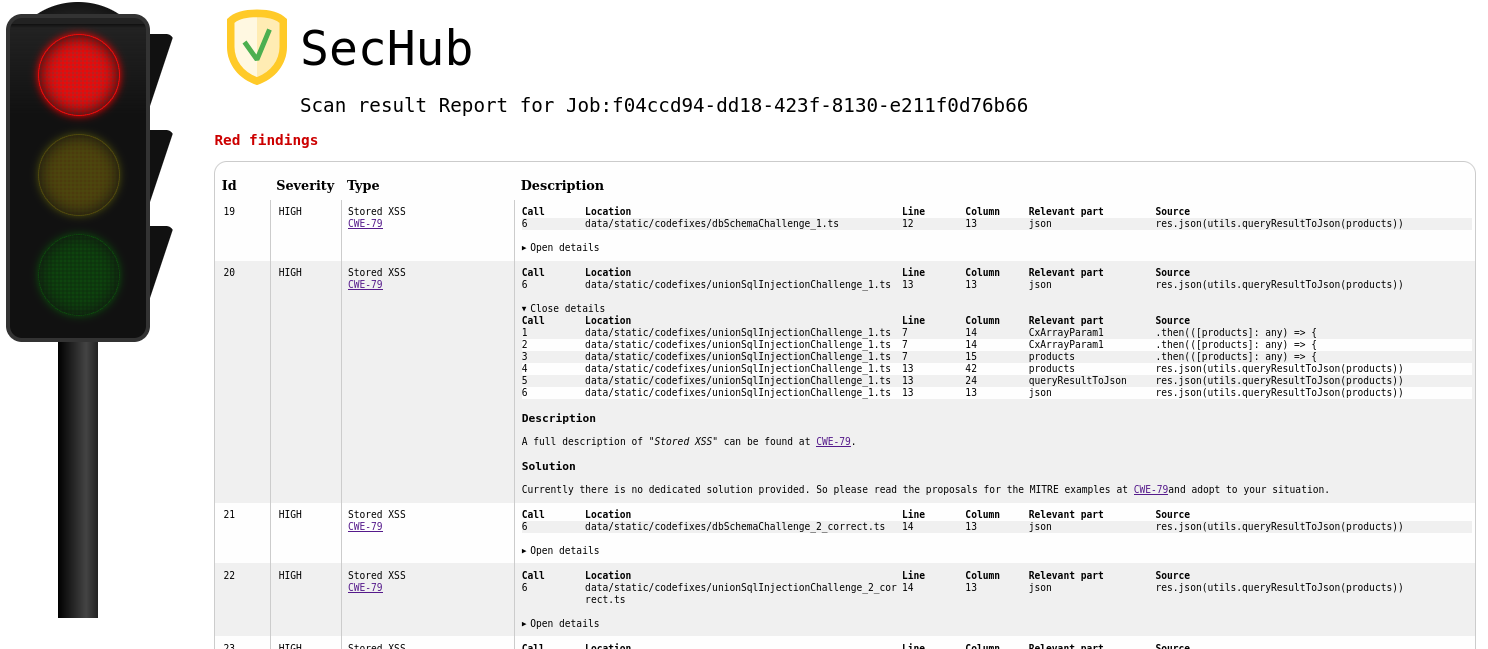
At the top of the report you find the most critical parts - in this example it is a "red" finding with finding ID 19 which is a "Stored XSS".
The second finding with ID 20 is of the same type. Here the details view is opened so more details can be seen.
If available, you can find the corresponding CWE-Id (Common Weakness Enumeration)
as a link to the knowledge base of MITRE in the Type column.
| The SecHub client will exit with a non-zero return code per default only at a RED traffic light, but you can also configure the client to do this on color YELLOW. |
15.1.2. JSON
This is the machine readable report format.
15.1.2.1. Example code scan report with yellow traffic light
{
"jobUUID": "6cf02ccf-da13-4dee-b529-0225ed9661bd", (1)
"trafficLight": "YELLOW", (2)
"messages": [],
"status": "SUCCESS",
"reportVersion": "1.0",
"result": {
"count": 2,
"findings": [
{
"id": 1, (3)
"description": "",
"name": "Absolute Path Traversal", (4)
"severity": "MEDIUM", (5)
"code": {
"location": "java/com/mercedesbenz/sechub/docgen/AsciidocGenerator.java", (6)
"line": 28, (7)
"column": 35,
"source": "\tpublic static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {",
"relevantPart": "args",
"calls": { (8)
"location": "java/com/mercedesbenz/sechub/docgen/AsciidocGenerator.java",
"line": 33,
"column": 17,
"source": "\t\tString path = args[0];",
"relevantPart": "args",
"calls": {
"location": "java/com/mercedesbenz/sechub/docgen/AsciidocGenerator.java",
"line": 33,
"column": 10,
"source": "\t\tString path = args[0];",
"relevantPart": "path",
"calls": {
"location": "java/com/mercedesbenz/sechub/docgen/AsciidocGenerator.java",
"line": 34,
"column": 38,
"source": "\t\tFile documentsGenFolder = new File(path);",
"relevantPart": "path",
"calls": {
"location": "java/com/mercedesbenz/sechub/docgen/AsciidocGenerator.java", (9)
"line": 34, (10)
"column": 29,
"source": "\t\tFile documentsGenFolder = new File(path);", (11)
"relevantPart": "File" (12)
}
}
}
}
},
"type": "codeScan",
"cweId": 778
},
{
"id": 2,
"description": "",
"hostnames": [],
"name": "Insufficient Logging of Exceptions",
"references": [],
"severity": "INFO",
"code": {
"location": "java/com/mercedesbenz/sechub/docgen/usecase/UseCaseRestDocModelDataCollector.java",
"line": 137,
"column": 5,
"source": "\t\t} catch (IOException e) {",
"relevantPart": "catch"
},
"type": "codeScan",
"cweId": 778
}
]
}
}| 1 | SecHub job UUID |
| 2 | Traffic light color of report - here YELLOW |
| 3 | Finding ID inside report |
| 4 | The name of the vulnerability in our case an Absolute path traversal where attackers could try to manipulate path input, so output could contain unwanted content/wrong file (e.g. a passwd file etc.) |
| 5 | The severity of this finding (will be used to calculate the traffic light color) |
| 6 | Entry point location in this case the Java class where the potential malicious input starts |
| 7 | Line number of entry point |
| 8 | Next call hierarchy element this is the next element of the call hierarchy, means what is called by entry point with potential malicious content as parameter. This is ongoing until last entry inside call hierarchy which is the so called "data sink" |
| 9 | Data sink location |
| 10 | Line number inside data sink |
| 11 | Source snippet |
| 12 | Relevant code part where the found vulnerability lies/could be exploited |
16. System tests
This chapter describes the system test framework.
16.1. Purpose
Integration tests do rely on SecHub running in integration test mode, using one PDS server in integration test mode.
In this scenario, the integration test API can fetch internal meta data and is able to check correctness of the logic inside SecHub and also inside PDS. But it does not test real product execution - in the end it only uses mocked test scripts and static test data.
"The system tests are different to integration tests: Their main purpose is to test SecHub server(s) in combination with one or multiple PDS solutions in real live scenarios. This helps developers of PDS solutions to drastically reduce development time and to write automated tests without having to constantly test manually. To run the system tests a command line call in the OS shell or calling a unit test is sufficient.
|
The system test framework is designed, to make things easier for developers when testing SecHub / PDS. It provides as many defaults as possible, therefore it is usually not necessary to explicitly define much to have a running system test! Try to only define the necessary minimum and let the system test framework do the rest. It is also possible to use already running local servers (SecHub and/or PDS). For example: When you are developing a PDS solution you can start a local SecHub server in your IDE and run your tests only with start definitions for your PDS solution! This will increase speed, because the test will not spawn (and also not shutdown) the SecHub server instance! |
16.2. Write a system test configuration file
This section describes the different parts inside the test configuration model.
System tests can be written in two ways:
-
Write a JUnit test and use methods provided by
SystemTestAPIor -
Write a JSON file and execute it with
pds-tools.
It does not matter if you write the configuration directly in JSON or with the Java SystemTestFramework API - the underlying model is the same.
16.2.1. Script definitions
At many locations it is possible to define script execution steps (e.g. SecHub start/stop, PDS start/stop or at test preparation)
As the name indicates the system test will execute a script.
You can define the following:
-
path
-
arguments (optional)
-
envVariables (optional)
as a map -
workingDirectory_(optional)_
-
process (optional)
-
timeout (optional)
-
-
stageWaits (optional)
iftruethe stage will wait until this script is executed and has successfully finished.
The default isfalse- please set this totrueonly when really necessary. E.g. for a prepare
script which must be done before a next step.
16.2.1.1. Example snippet
"script" : {
"path" : "./01-start-single-docker-compose.sh", (1)
"arguments" : [ "alpine" ],(2)
"envVariables" : { (3)
"NAME1" : "value1",
"NAME2" : "value2"
}
"workingDirectory" : "./../my-preparaton-folder1", (4)
"process" : { (5)
"timeOut" : {
"amount" : 10, (6)
"unit" : "MINUTES"
}
},
"stageWaits" : false (7)
}| 1 | The path for the executable script |
| 2 | Arguments (optional) |
| 3 | Environment variables (optional) |
| 4 | The working directory (optional, per default the working directory of system test call) |
| 5 | The process definition (optional). A user can define here some additional constraints for the created process (currently only a time out is supported). |
| 6 | Time out definition. When not defined, the default is 5 minutes. When a time out happens, the test will fail and the system test runtime will shutdown. |
| 7 | Defines if the current stage (e.g. test preparation) needs to wait for this script to be executed before next stage can be entered (e.g. test execution) |
16.2.2. Comments
If you want to comment your configuration file setup, you have different options, depending how you use the framework.
16.2.2.1. PDS-Tools using a JSON configuration file
Here you have two options:
-
Use Javascript comments inside your JSON (the framework just ignores it) - for example:
// I am commentor -
use the
commentattribute
16.2.2.2. JUnit tests
The SystemTestAPI configuration builder provides for many attributes a comment method
as well. Those parts will be transformed to corresponding JSON attribute inside the model.
16.2.3. Variables
16.2.3.1. Environment variables
You can use environment variables inside the test configuration.
The prefix for those variables is env.
For example, when you want to use the environment variable USER_NAME inside the
configuration you reference it by ${env.USER_NAME}.
|
It is forbidden to use environment variables which have |
16.2.3.2. Secret environment variables
When an error appears, the altered configuration model will be logged as JSON to make it easier to understand the problem.
But inside this output, all standard variables (environment, runtime, user variables) are revealed and will be shown in plain text.
To hide sensitive information you can use secret environment variables.
Secret environment variables are hidden in the log output. Use secret information for all sensitive information (secrets, passwords, credentials, personal information etc.).
|
It is forbidden to use secret environment variables which have |
The prefix for those variables is secretEnv.
For example, when you want to use the environment variable USER_PASSWORD inside the
configuration you reference it by ${secretEnv.USER_PASSWORD}.
|
When you are using secret environment variables but they are not defined at runtime, the system test framework will fail with an error about the missing variables. |
But those variables can only be used in some locations:
16.2.3.2.1. Inside script environments
"script" : {
"envVariables" : {
"D_RESOLVED_SECRET" : "${secretEnv.USER_PASSWORD}" (1)
},
"path" : "./05-start-single-sechub-network-docker-compose.sh",
"arguments" : [ "will-not-be-revealed-as-argument:${secretEnv.USER_PASSWORD}" ] (2)
}| 1 | This works, at runtime the environment entry for the script will contain USER_PASSWORD inside
variable D_RESOLVED_SECRET. |
| 2 | The secret will not be sent as an argument (for security reasons we only allow env entries) |
16.2.3.2.2. Inside credentials
This is possible for tech users and also for admin credentials.
16.2.3.3. User variables
You can define your own variables inside the test configuration.
The prefix for those variables is variables.
For example, if you have defined the variable uploadFolder inside the
configuration you can reference it by ${variables.uploadFolder}.
16.2.3.4. Runtime variables
Some variables are created by the test framework and are available at runtime.
You can use such variables inside the test configuration with the prefix runtime.
| Variable name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Contains the absolute path to the folder for the current test inside the workspace. This will be calculated at runtime. This variable can only be used in test preparation script definitions or in runSecHubJob definitions! |
|
Containts the absolute path for a folder were additional resources can be found. For example a suite of preparation scripts which shall be used inside tests. If not explicit defined, the variable points to the location where the system tests has been started from |
16.2.3.4.1. Workspace root
A workspace root for a system test means the root folder location where all data
for the current system test is stored. This includes test folders and also the .runtime folder
which contains information about processes and their output and error streams.
If not defined a temporary workspace folder will be created and can be used inside the configuration.
16.2.3.4.2. Test folders
The test folders are located inside the workspace root folder. Every executed test has its own sub folder.
Uploads for SecHub etc. must be done with relative paths from this location. You need to copy necessary parts for testing in a prepare step to the current test folder (see runtime variables tables for names etc.)
16.2.4. Default fallbacks
Following parts will be automatically defined in preparation phase when not defined explicit inside system test configuration model:
| Type | Scope | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Project id |
|
|
Profile id |
|
|
SecHub url |
|
|
SecHub admin user |
|
|
SecHub admin token |
|
|
PDS admin user |
|
|
PDS admin token |
|
|
PDS tech user |
|
|
PDS tech user token |
|
|
PDS url |
|
|
PDS wait for available |
|
|
SecHub wait for available |
|
|
Upload reference id |
|
|
16.2.5. Setup
Inside the setup we define things necessary to setup our system test environment.
It is possible to run system tests locally and start & configure SecHub and PDS solutions automatically.
But it is also possible to use an existing real SecHub platform and run the defined tests using a remote setup. In this setup it is not possible to change any existing configuration. This means that executor configurations, users, projects, profiles etc. must all be configured on the server side by administrators before the start of the remote tests.
16.2.5.1. Local
When we run system tests in a local environment, all necessary settings and the setup will be done by the system testing framework. This means an administrator account is necessary to setup the system.
If not defined, the default credentials for integration test server will be used. If you do not define SecHub or PDS you can also use a running local servers (for example integration test servers) and only start the tests.
16.2.5.1.1. Start
With a script definition the start process for the SecHub server instance(s) can be defined.
16.2.5.1.2. Stop
With a script definition the stop process for the SecHub server instance(s) can be defined.
16.2.5.1.3. Configure
The configuration can contain one or more product executor configurations.
16.2.5.2. Remote
It is also possible to use an existing real SecHub platform and run the defined tests there. The configuration is not changed here - executor configurations, users, projects and profiles must be already configured by administrators. A remote setup does not require an administrative account, a normal user account which has access to the project is sufficient.
The framework does help you by setting fallback default values when you do not configure some parts. But if those fallbacks are in use, you must ensure that the remote environment can handle it.
An example: if you did not define a project inside the configuration, the default project name will be used at system test runtime. In this case you must have created a project with this name at your remote SecHub server before.
16.2.5.3. Example snippet
setup" : {
"local" : {
"secHub" : {
"admin" : { (1)
"userId" : "${secretEnv.ADMIN_USERID}",
"apiToken" : "${secretEnv.ADMIN_APITOKEN}"
},
"start" : [ {(2)
"script" : {
"path" : "./01-start-single-docker-compose.sh",
"arguments" : [ "alpine" ]
}
} ],
"configure" : {
"executors" : [ {(3)
"pdsProductId" : "NEW_FANCY_PRODUCT",
"name" : "system-test-codescan-new-fancy"
} ]
},
"stop" : [ {(4)
"script" : {
"path" : "./01-stop-single-docker-compose.sh"
}
} ]
},
"pdsSolutions" : [ {
"name" : "new-fancy",(5)
"url" : "${env.PDS_SERVER}",
"start" : [ {
"script" : {
"path" : "./05-start-single-new-fancy-pds-docker-compose.sh",
"arguments" : [ "2" ]
}
} ],
"stop" : [ {
"script" : {
"path" : "./05-stop-single-new-fancy-pds-docker-compose.sh"
}
} ],
"techUser" : {
"userId" : "${secretEnv.PDS_USERID}",
"apiToken" : "${secretEnv.PDS_APITOKEN}"
}
} ]
}
| 1 | defines SecHub administrator credentials to use for communication |
| 2 | starts the SecHub server by executing the script |
| 3 | configures executors and their products to use. It’s a good style to define a name here for the executor so restarting the system test will override always the same executor configuration. The scan type is automatically determined from meta information inside the PDS configuration file. |
| 4 | stop script to shutown the SecHub server |
| 5 | define a pds solution defintion for "new-fancy" (not existing, but would be inside a folder new-fancy below
sechub-pds-solutions folder. In this example "new-fancy" would have "NEW_FANCY_PRODUCT" as product identifier inside
its PDS configuration file. |
16.2.6. Tests
Tests are defined at root level of the configuration file. It is possible to define multiple tests in one configurationfile.
16.2.6.1. Prepare
A test can have one or more preparation steps where following commands can be executed:
-
copy
Provides parameters "from" and "to" and enables users to copy folders or files to other locations -
script
Provides the possibility to execute a script
16.2.6.2. Execute
The test execution phase can contain currently:
-
runSecHubJob
Here we can define the uploads and also the different scan types. When nothing is defined, the default reference identifier will be used, but it is also possible to define more complex data structures with different content and identifiers.
16.2.6.3. Assert
Asserts are done after the execution phase. Following steps are possible
-
secHubResult
Here we assert there is a SecHub result (JSON report) available (the job is automatically started by system test framework). We have following possibilities to check the content:-
hasTrafficLight
Checks if the report has the expected traffic light -
containsStrings
Asserts that the JSON report contains all of the defined strings inside the given array -
equalsFileLoads the given template report file and asserts that if the SecHub JSON report matches the template. Following place holders are supported to handle dynamic content:-
{sechub.jobuuid}- can be used at any location inside the report if there is the job uuid inside the report -
{*:n}-nrepresents the number for characters to be ignored.
-
-
16.2.6.4. Cleanup
A test can have one or more cleanup steps where following commands can be executed:
-
copy
Provides parameters "from" and "to" and enables users to copy folders or files to other locations -
script
Provides the possibility to execute a script
16.2.6.5. Example snippet
"tests" : [ {
"name" : "test1",
"prepare" : [ {
"copy" : { (1)
"from" : "./../sechub-cli/src",
"to" : "${runtime.currentTestFolder}/testsources/src"
}
} ],
"execute" : {
"runSecHubJob" : {
"uploads" : [ {
"sourceFolder" : "./testsources/src" (2)
} ],
"codeScan" : { }
}
},
"assert" : [ {
"sechubResult" : { (3)
"hasTrafficLight" : "YELLOW",
"containsStrings" : {
"values" : [ "MEDIUM" ]
}
}
} ]
} ]| 1 | copies sources to current test folder at subfolder "testsources" |
| 2 | uploads source folder (files which were previously copied) |
| 3 | assert that there is an ended SecHub job for this test where the SecHub report has traffic light yellow and contains at least one time a string "MEDIUM" inside JSON report. |
16.3. Example configurations
16.3.1. Testing with already running integration test servers
|
This example is being used inside integration test |
{
"variables" : {
"testSourceUploadFolder" : "${runtime.currentTestFolder}/testsources"
},
"setup" : {
"local" : {
"secHub" : {
"comment" : "We do not define start/stop here, because reuse running local SecHub server",
"url" : "https://localhost:8443",
"admin" : {
"userId" : "${env.TEST_INTTEST_ADMIN_USERID}",
"apiToken" : "${secretEnv.TEST_INTTEST_ADMIN_APITOKEN}"
},
"configure" : {
"executors" : [ {
"comment" : "This executor will be re-created by the framework",
"pdsProductId" : "PDS_INTTEST_PRODUCT_CODESCAN",
"name" : "system-test-codescan-exec1",
"parameters" : {
"product1.qualititycheck.enabled" : "true",
"product1.level" : "A",
"pds.mocking.disabled" : "true"
}
} ],
"projects" : [ {
"name" : "default-test-project",
"whitelistedURIs" : [ "https://example.org/testproject1" ]
} ]
}
},
"pdsSolutions" : [ {
"comment" : "We do not define start/stop here, because reuse running local PDS server",
"name" : "PDS_INTTEST_PRODUCT_CODESCAN",
"url" : "https://localhost:8444",
"pathToPdsServerConfigFile" : "./../sechub-integrationtest/src/main/resources/pds-config-integrationtest.json",
"techUser" : {
"userId" : "${env.TEST_INTTEST_PDS_TECHUSER_USERID}",
"apiToken" : "${secretEnv.TEST_INTTEST_PDS_TECHUSER_APITOKEN}"
},
"admin" : {
"userId" : "${env.TEST_INTTEST_PDS_ADMIN_USERID}",
"apiToken" : "${secretEnv.TEST_INTTEST_PDS_ADMIN_APITOKEN}"
}
} ]
}
},
"tests" : [ {
"name" : "test1",
"prepare" : [ {
"script" : {
"path" : "./prepare-inttest-copy-codescan-medium-findings.sh",
"workingDirectory" : "./src/test/resources/additional-resources/preparation",
"arguments" : [ "${variables.testSourceUploadFolder}" ],
"process" : {
"timeOut" : {
"amount" : 5,
"unit" : "MINUTES"
}
}
}
} ],
"execute" : {
"runSecHubJob" : {
"uploads" : [ {
"sourceFolder" : "${variables.testSourceUploadFolder}"
} ],
"codeScan" : { }
}
},
"assert" : [ {
"sechubResult" : {
"hasTrafficLight" : "YELLOW",
"equalsFile" : {
"path" : "./src/test/resources/additional-resources/expected-output/sechub-result1.json"
},
"containsStrings" : {
"values" : [ "MEDIUM", "ERROR", "WARNING", "INFO", "SUCCESS", "integration test code only!" ]
}
}
} ]
} ]
}16.3.2. A full blown example
|
This example is just an overview what steps could be configured at all. It is not used in any real world scenario but only for documentation. |
{
"variables" : {
"var1" : "1",
"custom_data_txt" : "${env.FROM_OUTSIDE}/subfolder1/data.txt"
},
"setup" : {
"local" : {
"comment" : "This is a local setup - it does not use existing SecHub infrastructure, instead it does build up all by its own",
"secHub" : {
"comment" : "If there are variants defined, the further defined tests will be run with all of those variants by the framework! ADDITION: we could introduce here start/stop step like in pds solutions to build the sechub container from scratch as well (with different jdks etc.)",
"admin" : {
"userId" : "${secretEnv.SECHUB_ADMIN_USERID}",
"apiToken" : "${secretEnv.SECHUB_ADMIN_TOKEN}"
},
"start" : [ {
"script" : {
"path" : "./01-start-single-docker-compose.sh",
"arguments" : [ "alpine" ],
"process" : {
"timeOut" : {
"amount" : 5,
"unit" : "MINUTES"
}
}
}
} ],
"configure" : {
"comment" : "Here we can configure sechub. At least one executor entry is mandatory (we must know which products shall be inside the profile). Projects is optional. If not defined only a default project and a default profile for the given executors will be automatically created and used.",
"executors" : [ {
"pdsProductId" : "GOSEC",
"parameters" : {
"gosec.additional.parameter" : "${variables.custom_data_txt}",
"pds.reuse.sechubstorage" : "false (overrides default)"
},
"baseURL" : "https://gosec_pds.example.com:8443"
} ],
"projects" : [ {
"comment" : "The profile can define a profile. When nothing is defined, the default will be 'default-test-profile'",
"name" : "a-project-id-when-not-default-used",
"profiles" : [ "a-defined-profile-when-not-default-used" ]
} ]
},
"stop" : [ {
"comment" : "One single step to finally stop the gosec PDS solution when tests have been done.",
"script" : {
"path" : "./01-stop-single-docker-compose.sh",
"process" : {
"timeOut" : {
"amount" : 5,
"unit" : "MINUTES"
}
}
}
} ]
},
"pdsSolutions" : [ {
"comment" : "Test solution1, the scan types etc. cannot be defined, because runtime loads all meta information from config file. Basedir is optional, normally calculated automatically by name",
"name" : "gosec",
"baseDir" : "${env.base_dir}/pds-solutions/gosec",
"techUser" : {
"userId" : "${secretEnv.GOSEC_PDS_TECHUSER_USERID}",
"apiToken" : "${secretEnv.GOSEC_PDS_TECHUSER_TOKEN}"
},
"admin" : { },
"start" : [ {
"comment" : "In first start step, we build the image",
"script" : {
"path" : "./01-build-the-image.sh ${variables.myContainer.values}",
"workingDirectory" : "./",
"process" : {
"timeOut" : {
"amount" : 5,
"unit" : "MINUTES"
}
}
}
}, {
"comment" : "As last start step... start the gosec PDS solution",
"script" : {
"path" : "./05-start-container.sh",
"process" : {
"timeOut" : {
"amount" : 5,
"unit" : "MINUTES"
}
}
}
} ],
"stop" : [ {
"comment" : "One single step to finally stop the gosec PDS solution when tests have been done.",
"script" : {
"path" : "./01-build-the-image.sh ${variables.myContainer.values}",
"workingDirectory" : "./",
"process" : {
"timeOut" : {
"amount" : 5,
"unit" : "MINUTES"
}
}
}
} ]
} ]
},
"remote" : {
"comment" : "This is a remote setup - we use an existing and configured SecHub cluster/instance",
"secHub" : {
"url" : "https://sechub.example.com:8443",
"user" : {
"userId" : "testuser",
"apiToken" : "${env.SYSTEM_TEST_USER_TOKEN}"
}
}
}
},
"tests" : [ {
"comment" : "This test does a git checkout of a simple gosec application. After this we ensure the sechub result json file is as expected.",
"name" : "Test1",
"prepare" : [ {
"script" : {
"comment" : "The script call here would call the script inside the 'tests' subfoler of the solution",
"path" : "./../tests/checkout-simple-go-project-withouth-sechub-json.sh ${runtime.currentTestFolder}/checkout",
"process" : {
"timeOut" : {
"amount" : 5,
"unit" : "MINUTES"
}
}
}
}, {
"script" : {
"comment" : "Just another script call as an example for possibility of multiple scripts + an environment variable from 'outside'...",
"path" : "${env.FROM_OUT_SIDE}/do-something-else.sh",
"process" : {
"timeOut" : {
"amount" : 5,
"unit" : "MINUTES"
}
}
}
} ],
"execute" : {
"comment" : "This part can be defined only once. It describes what is executed",
"runSecHubJob" : {
"comment" : "If a project is defined, it will be used, otherwise always 'default-test-project' is used as default",
"project" : "a-project-id-when-not-default-used",
"uploads" : [ {
"comment" : "Here we can define either binaries or sources to upload - we define the folders, framework will create tars/zips automatically. When no upload reference id is defined, default-ref is used as default",
"sourceFolder" : "./checkout/sources",
"referenceId" : "an-upload-reference-id"
} ],
"codeScan" : {
"use" : [ "an-upload-reference-id" ]
},
"secretScan" : {
"use" : [ "an-upload-reference-id" ]
}
}
},
"assert" : [ {
"sechubResult" : {
"hasTrafficLight" : "GREEN",
"equalsFile" : {
"comment" : "At execution time, the different job uuids inside the two reports may are handled automatically. The given file is just a normal report but dynamic parts can be marked with parameters.",
"path" : "./../tests/expected-sechub-json.json"
},
"containsStrings" : {
"comment" : "Checks if the sechub result file contains the given strings.",
"values" : [ "CWE-89", "SQL-Injection", "Improper" ]
}
}
} ]
} ]
}16.4. How to execute system tests
16.4.1. With PDS tools
As a first step, download the latest release of pds-tools from https://github.com/mercedes-benz/sechub/releases.
Execute:
java -jar sechub-pds-tools-cli-<version>.jar systemTest --file ${pathToTestConfigurationJson} --pds-solutions-rootfolder ${pathToPDSSolutions}
16.4.2. JUnit tests
Just execute the Junit test from your IDE.
16.5. Behavior
16.5.1. Stages
We have different stages:
-
Setup
-
Test
-
Shutdown
Every stage can contain different steps inside. For example: The setup phase contains start scripts from SecHub and/or PDS solutions.
Before a stage can be left and another is started, a check is done, if there is a need to wait for any processes to be finished. When a script of the stage times out in mean time, the framework will stop with a failure message.
If not explicit defined, the test framework automatically uses dedicated defaults for script steps inside the stage, but it is possible to change the defaults inside the configuration. Here is an example:
{
"script" : {
"path" : "./01-start-single-docker-compose.sh",
"process" : {
"timeOut" : { (1)
"amount" : 2, (2)
"unit" : "minutes", (3)
}
"stageWaits" : true (4)
}
}
}| 1 | Defines the timeout before the process will be forcibly terminated. The default is 5 Minutes When a timeout happens, the system test will fail! | ||
| 2 | Accepted amount of time before timeout happens | ||
| 3 | Time unit, can be milliseconds, seconds, minutes, hours |
||
| 4 | When stageWaits is true the stage will wait for the process to be done. The default is false.
|
|
You do not need to define |
16.5.2. Auto configuration
16.5.2.1. Remote run
At a remote run, the configuration of the remote exissting SecHub and PDS environments will not be changed!
|
There is no auto configuration phase on a remote run. All elements (profiles, executors, project, etc. must all be configured before the test is run. |
16.5.2.2. Local run
16.5.2.2.1. Projects
The defined projects will be created automatically. If a project exists with the defined name (e.g. when a system test is restarted locally) the existing project will be deleted!
16.5.2.2.2. Executor configurations
Every system test start will just create new executor configurations.
16.5.2.2.3. Profiles
The defined profiles inside test configuration model will be created and connected with the created executor configurations. If a profile does already exist with the defined project id, the existing one will be deleted.
